Giant Day Geckos (Phelsuma grandis) are a species of large, arboreal lizards within the family Gekkonidae (10, 12, 13). Known for their vibrant green coloration and climbing abilities (15), they are native to northern Madagascar but have established populations in other regions, including Hawaii and Florida (8, 9).
Adults typically reach a total length of 9 to 11 inches (23 to 28 cm), living on a diet that includes both insects and plant-based foods such as nectar and pollen (3). Their diurnal nature makes them active throughout the day (7), using specialized toe pads to navigate vertical and inverted surfaces with ease. The species is currently listed as Least Concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) (14).
This guide offers an in-depth examination of this unique reptile, exploring its physical characteristics, natural habitat, and its role within the ecosystem. From its distinctive behaviors to its status as a popular pet and a potential invasive species, a comprehensive understanding of the Giant Day Gecko is possible. Understanding the true nature of this reptile begins with its scientific classification.

What Are Giant Day Geckos?
Giant Day Geckos (Phelsuma grandis) are a species of large, diurnal, and highly arboreal lizards. Native to the tropical rainforests of northern Madagascar, they have also established thriving non-native populations in various regions, including Hawaii and Florida (8, 9).
This reptile belongs to the family Gekkonidae, a diverse group of over 1,500 species, within the larger order Squamata, which includes all snakes and lizards. While often referred to by common names like Madagascar Giant Day Gecko or simply Grandis, a taxonomic debate has persisted regarding its classification.
A 2016 study on morphology and molecular data officially elevated the species from a subspecies, Phelsuma madagascariensis grandis, to its current full species status (5).
The scientific community widely accepts this reclassification, though some older literature may still use the subspecies designation (5), which can lead to confusion for enthusiasts and researchers alike. A clear understanding of its classification is a first step toward understanding its unique place among reptiles.
With its status clarified, the focus shifts to the gecko’s distinct physical characteristics. Let’s examine what truly makes them stand out visually and what special features they possess.

