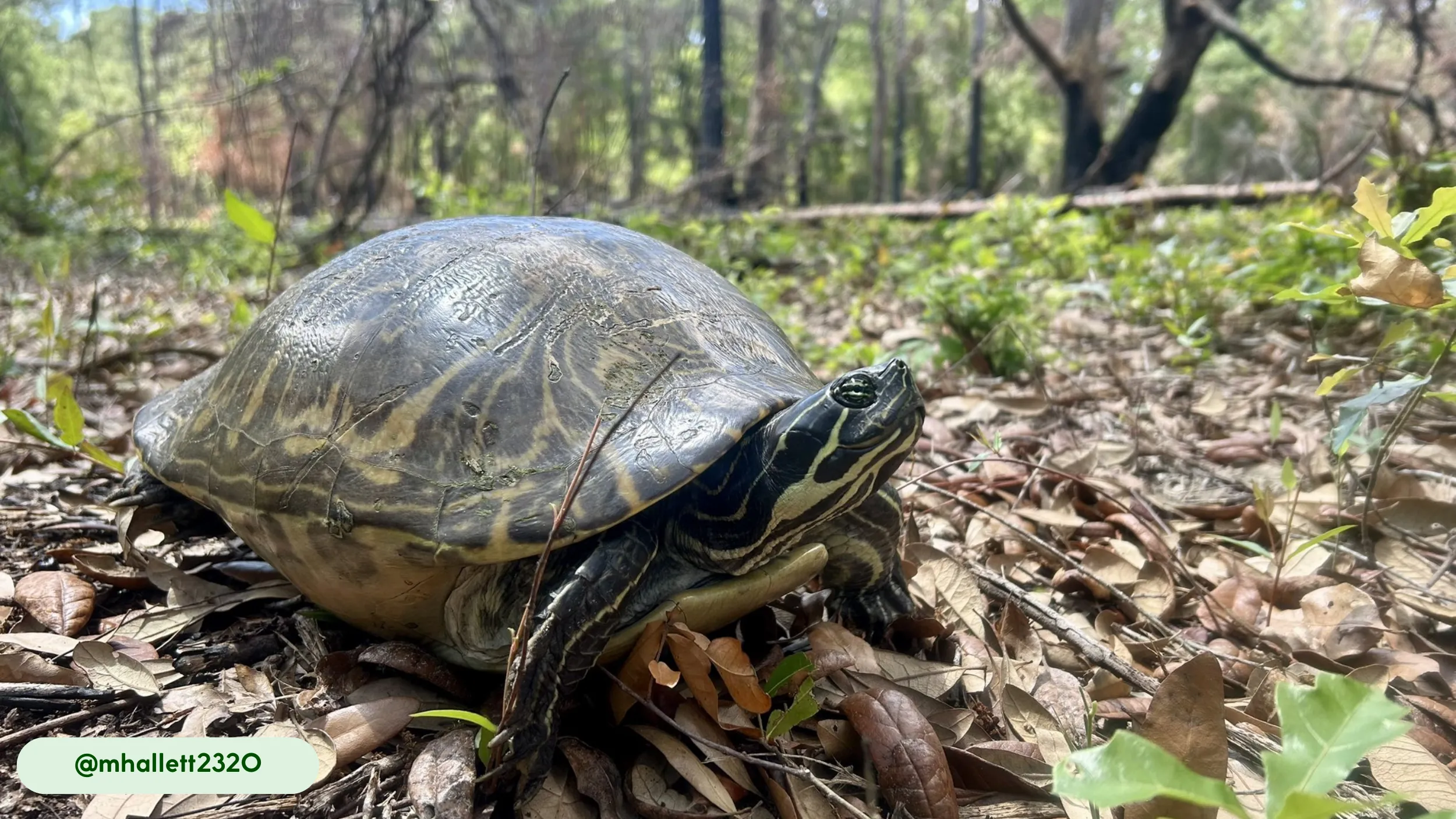
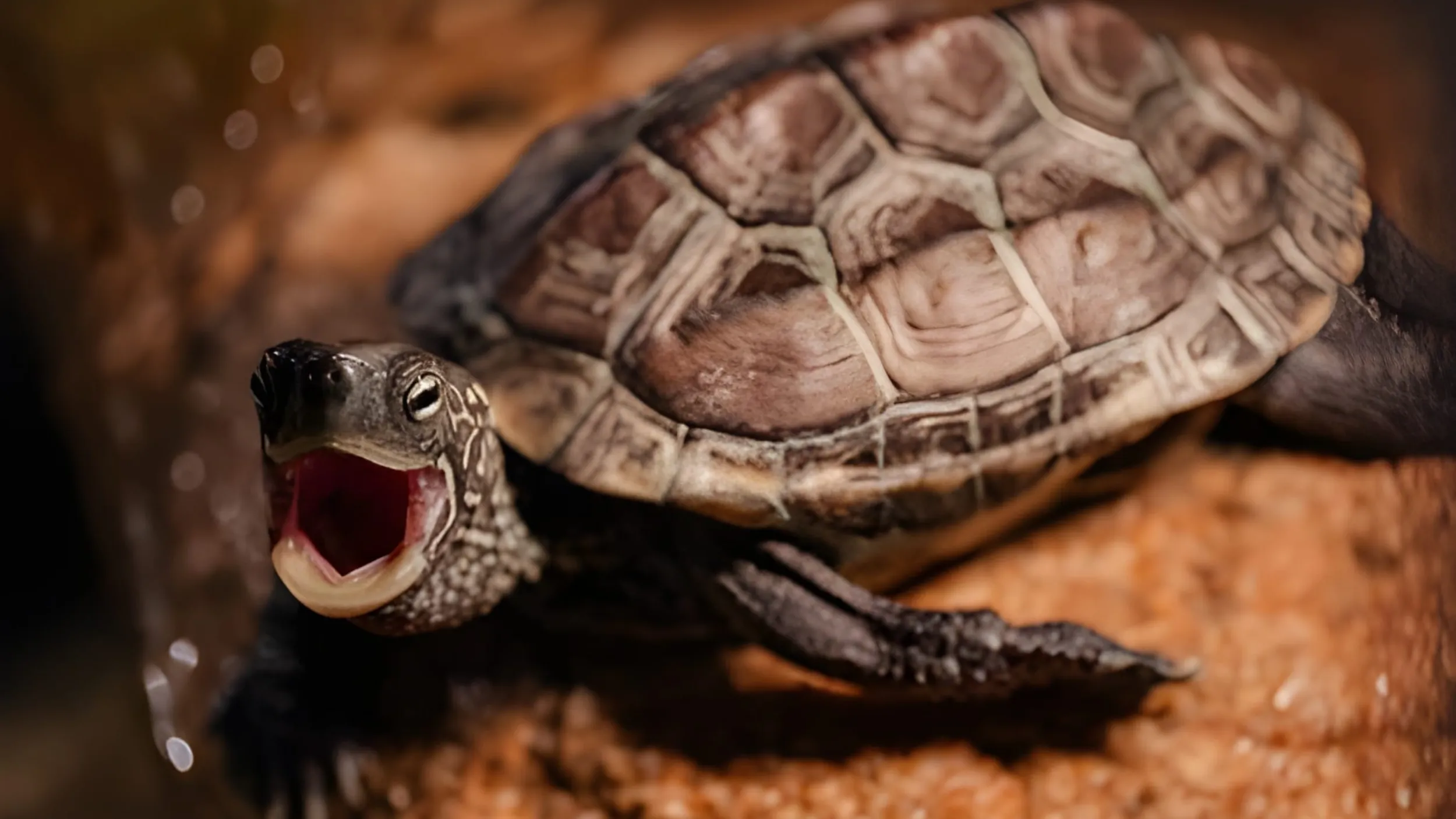
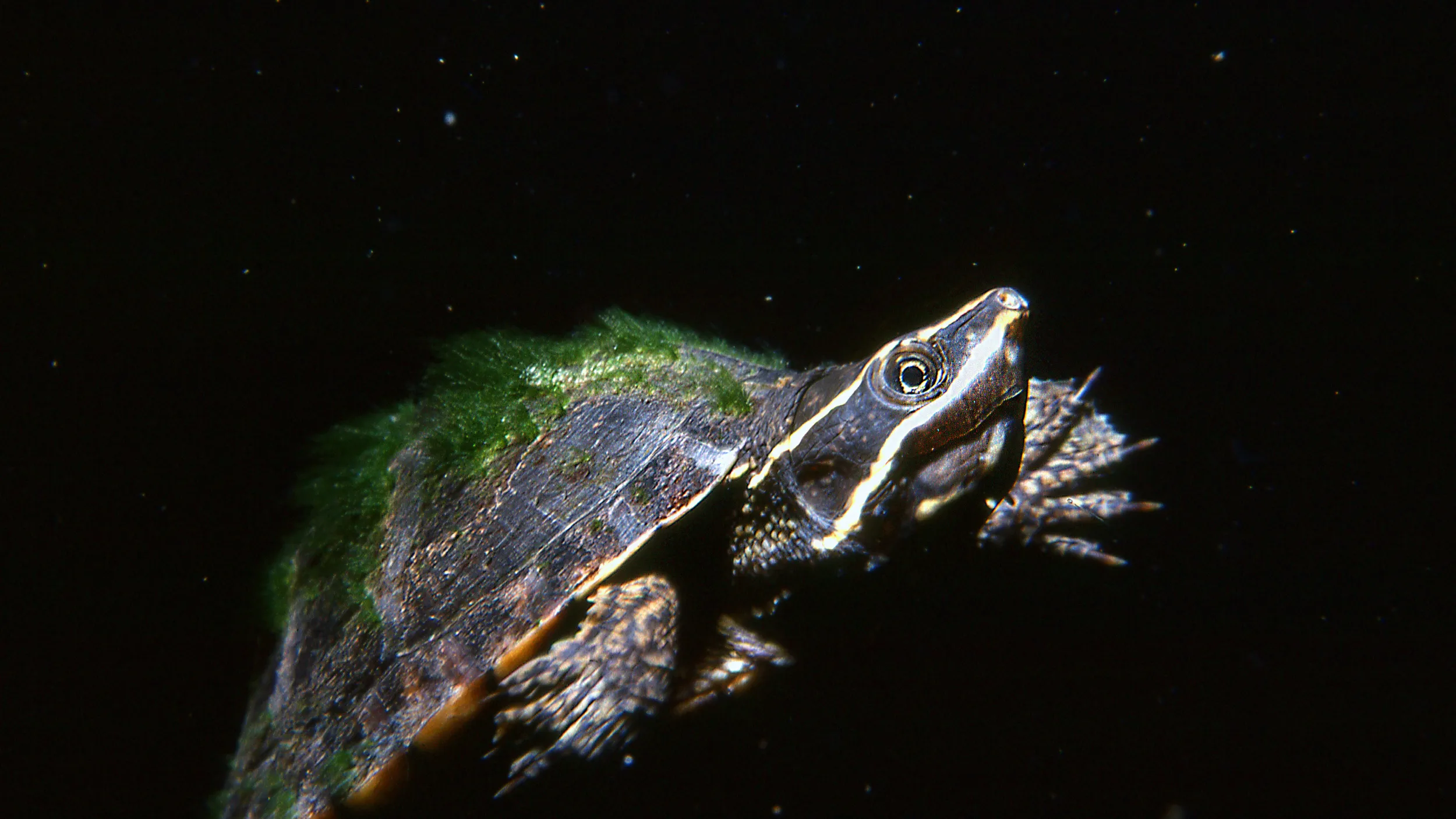
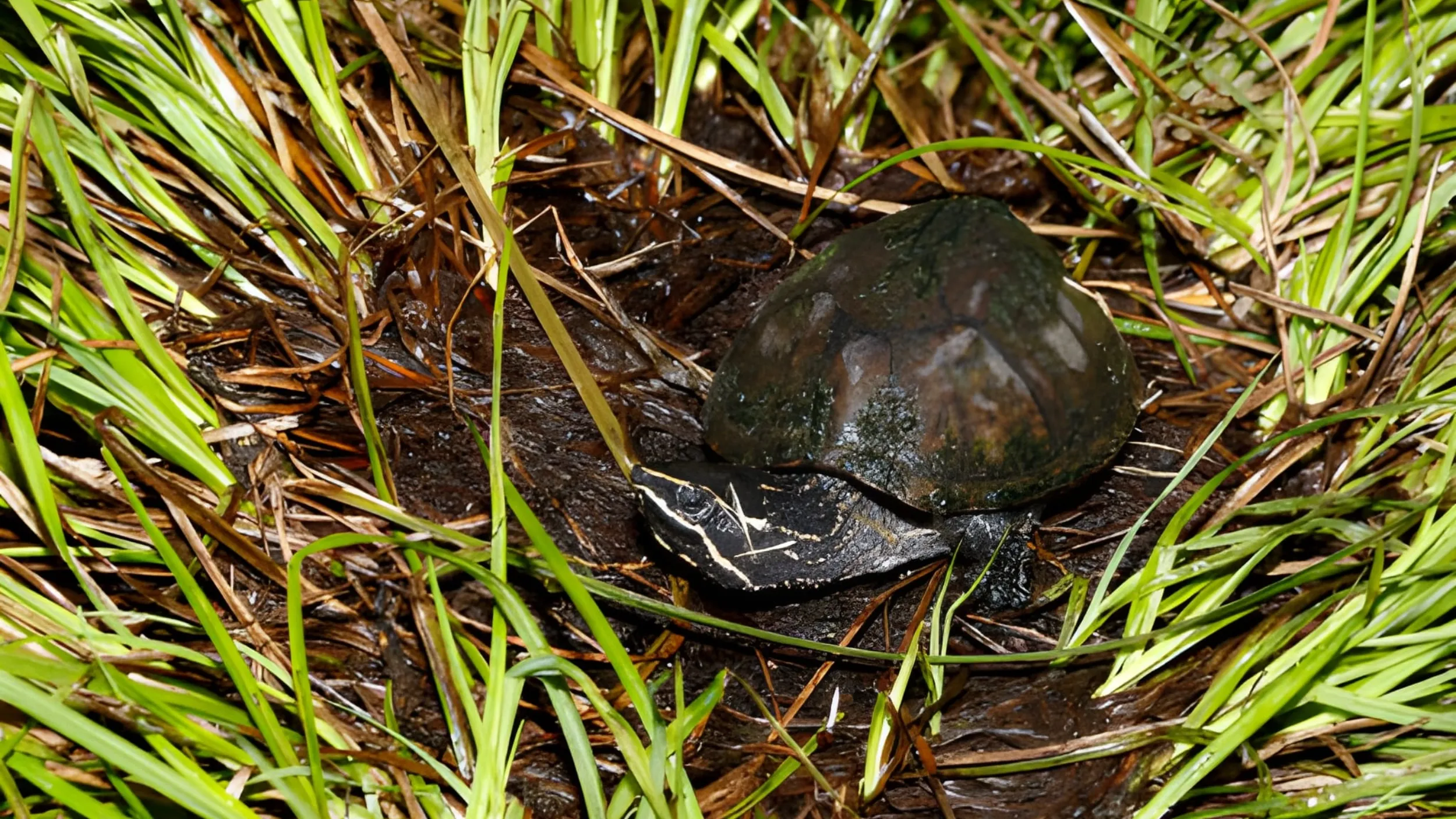
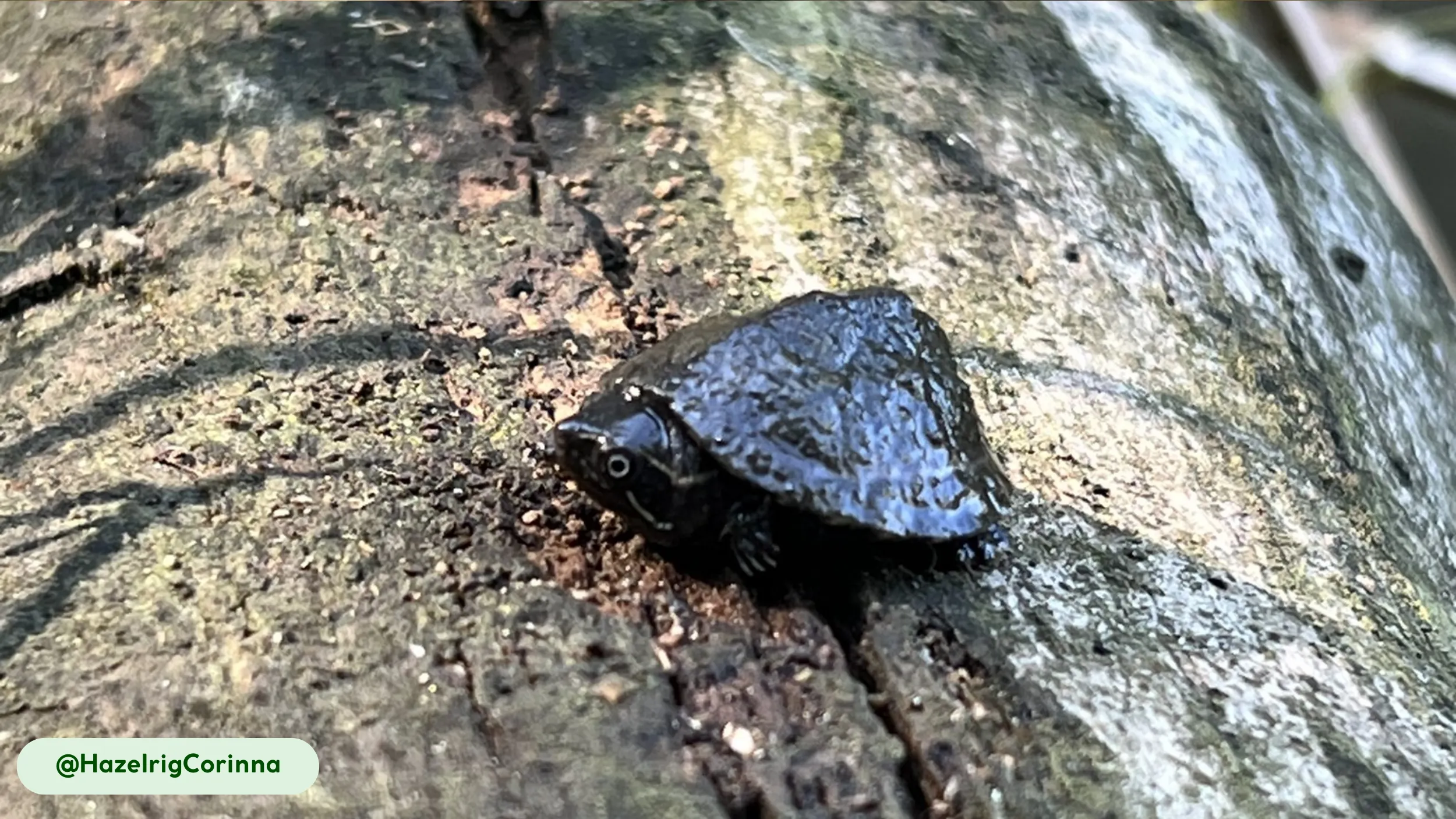
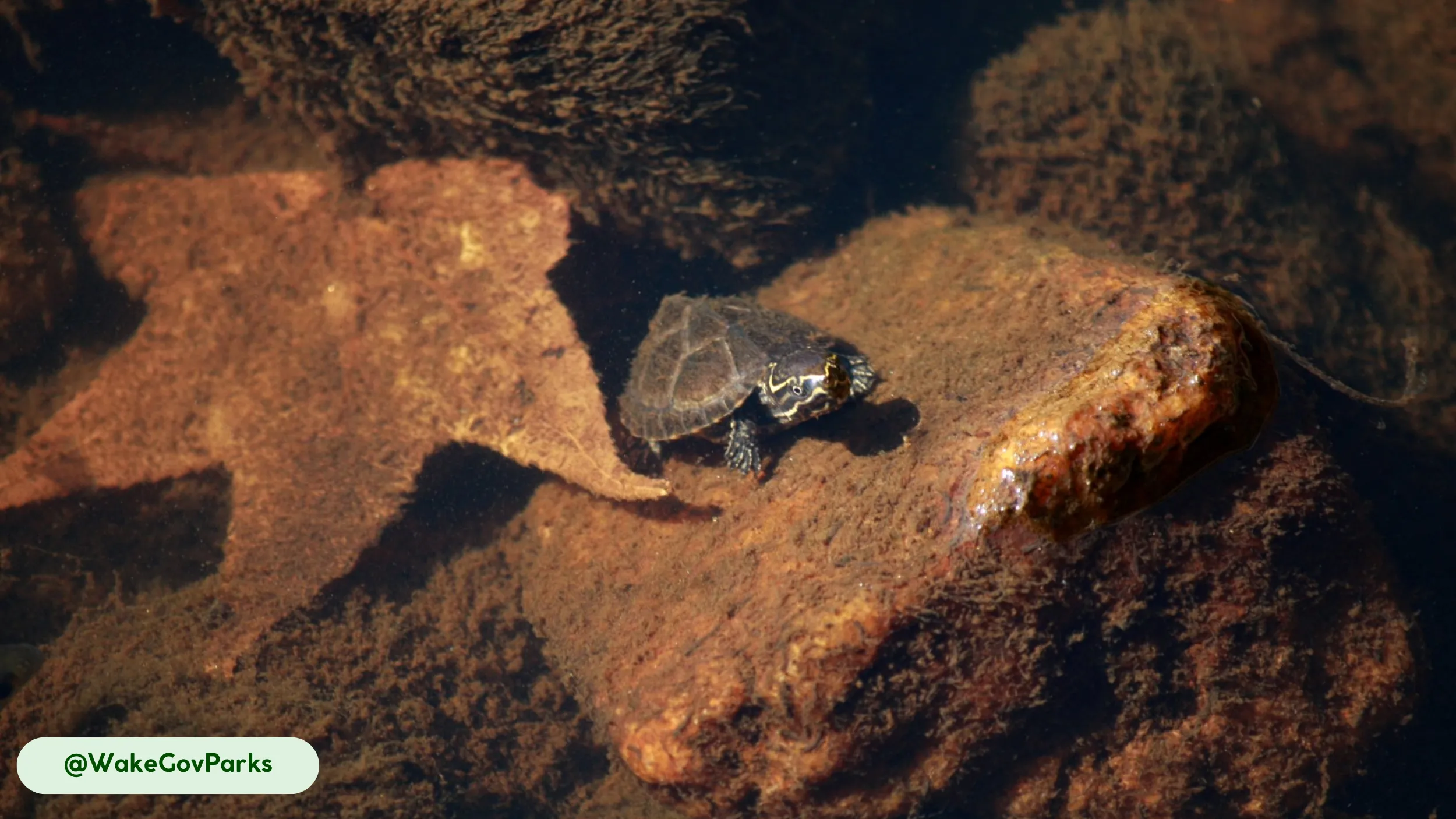
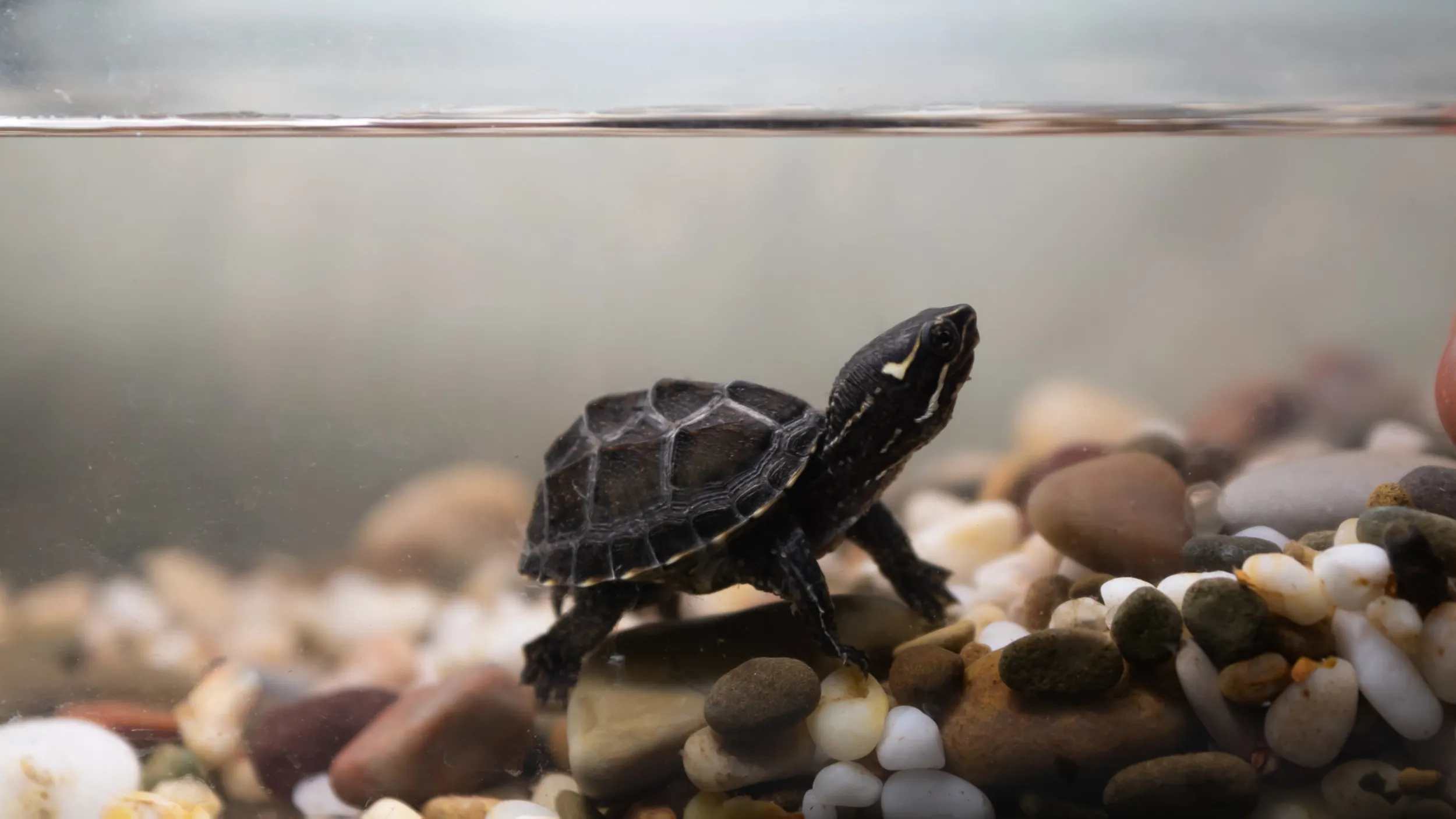
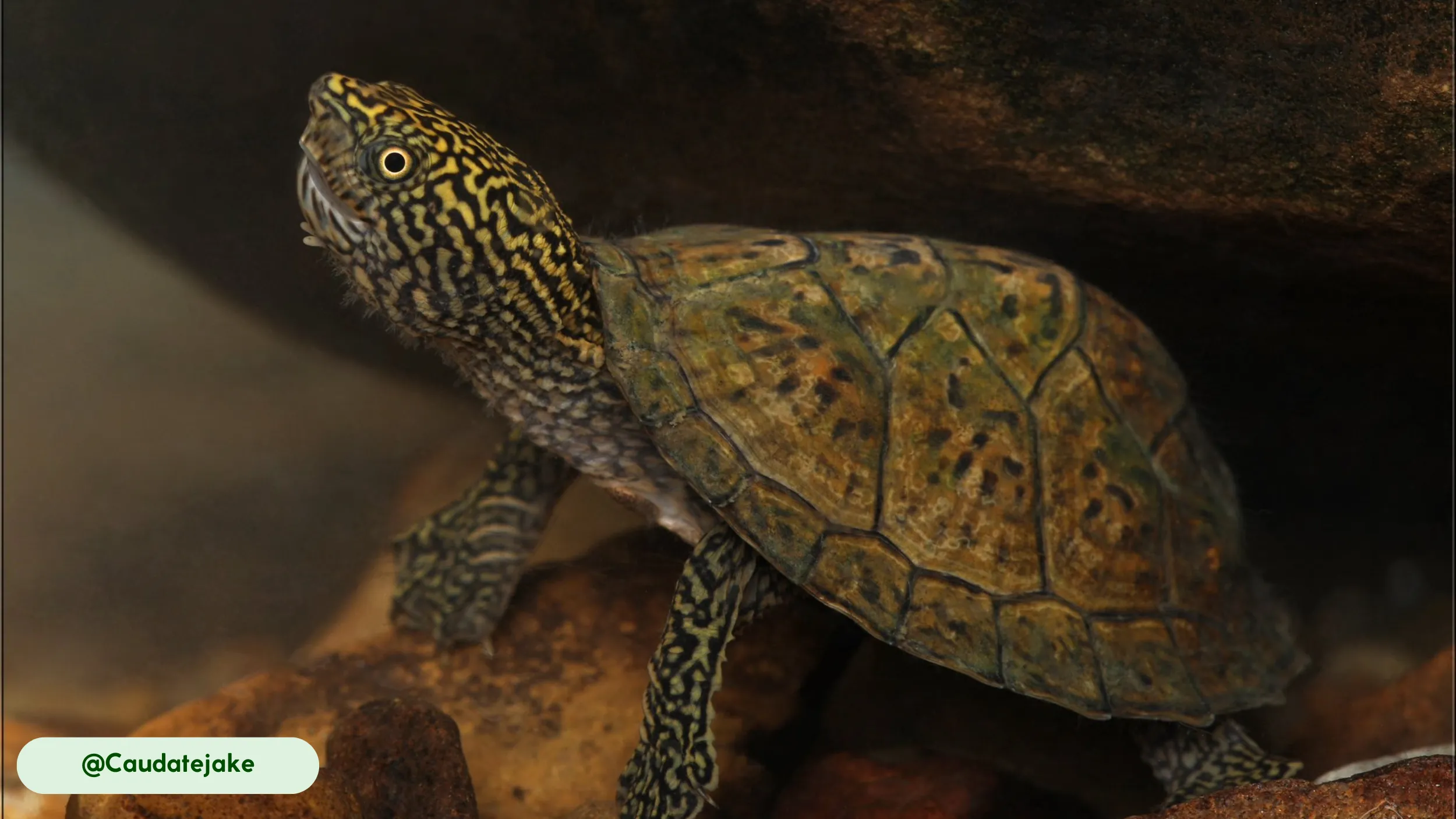
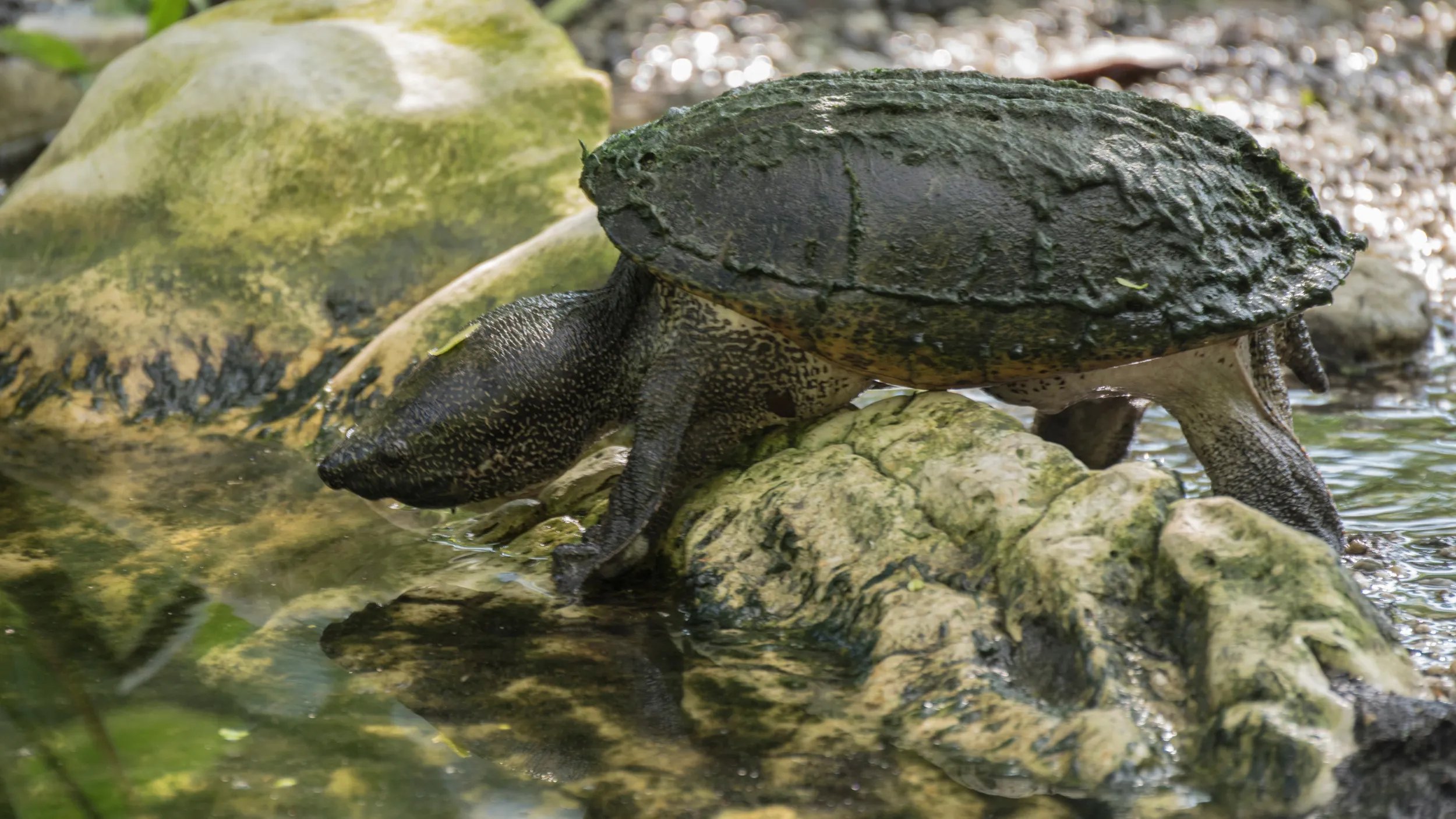
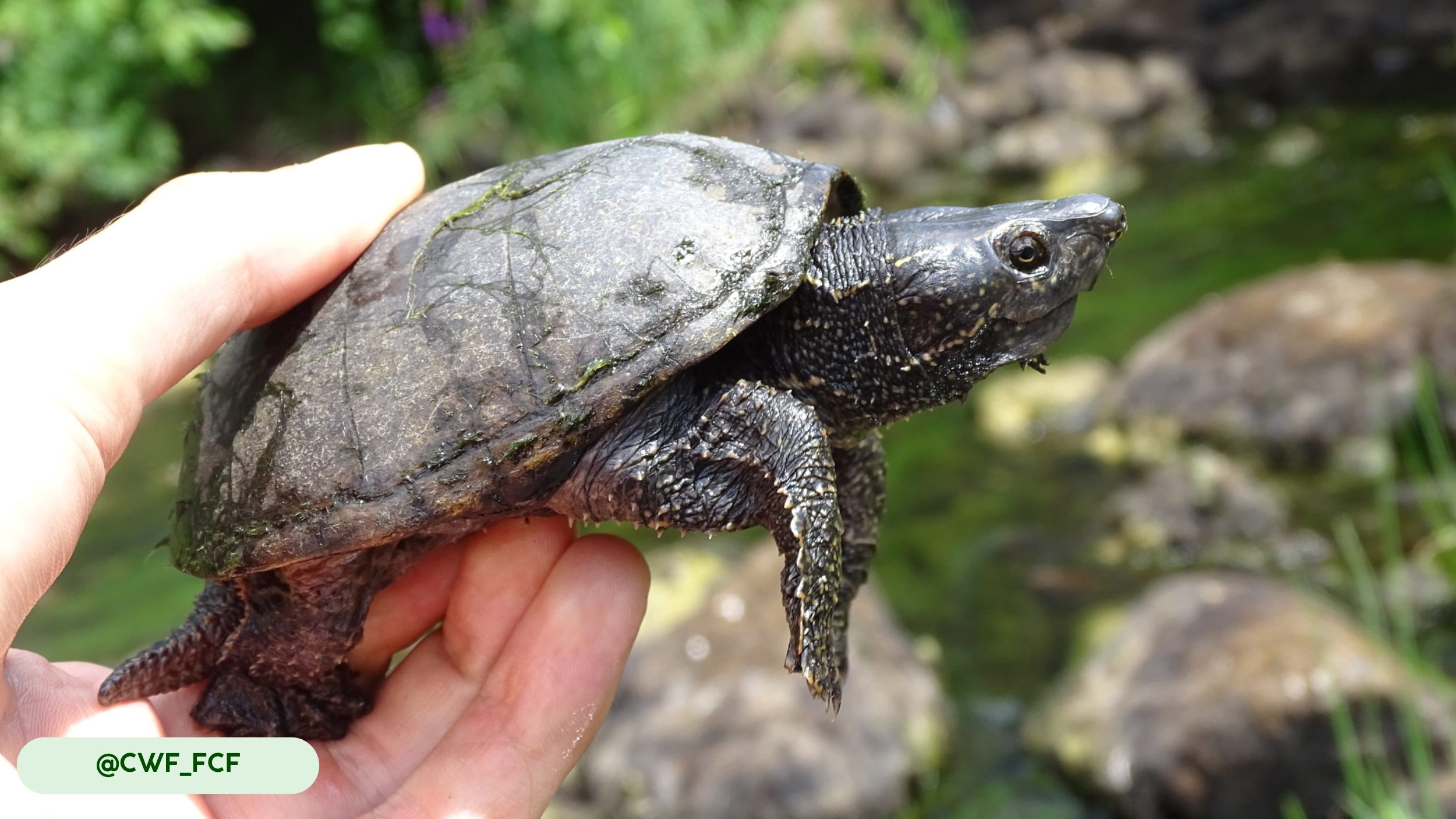
The Common Musk Turtle (Sternotherus odoratus) is a small freshwater turtle species native to North America. Its common name references the musky odor it can release from specialized glands as a defense mechanism, a characteristic that also gives it the colloquial nickname “stinkpot” (3, 4). This species belongs to the Kinosternidae family, a