What Do Giant Day Geckos Look Like?
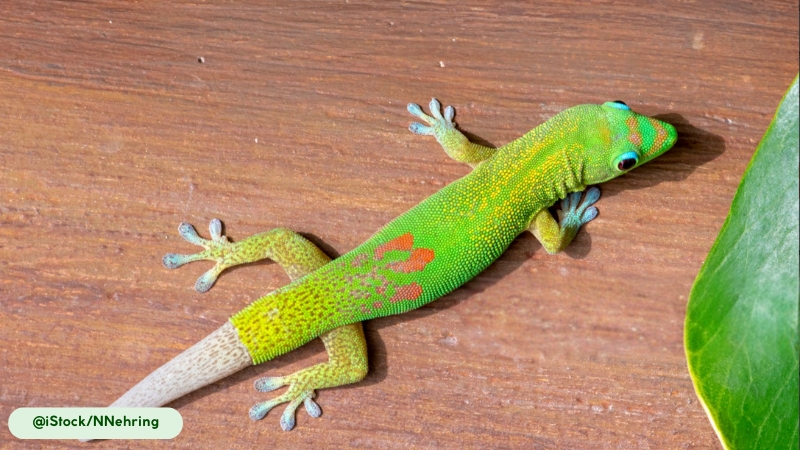
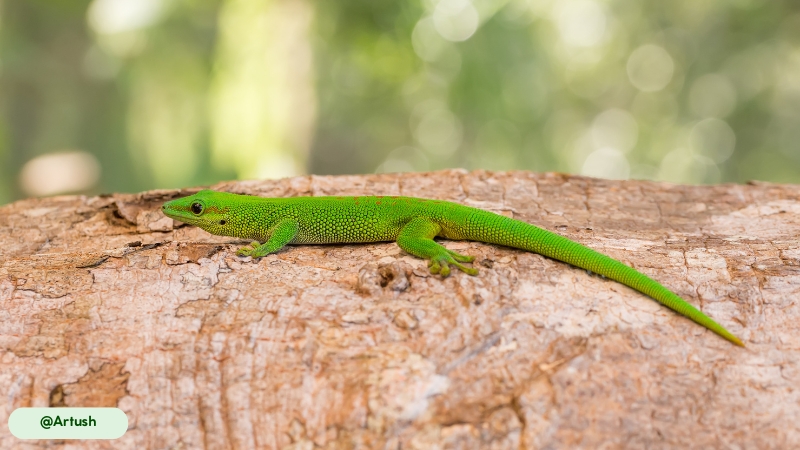
The Giant Day Gecko exhibits a streamlined, arboreal physique. Its overall coloration is a vibrant green or bluish-green, marked by red stripes that run from the nostril to the eye and scattered red spots or bars along its back. The skin has a smooth texture, providing camouflage among foliage. This species possesses several distinctive physical characteristics tailored for its lifestyle.
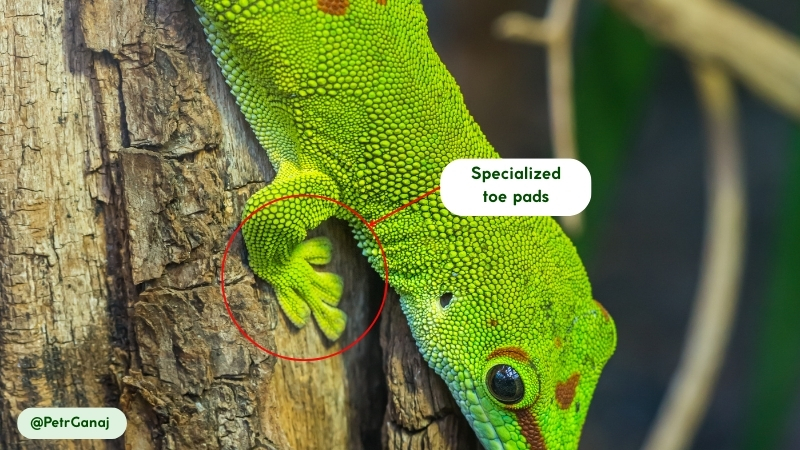
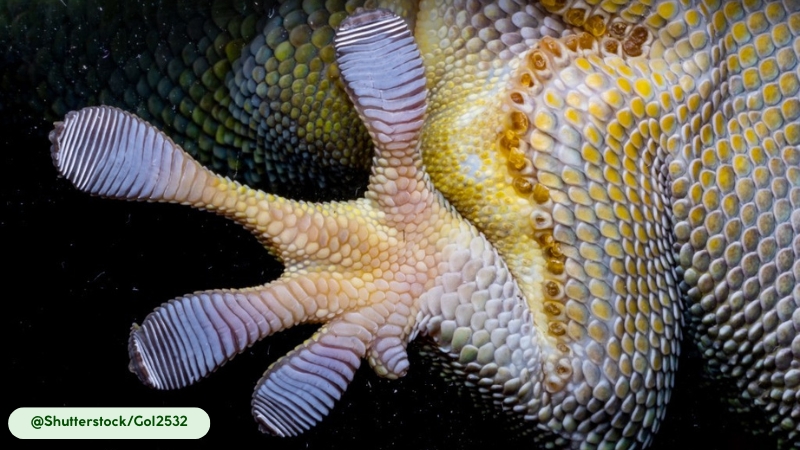
- Adhesive Toe Pads: Its four long limbs end in flattened toe pads called lamellae, which are covered in thousands of microscopic hair-like structures known as setae. These specialized structures generate powerful adhesive forces through van der Waals interactions, allowing the gecko to climb smooth, vertical surfaces with precision and speed (15).
- Long, Cylindrical Tail: The tail is long and cylindrical, serving as a critical tool for balance while the gecko navigates complex vertical habitats. A defensive adaptation called autotomy allows the gecko to detach its tail to distract predators, though the tail will eventually regenerate.
- Unique Head and Ocular Features: The head is rounded with a short snout. The large eyes have round pupils ringed in a striking blue color. These geckos lack eyelids and maintain eye moisture by regularly licking their eyes with their tongues.
Sexual dimorphism is evident in the species’ physical appearance. Males are generally larger and more robust, with broader heads and more pronounced coloration than females.
Males also possess visible femoral pores along their hind legs, which are used to mark territory and attract mates. The physical traits of a Giant Day Gecko are directly related to its impressive size. From their beautiful coloration to their surprising dimensions, their appearance is full of fascinating details.

How Big Are Giant Day Geckos?
Giant Day Geckos are the largest species in the genus Phelsuma, a fact reflected in their common name (14). Adults typically have a total length of 9 to 11 inches (23 to 28 cm) and weigh about 2 ounces (57 g). Males are generally larger than females.
| Measurement | Male | Female |
| Length | 9-11 inches | 9-11 inches |
| Weight | ~2 ounces | ~2 ounces |
The growth of Giant Day Geckos progresses through distinct stages. Hatchlings measure approximately 2.2 to 2.4 inches (55 to 60 mm) in length, roughly the size of a standard house key. They grow rapidly, reaching sexual maturity within one to two years. Their considerable size allows them to dominate their specific ecological niches. These large bodies and the environments they inhabit are closely connected to how they behave.

Where Do Giant Day Geckos Live?
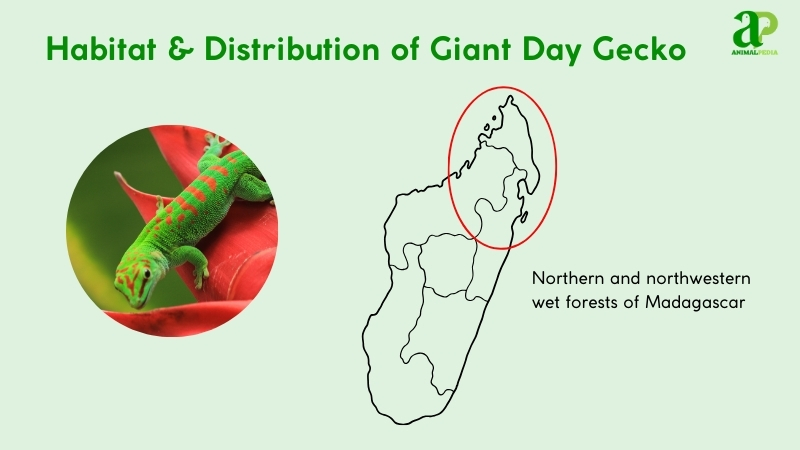
Giant Day Geckos are primarily found in the tropical, wet forests of Madagascar, where they are native to the northern and northwestern parts of the island (11). They inhabit a variety of arboreal environments, including bamboo forests, palms, and other broad-leafed trees.
Their adaptability has also enabled them to thrive in modified environments, often living on the sides of houses and in gardens (3). This species requires a consistently warm and humid climate to maintain its thermal regulation and physiological functions (6).
The species is highly territorial, with a single individual or a mated pair defending a specific area of trees or foliage from other geckos. This behavior is a critical aspect of their ecology and population dynamics within both their native and non-native ranges.
The elevation range of their natural habitat is from sea level to approximately 2,000 feet (609 m), though this can vary (14). The gecko’s ability to survive in both pristine and disturbed habitats is a key factor in its successful introduction to places like Florida (8). Knowing where they live is just the beginning of understanding them. Now we will explore their fascinating habits and behaviors.
How Do Giant Day Geckos Behave?
Giant Day Geckos are a highly active and territorial species with distinct daily patterns, movement abilities, and feeding habits. They are known for their diurnal nature and a diet of both insects and plant-based foods. Their behaviors are finely tuned for life in their arboreal habitats.
Diet and Feeding
Giant Day Geckos are classified as omnivores, with a diet consisting of invertebrates and plant-based foods. Their prey includes small insects, spiders, and other arthropods. Additionally, a significant part of their diet is composed of sugary plant matter such as fruit, pollen, and nectar (3). This varied consumption pattern allows them to adapt to different food sources.
When hunting, they act as ambush predators, waiting for prey to come within striking distance. They also actively stalk their prey, using their keen eyesight to locate movement. Their long, specialized tongue allows them to efficiently lap up nectar from flowers and to consume soft fruits.
The ability to utilize a wide range of food sources is a key factor in their success in both native and non-native environments. Their feeding habits are just one aspect of their overall survival strategy. They are also highly specialized movers with impressive physical abilities.