group of turtles known for their bottom-dwelling habits. Its small size, typically between 5-14 cm (2-5.5 inches) in length, makes it one of the smaller turtle species in its range (3).
Found across the eastern and central United States and parts of southeastern Canada, the musk turtle is an omnivore, primarily foraging on mollusks and aquatic insects in shallow, slow-moving waters (3, 15). While it is a slow swimmer, its primary mode of travel involves bottom-walking, and it is known for its ability to climb vertical surfaces to bask (3). The species is currently classified as Least Concern by the IUCN, though it faces threats from habitat loss and the pet trade (3).
This guide provides a detailed look at the Common Musk Turtle, covering its scientific identity, physical characteristics, and behaviors. By examining its physical adaptations, natural habitat, and ecological interactions, we can understand the factors that shape the life of this unique animal. From its distinctive defensive odor to its surprising climbing abilities, this comprehensive profile offers insights into the world of one of North America’s most fascinating reptiles.

What is Musk Turtle?
The Common Musk Turtle is a reptile of the Kinosternidae family, found across the eastern United States and parts of Canada, distinguished by its musky defensive secretion (3, 15). The scientific name, Sternotherus odoratus, directly reflects its unique traits. Sternotherus is derived from Greek words for “chest” and “animal,” alluding to its small, hinged plastron that resembles a chest plate. The species name odoratus is a Latin term for “fragrant” or “odorous,” a clear reference to its signature musk (8).
Known by several common names, including the Eastern Musk Turtle and Stinkpot, the species’ taxonomy is firmly established. While there were historical debates about its relationship with the Kinosternon genus, genetic evidence confirms Sternotherus as a distinct lineage within the Testudines order (6). The turtle is classified as a reptile in the phylum Chordata and kingdom Animalia (3). These taxonomic relationships clarify its place among other animals and emphasize its evolutionary history as a unique, self-contained species with no known subspecies.
Knowing what defines this turtle as a species is a great starting point. We can now observe its unique physical features, which are perfectly adapted for its aquatic lifestyle.

What Do Musk Turtles Look Like?
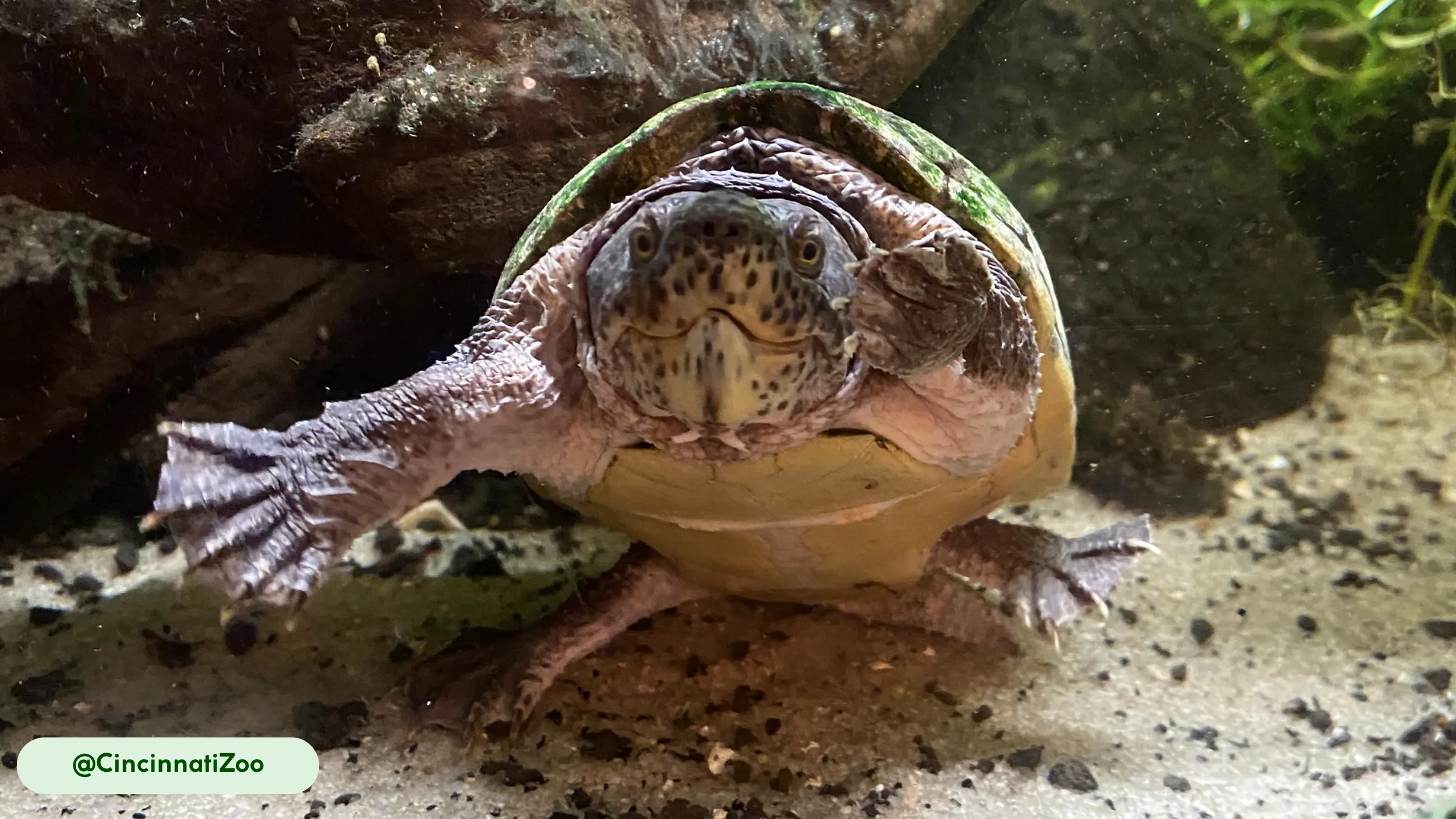
The Common Musk Turtle possesses a compact, robust body with a highly domed, oval-shaped carapace that provides protection in its aquatic environment (3, 8). The carapace, or upper shell, is typically dark brown, black, or olive and is often covered in green algae, which serves as natural camouflage and aids in thermal regulation (3). The turtle’s skin is a grayish-black color, with distinct yellow spots or stripes on the neck, limbs, and head, which fade with age (3). The head is relatively large compared to its body size, and it has a pointed snout that is highly sensitive to olfaction (3, 8). A study on the embryonic chondrocranium highlighted the structural similarities to soft-shelled turtles, an adaptation related to their mollusk-heavy diet (8).
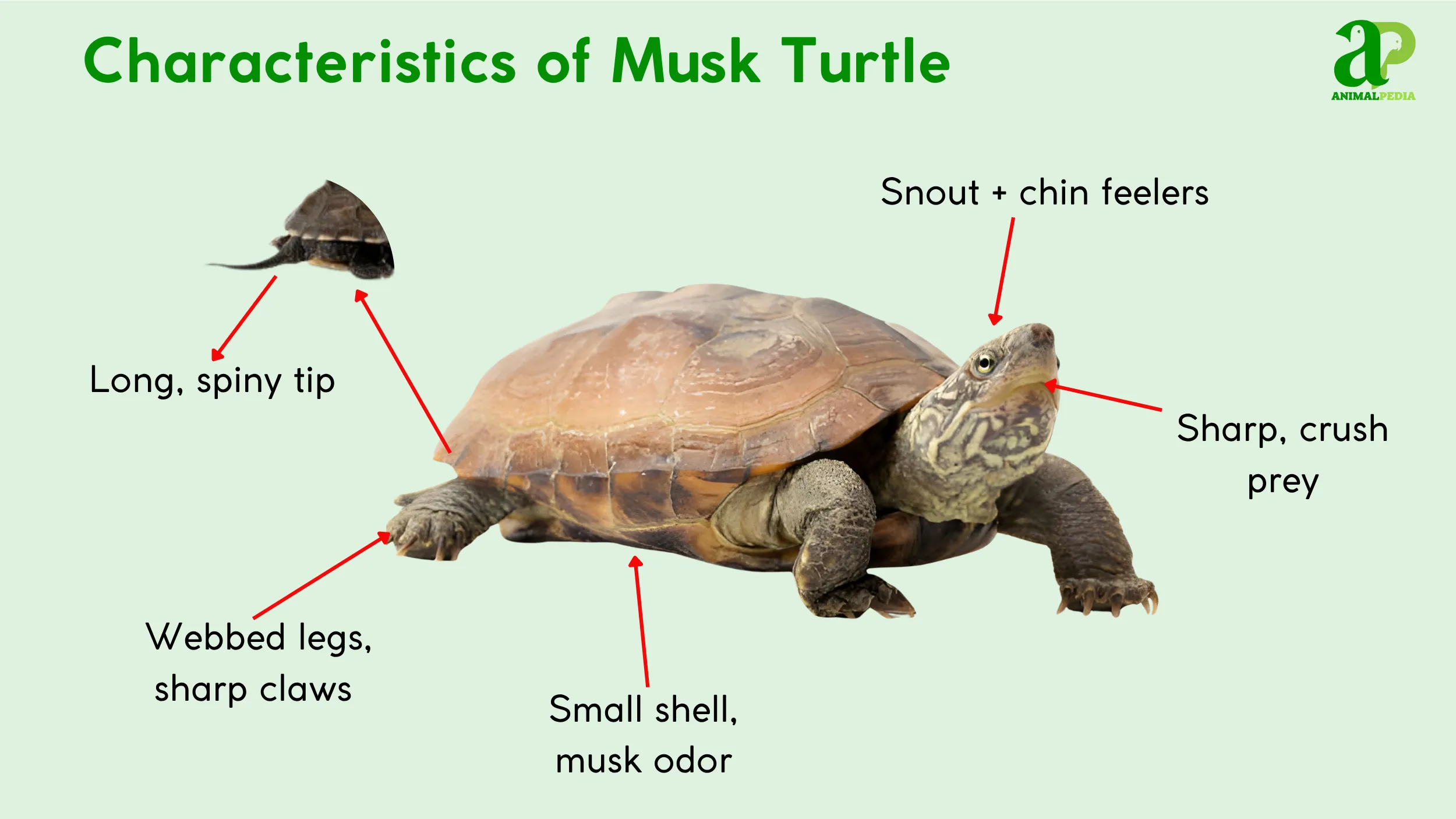
The musk turtle’s body is characterized by several distinctive features. These physical attributes, from its head to its tail, support its bottom-dwelling lifestyle and defensive capabilities (3, 8).
- Conical Head and Sensory Barbels: The turtle’s conical head features a pointed snout with small nostrils, a design that assists in probing muddy substrates for food (3). The most unique aspect of its facial structure is the presence of two pairs of fleshy filaments, or barbels, on the chin and throat, which function like taste buds to detect prey in dark or turbid waters (3).
- Webbed Feet and Sharp Claws: The turtle has four short, sturdy legs with webbed feet, enabling it to walk on the bottom of its habitat (3, 8). Sharp claws assist in digging through mud for food and in climbing on submerged logs or other debris, a behavior unusual for an aquatic turtle (3).
- Hinged Plastron and Musk Glands: The plastron, or lower shell, is small and cross-shaped with a movable hinge (3). This small size exposes a significant portion of the skin, a feature balanced by the presence of musk glands along the edges of the plastron (4). When threatened, the turtle releases a foul-smelling, musky secretion from these glands (3).
- Sharp, Horny Beak: Lacking true teeth, the Common Musk Turtle has a sharp, horny beak designed for crushing the shells of its mollusk prey and tearing other food items (3). This strong beak is a primary component of its defense, allowing the turtle to deliver a painful bite when provoked (3).
- Long Tail in Males: There is sexual dimorphism in the species, with males possessing a longer, thicker tail tipped with a spiny claw (3). This specialized tail, along with rough scales on the inner thighs, helps the male grip the female’s shell during mating (3).