Movement and Abilities
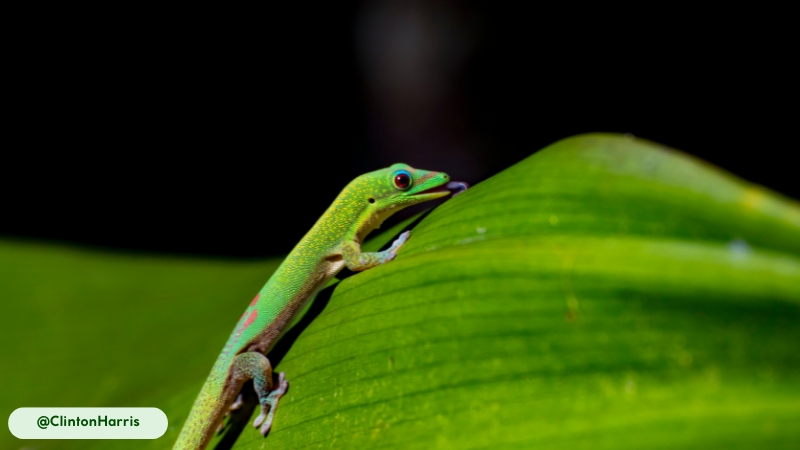
Giant Day Geckos move with swift, agile, and highly arboreal locomotion. Their primary mode of movement is climbing. They are exceptionally skilled at navigating vertical surfaces due to their specialized toe pads, which allow them to adhere to smooth surfaces like glass (15). The microscopic setae on their lamellae create adhesive forces through van der Waals interactions, enabling them to move across tree trunks and even ceilings.
In addition to climbing, Giant Day Geckos are known for their impressive agility, often making swift leaps between branches. This ability to jump with precision is a key part of their evasive behavior and hunting strategy. Another specialized trait is autotomy, a defensive mechanism in which the gecko can detach its tail to distract a predator.
The detached tail will continue to writhe for a short period, allowing the gecko to escape (14). Now that we’ve covered their physical agility, let’s learn more about their daily routine.

Daily/Seasonal Patterns
Giant Day Geckos are a diurnal species, meaning they are active during the day. Their daily cycle is structured around sunlight and temperature, which they use to regulate their body heat. Their primary period of activity occurs in the morning and late afternoon.
The typical daily activity cycle includes:
- Morning (7 AM – 11 AM): Basking in the sun to warm up their bodies, followed by an active period of foraging for food.
- Midday (11 AM – 3 PM): Seeking out shaded areas to avoid overheating, resulting in a decrease in activity.
- Late Afternoon (3 PM – 6 PM): A second peak in foraging activity and social interactions before sunset.
Their native tropical climate provides consistent warmth and food availability throughout the year, so they do not exhibit significant seasonal migration or periods of torpor.
Their activity levels remain relatively stable throughout the year, unlike species in temperate climates, which may experience reduced activity during colder months. They are territorial and do not migrate. From their daily routines, we can move on to a fundamental aspect of life itself.
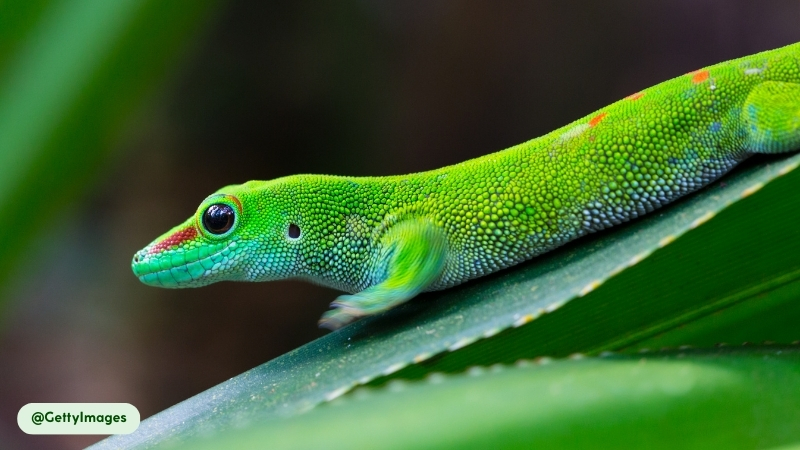