The musk turtle’s body is a marvel of adaptation, but how does its size compare to other turtles? We can now measure its dimensions and understand the surprising facts about its small stature.
How Big Are Musk Turtles?
Adult Common Musk Turtles are small, typically ranging in length from 2 to 5.5 inches (5 to 14 cm) (3). They weigh approximately 0.5 to 1.3 pounds (0.2 to 0.6 kg) (3). The species shows minor sexual dimorphism; males have larger heads and longer, thicker tails, while females are slightly smaller overall (3, 8).
| Category | Male | Female |
| Length | Up to 5.5 in (14 cm) | Up to 5 in (12.7 cm) |
| Weight | Up to 1.3 lbs (0.6 kg) | Up to 1.1 lbs (0.5 kg) |
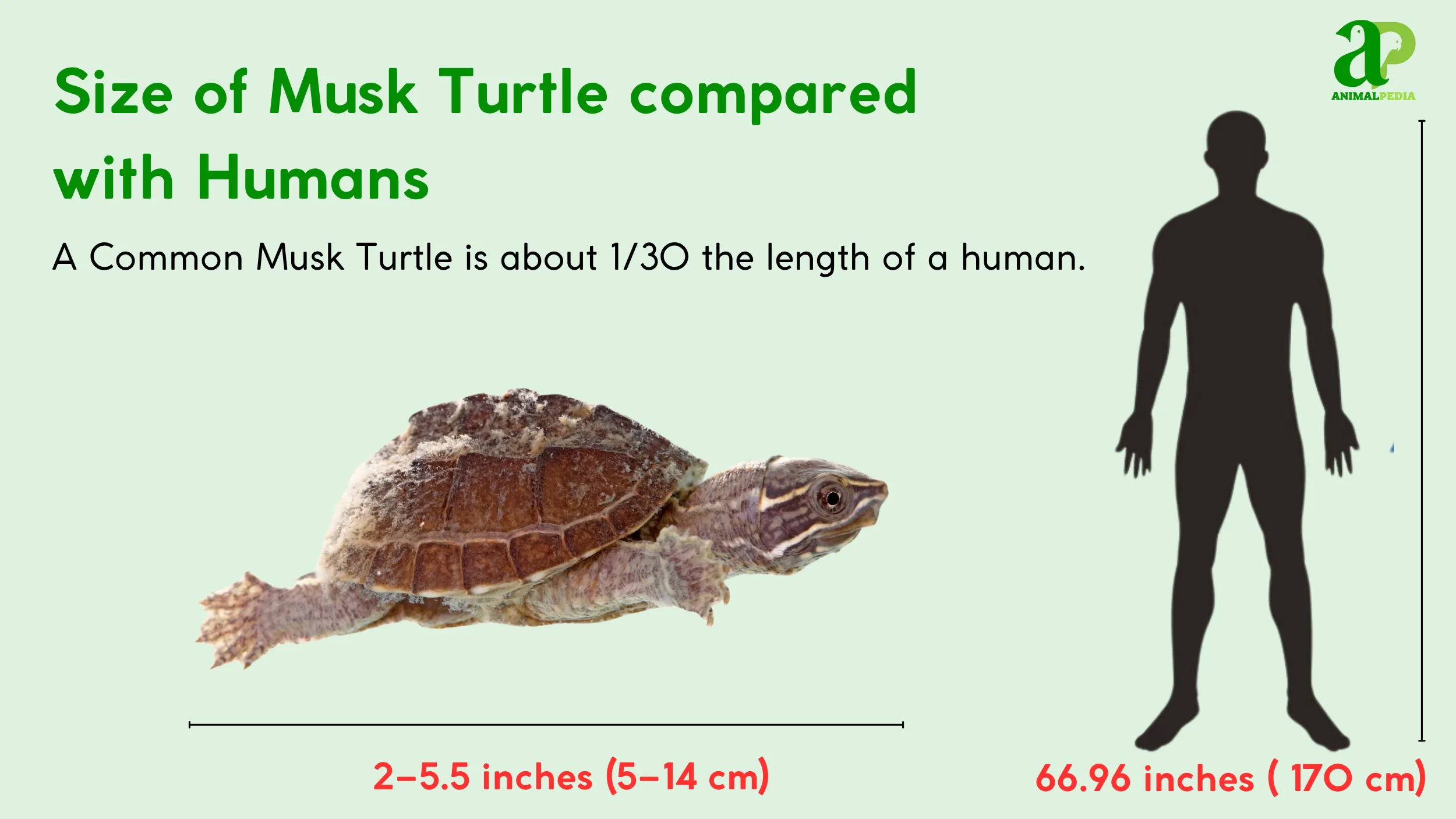
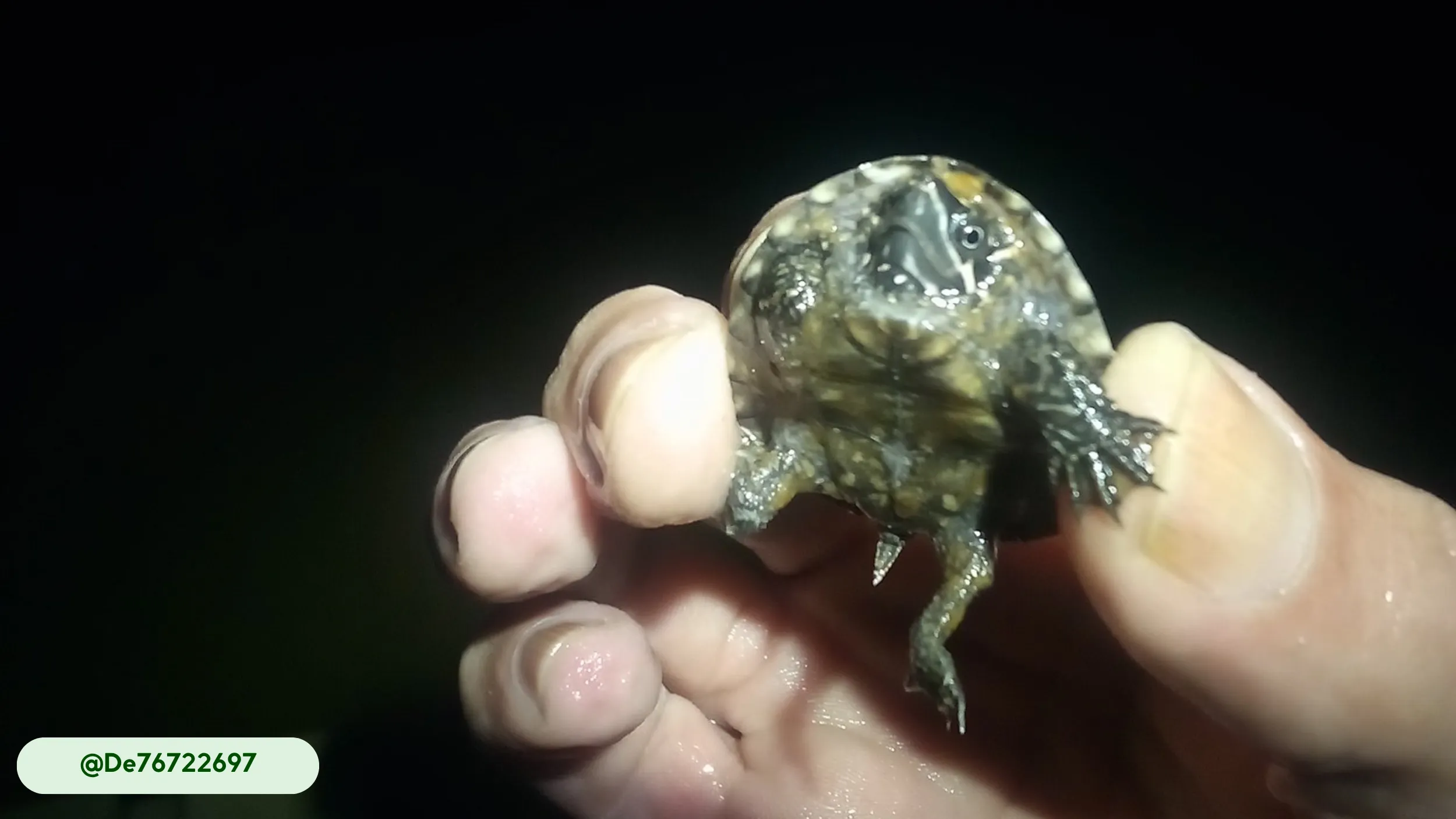
A newly hatched musk turtle is diminutive, measuring only 0.7 to 1 inch (1.8 to 2.5 cm) long and weighing just 0.004 to 0.007 pounds (1.6 to 3.2 g) (3). These turtles reach sexual maturity in four to eleven years (3).
Their modest size influences more than just their appearance; it also plays a significant role in their habitat preferences. We can now journey into the environments they call home and see how they thrive.
Where Do Musk Turtles Live?
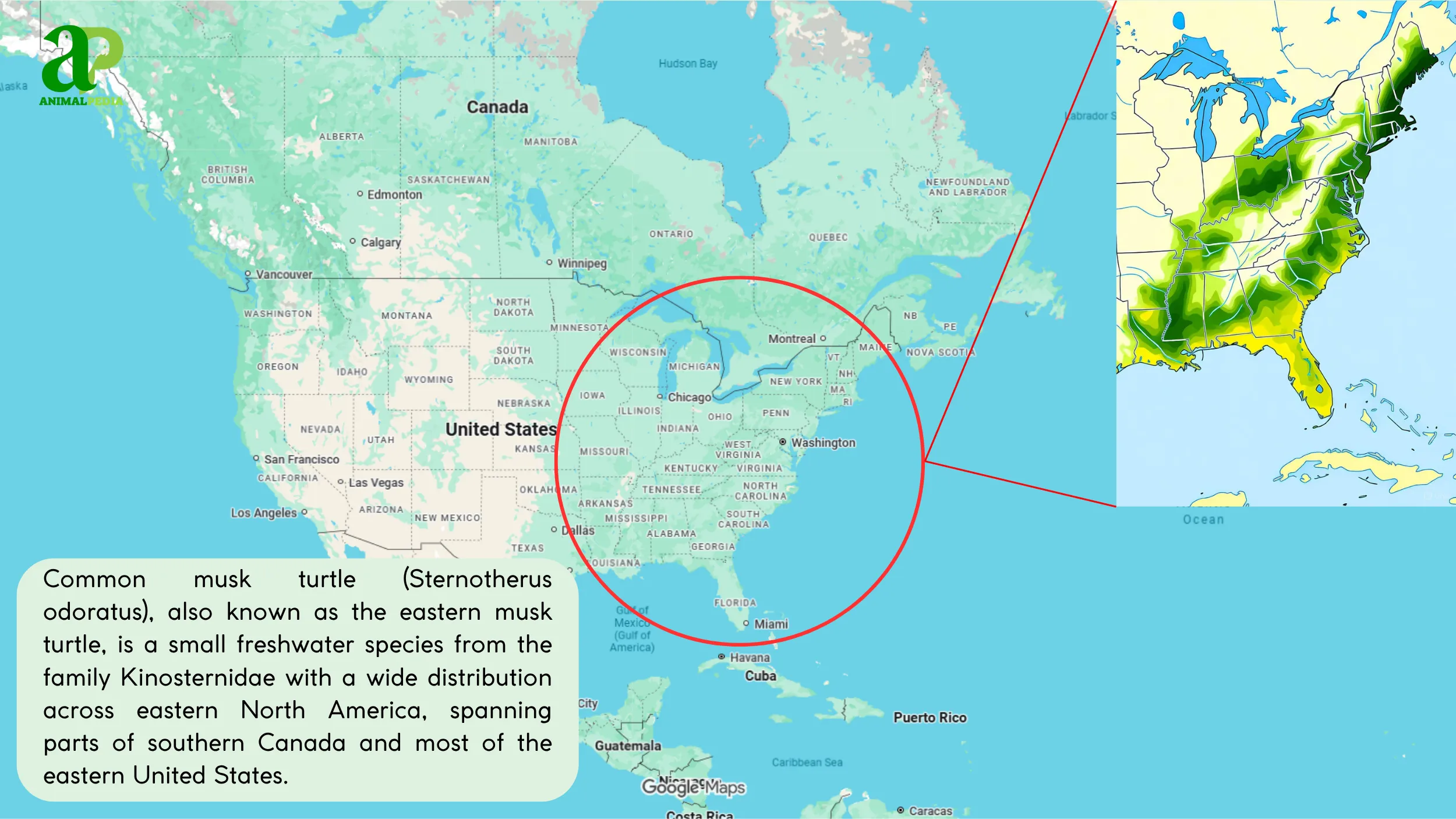
The Common Musk Turtle inhabits slow-moving freshwater environments throughout a wide range in North America (3, 15). Its geographic distribution extends from southern Ontario, Canada, south to the Florida Keys, and as far west as central Texas and eastern Kansas (3). These reptiles prefer shallow waters with soft, muddy or sandy substrates and dense aquatic vegetation, which provide ample foraging grounds and cover (3). They live in various habitats, including ponds, lakes, rivers, canals, and swamps (3).
Musk turtles are generally aquatic but will sometimes leave the water to bask or find new territory (4). They are not known to be territorial and can coexist with many other turtles, often found in high densities where their habitat is suitable (11). They do not require specific elevation ranges, but they need a temperate climate with access to soft bottom substrates for burrowing and hibernation (3). During colder months, they bury themselves in the mud, staying dormant until temperatures rise (3, 5).
The environment a musk turtle inhabits directly shapes its daily routines and survival strategies. It is time to observe the fascinating behaviors that allow this species to flourish in its specific niche.
How Do Musk Turtles Behave?
The Common Musk Turtle’s behavior is defined by its bottom-dwelling habits, slow movements, and crepuscular and nocturnal feeding patterns. These behaviors, along with specialized physical adaptations, allow the species to thrive in its aquatic niche.
- Diet and Feeding: They are opportunistic omnivores that forage for mollusks, insects, and other aquatic invertebrates on the bottom of their aquatic habitats.
- Movement and Abilities: These turtles are slow bottom-walkers with specialized physical capabilities, including surprising climbing skills.
- Daily/Seasonal Patterns: They exhibit a crepuscular and nocturnal activity cycle, becoming dormant during the cold winter months for brumation.
The Common Musk Turtle’s existence is a testament to its unique adaptations. How do these behavioral patterns shape its daily life and its role in the ecosystem?
Diet and Feeding
The Common Musk Turtle is a carnivorous omnivore that primarily preys on aquatic invertebrates. Its diet is heavily focused on mollusks, crustaceans, and insects, although it also consumes carrion and small amounts of aquatic vegetation (3, 11). Studies indicate that snails, clams, and aquatic insect larvae constitute a significant portion of its diet (7).
The turtle actively forages along the bottom of its habitat, using its heightened sense of smell and the sensory barbels on its chin to locate prey in low visibility conditions (3, 11). The powerful, hooked beak allows it to crush the hard shells of mollusks and manipulate other food items with ease. This active, opportunistic feeding strategy enables the turtle to thrive in a wide range of freshwater environments where its preferred prey is abundant (6).

Movement and Abilities
The Common Musk Turtle moves primarily by walking on the bottom of its aquatic environment, with limited swimming and terrestrial movement. These turtles use their short, sturdy legs to walk along the substrate, a slow but effective method for navigating their shallow habitat (11). While largely aquatic, the musk turtle will sometimes leave the water, particularly to find a new habitat or lay eggs (4). Although it can swim, it is not a strong or fast swimmer, and this is not its primary mode of movement (11). Due to its slow-moving nature, the species does not achieve high speeds. There is no widely cited data for its top speed, as its movement is better described as a deliberate, slow crawl along the bottom of a pond or river (11). This bottom-dwelling behavior allows it to conserve energy while foraging.
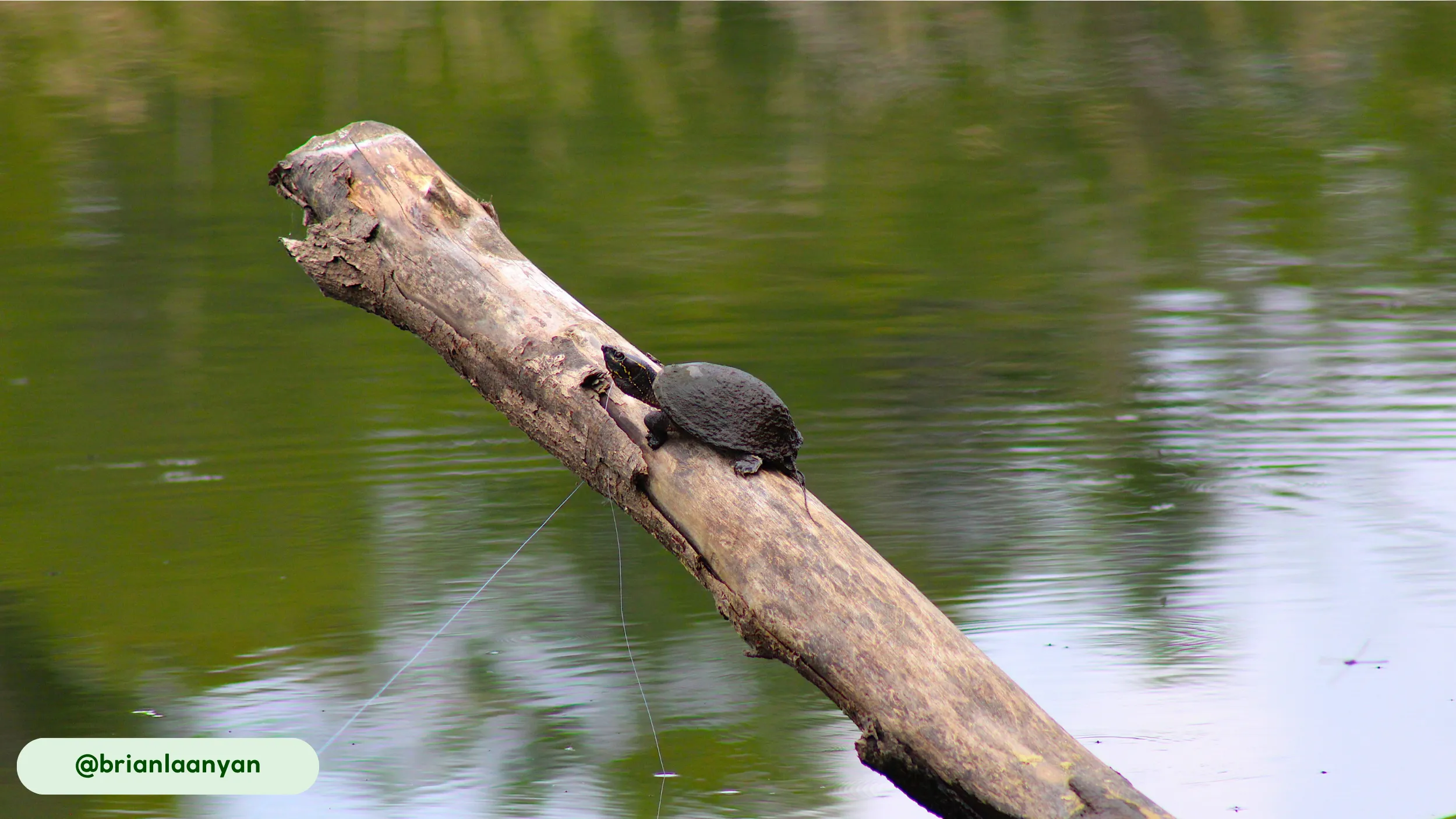
One of the most unique abilities of the Common Musk Turtle is its capacity for climbing (11). These reptiles are known to scale vertical objects like submerged logs, branches, and even floating docks to bask in the sun. This behavior helps with thermoregulation and is a surprising trait for an aquatic turtle. Its strong claws and powerful grip facilitate this unexpected skill.