How Do Giant Day Geckos Reproduce?
Giant Day Geckos are an oviparous species, meaning they reproduce by laying eggs. This species does not exhibit a distinct, seasonal breeding pattern; instead, it reproduces throughout the year in its native tropical habitats. Male geckos engage in specific courtship rituals, which often include head-bobbing and tail-waving, to attract a female and assert dominance over their territory.
After a successful mating, the female lays a clutch of two hard-shelled eggs at a time. She typically finds a secure, secluded location to deposit her eggs, such as inside a hollow bamboo stalk or a crevice in a tree. The eggs require a consistent temperature and humidity to incubate, and they will hatch after approximately 45-60 days.
Once the eggs are laid, no further parental care is provided to the offspring. The reproductive cycle leads directly to the question of a Giant Day Gecko’s lifespan. Knowing how they come into the world helps us understand their journey through it.

How Long Do Giant Day Geckos Live?
Giant Day Geckos live an average of 6 to 8 years in the wild. In a controlled environment, such as a vivarium, their lifespan can extend significantly, often reaching 15 to 20 years. This difference is due to the absence of natural predators, consistent access to a balanced diet, and dedicated health care (9, 14).
They reach sexual maturity early, typically within one to two years. This rapid development allows them to begin reproducing at a young age. Factors affecting their longevity include diet, habitat quality, predation, and human impact. The longevity of this species demonstrates its resilience and its value to humans. The benefits they offer are often overlooked.

Are Giant Day Geckos Beneficial to Humans?
Giant Day Geckos are a beneficial species to humans. They are not venomous or harmful and do not pose a threat to people. Their primary benefit is as a form of natural pest control. In their native habitats and in introduced populations, they consume a wide variety of arthropods, including many common household pests like flies, spiders, and cockroaches. Their role as an insectivore helps to manage local insect populations.
Beyond their ecological benefits, the Giant Day Gecko has also become a popular animal in the pet trade, which contributes to the global reptile hobby and education (9). While they may bite if they feel cornered or threatened, this defensive behavior is a minor concern and is not medically significant.
Their presence in human-modified environments is a testament to their adaptability and their generally harmless nature. This adaptability also has a direct effect on their conservation status. Their story is a reminder of the delicate balance between nature and human activity.
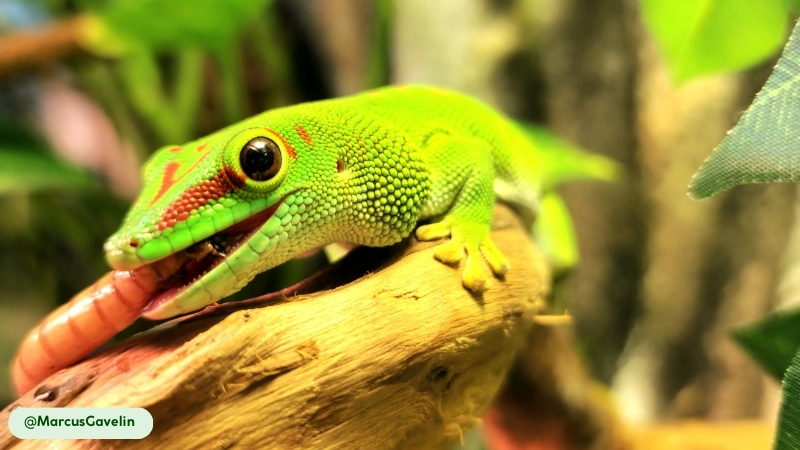

Are Giant Day Geckos Endangered?
Giant Day Geckos are not an endangered species. According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List, their conservation status is officially classified as Least Concern (14). This designation indicates that their wild populations are widespread and stable. Threats to the species’ survival include habitat degradation in their native Madagascar and their potential to become an invasive species in non-native habitats like Florida (1, 8, 9).
The species’ adaptability allows them to thrive in human-modified landscapes, which helps mitigate the direct effects of habitat loss. Their success in new environments, however, can disrupt local ecosystems by competing with native species for food sources.
Individual conservation efforts center on responsible pet ownership and preventing the release of these geckos into new environments. Beyond their official conservation status, the Giant Day Gecko offers a host of other fascinating facts that showcase its unique nature. It’s time to uncover some of their most surprising secrets.

Fascinating Facts About Giant Day Geckos
Giant Day Geckos exhibit a range of unique behaviors and traits that set them apart. These details provide a closer look at their biology and place in the animal kingdom.
- Pollinators of the Forest. In their native Madagascar, these geckos play a vital ecological role as pollinators. As they feed on the nectar of flowers, they transfer pollen, helping to reproduce various plant species (3). This role is similar to that of hummingbirds and butterflies.
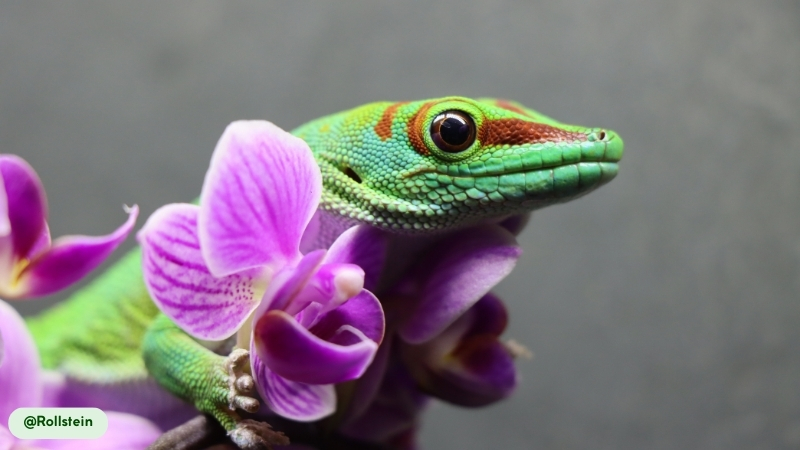

- A Loud, Territorial Chirp. Unlike most geckos, which are typically silent, Giant Day Geckos are known for their loud vocalizations. They emit a series of chirps and clicks, particularly by males, to communicate with rivals and mates over a distance and defend their territory (14).
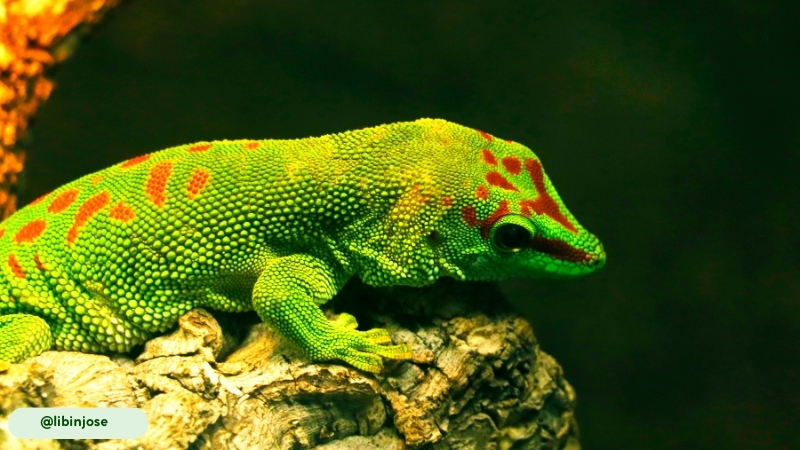

- Molting for Nutrition. They regularly shed their skin in a process called ecdysis. The gecko will often consume its own shed skin immediately after molting. This behavior is believed to be a way of regaining valuable nutrients and calcium, and a way to remove evidence that could attract predators.
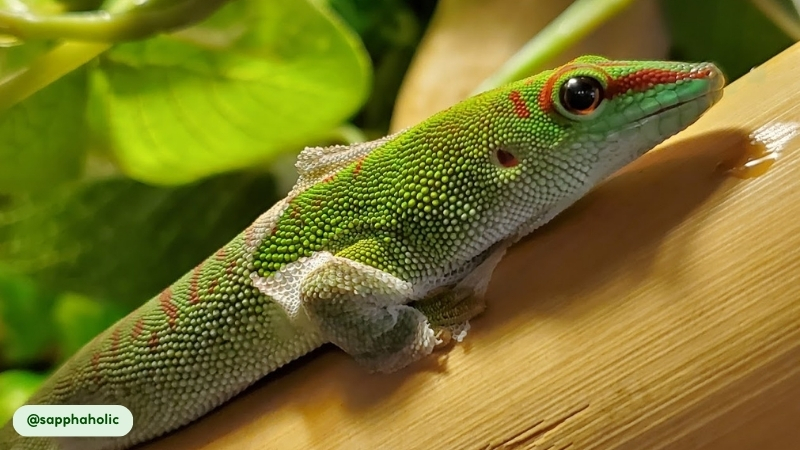

- Specialized Drinking Habit. Giant Day Geckos do not drink from standing water sources. Instead, they get the water they need by licking dew droplets or raindrops off of leaves and other surfaces in their environment.

- Self-Cleaning Toe Pads. The microscopic setae on their toe pads are not only adhesive but also self-cleaning. The structure prevents dirt and debris from adhering to the setae, enabling the gecko to maintain its climbing ability with minimal effort (15).

- Masters of the Leap. Beyond their climbing skills, these geckos are agile jumpers. They can leap between branches and surfaces, covering a distance of up to one foot (30 cm) or more, a key part of their hunting and escape tactics.
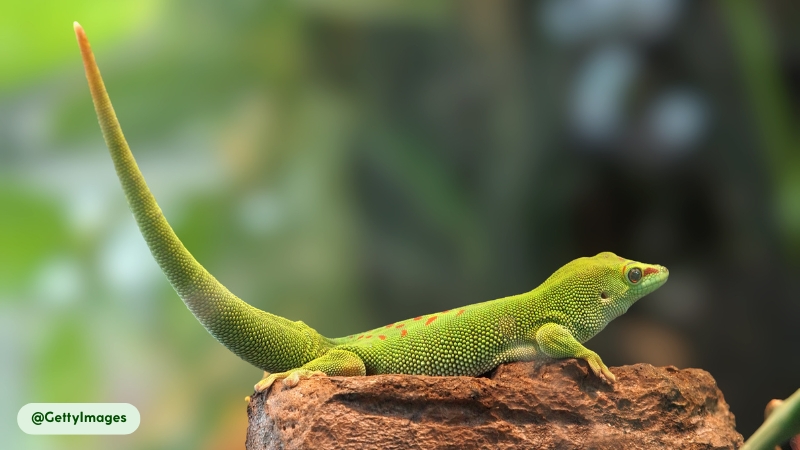

- Tail Regeneration. If a gecko detaches its tail to escape a predator, a new one will grow back. This regenerated tail may differ slightly in color, pattern, and texture from the original, a characteristic of the species (14).

- A Recent Species. The Giant Day Gecko was a subspecies of the Madagascar Day Gecko (Phelsuma madagascariensis) until a 2016 study reclassified it as a full species (Phelsuma grandis) (5). This reclassification highlights its distinct genetic and morphological characteristics.
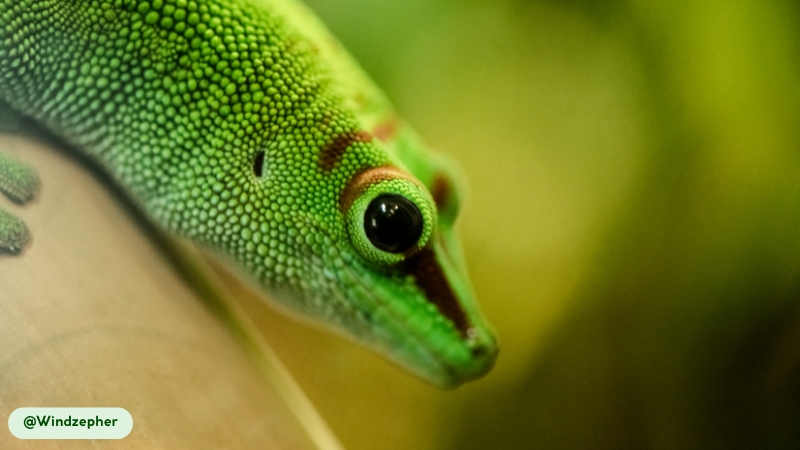

- Unique Eye Structure. They lack true eyelids, instead having a transparent scale over their eyes to protect them. To keep their eyes clean and moist, they regularly use their long tongues to wipe away any dust or debris.

- An Unofficial Mascot. The vibrant green gecko featured in a long-running series of television commercials for a major insurance company is a Giant Day Gecko. This pop culture exposure has contributed to the species’ popular recognition.

Now that we’ve covered the most interesting facts, let’s explore the most common questions people ask about this extraordinary creature.
Frequently Asked Questions About Giant Day Geckos
Are Giant Day Geckos Good Pets?
Giant Day Geckos are considered good pets for experienced keepers, as their specific needs, including a large vivarium, controlled temperature, and high humidity, require dedicated care. They thrive in a well-maintained environment, providing a rewarding experience for enthusiasts.
Do Giant Day Geckos Like To Be Held?
Giant Day Geckos generally dislike being held. Their delicate skin and propensity for tail autonomy when stressed make physical contact difficult and potentially harmful, so they are best suited for observation within their enclosure.
Can Giant Day Geckos Eat Bean Beetles?
Yes, Giant Day Geckos can eat bean beetles as part of a varied diet. These insects are soft-bodied, which makes them an easily digestible and nutritional food source when offered alongside other prey items and plant-based foods.
Do Giant Day Geckos Make Noise?
Yes, Giant Day Geckos make noise. They vocalize through a series of chirps and clicks, which are primarily used for communication. These sounds serve as a form of territorial display and are also part of their courtship rituals.
Do Giant Day Geckos Sleep With Their Eyes Open?
Yes, Giant Day Geckos sleep with their eyes open. This is a direct result of their unique eye structure, which lacks movable eyelids. Instead, a transparent spectacle covers and protects the eye while it rests.
Conclusion
The Giant Day Gecko is a stunning example of evolutionary adaptation and biological diversity. From its vibrant coloration and unique physical features, such as self-cleaning toe pads, to its role as a pollinator, this species stands out in its native and introduced habitats.
Its behavior, reproduction, and longevity paint a clear picture of a successful reptile. Its adaptability to human-modified environments makes it a common sight in some parts of the world, and its Least Concern status highlights the resilience of its global populations. This article has provided a comprehensive look into the world of the Giant Day Gecko, providing detailed and accurate information for enthusiasts and researchers alike.
At Animal Pedia, our commitment is to provide in-depth, scientifically accurate information about the animal kingdom through a visual-first and interactive learning experience. To continue your journey of discovery and learn about other fascinating species, we invite you to explore more of our extensive digital encyclopedia.