Daily/Seasonal Patterns
The Common Musk Turtle is most active during the crepuscular and nocturnal hours, becoming dormant during the colder months. The turtle’s daily activity cycle begins as the sun sets, when it becomes active in its search for food (3). This crepuscular and nocturnal behavior helps it avoid predators and capitalize on the activity of its prey (3). During the day, the turtle is often sedentary, resting on the bottom or basking on submerged objects to regulate its body temperature (11). It is most active seasonally during the warm spring and summer months (15). During this time, they engage in feeding, mating, and nesting behaviors (3, 11).

The species does not undertake long-distance migrations (4). Their movements are typically limited to short terrestrial journeys to find a new habitat or to reach nesting sites (4). During the winter, the musk turtle enters a state of dormancy known as brumation (11). It buries itself in the mud or soft substrate at the bottom of its aquatic habitat to survive the cold temperatures until spring arrives (5).
From their feeding habits to their movements, every aspect of a musk turtle’s behavior contributes to its survival. The cycle of life for this species continues with a look into their unique reproductive habits.
How Do Musk Turtles Reproduce?
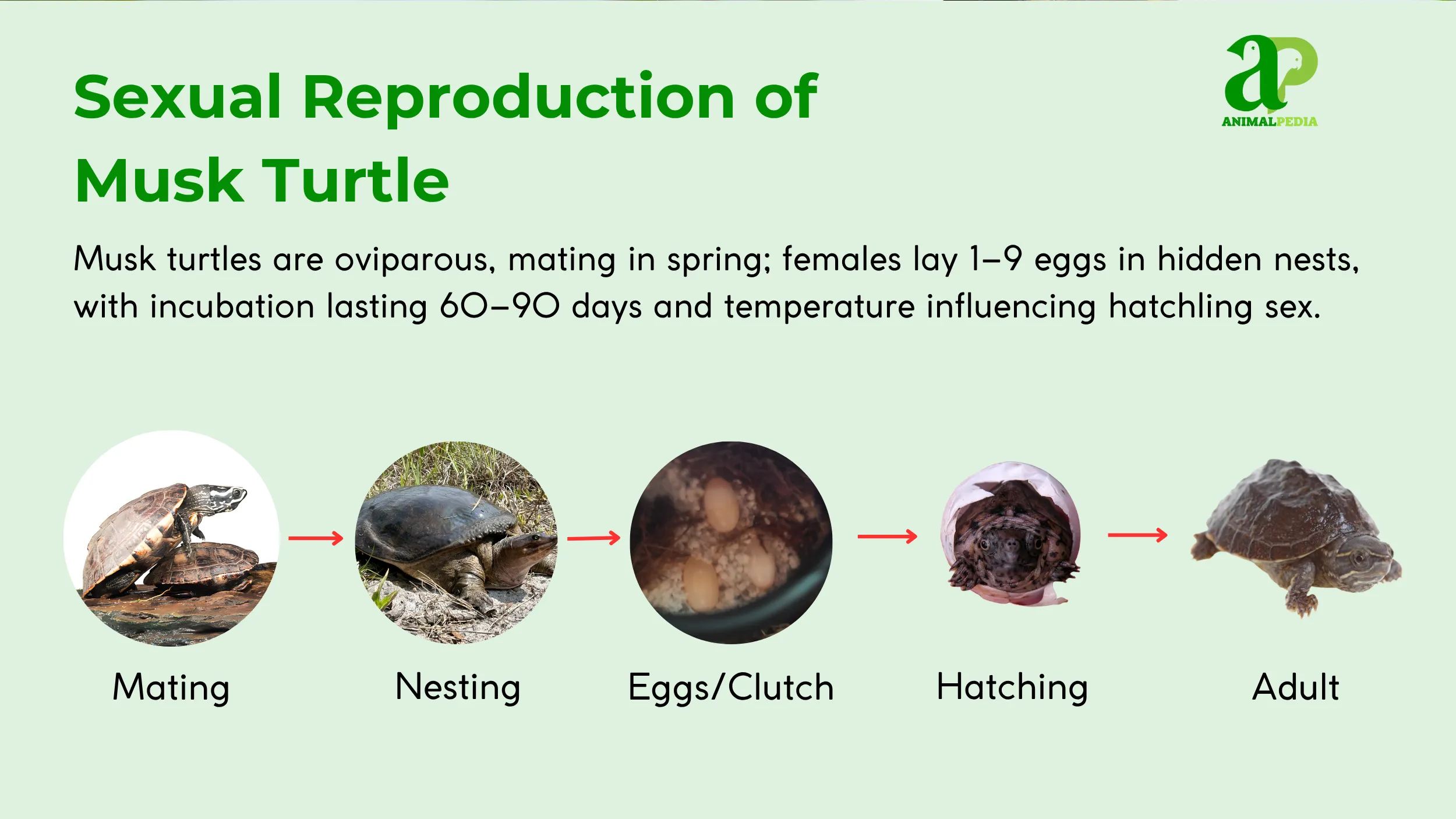
Musk turtles are oviparous, reproducing by laying eggs. Mating typically occurs in the spring, with males using a series of behaviors, including biting the female’s carapace and limbs, to initiate copulation (4, 11). Females create nests on land in shallow, concealed areas, such as under logs or in leaf litter (4, 11). The clutch size ranges from 1 to 9 eggs, with an average of 3, and multiple clutches are possible per year (11). The incubation period lasts approximately 60 to 90 days, with the temperature of the nest determining the sex of the hatchlings (4).
Reproduction ensures the continuation of the species. An animal’s lifespan is also a crucial part of its biology. Let’s examine the lifespan of these reptiles and the factors that influence their longevity.
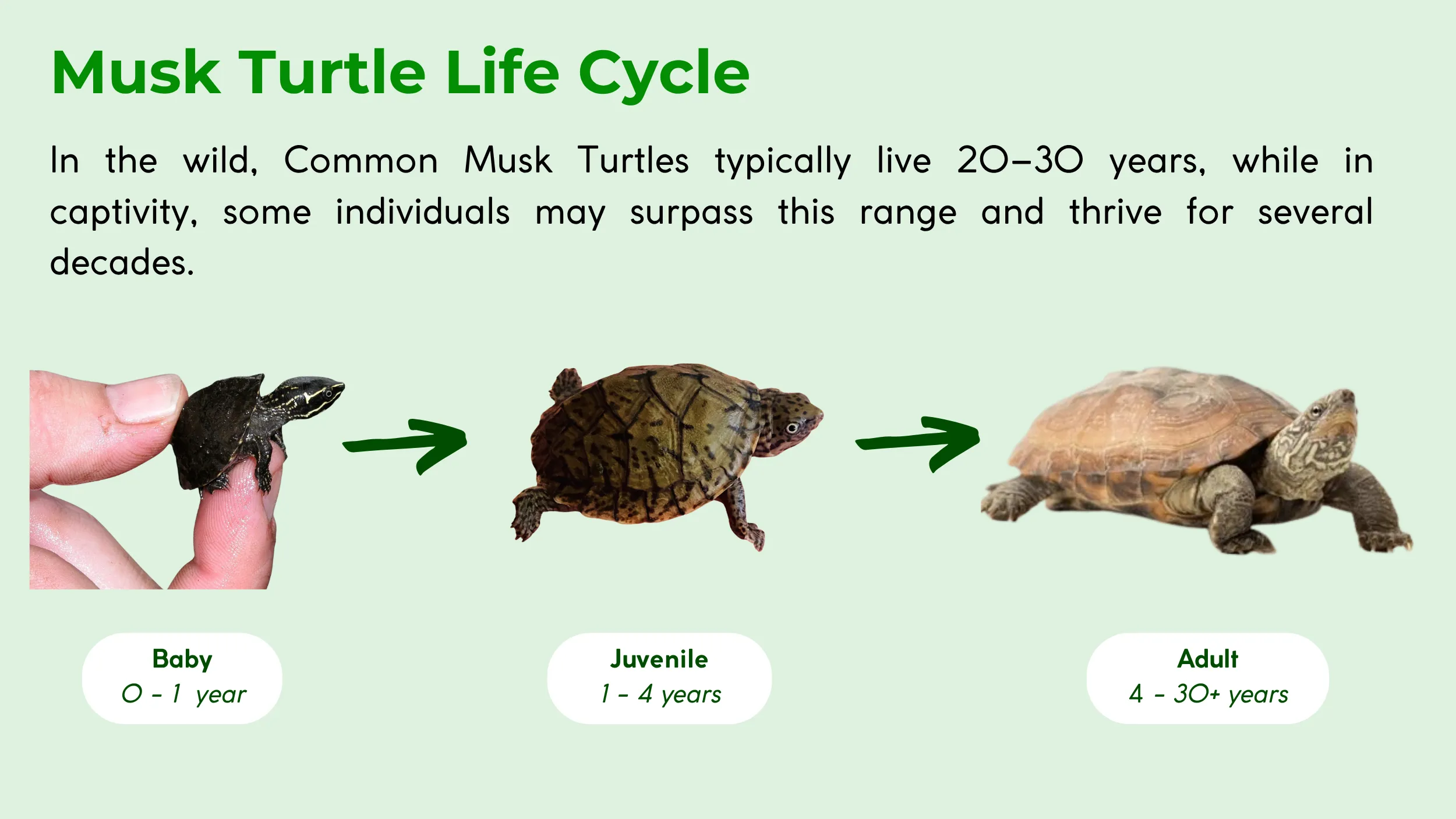
How Long Do Musk Turtles Live?
The Common Musk Turtle lives 20 to 30 years in the wild, with some individuals reaching older ages in captivity (2). Their longevity is influenced by factors like habitat quality, diet, and predation (4, 11). In a controlled captive environment, with consistent care, musk turtles can live for several decades, often surpassing their wild lifespan (2). The species reaches sexual maturity at a slow rate, between four and eleven years of age (3). This late maturity makes them susceptible to population declines due to environmental pressures.
While their long lives are a testament to their resilience, their interactions with humans are less about time and more about their unique defensive traits. We will now consider how these animals coexist with people.
Are Musk Turtles Beneficial to Humans?
Musk turtles are not directly beneficial or harmful to humans. When handled, they use a defensive tactic by releasing a foul-smelling musk from glands along their shells, earning them the nickname “stinkpot” (3, 11). They can also deliver a painful bite with their powerful, hooked beak, but they are not venomous (3). It is best to observe these turtles from a distance and avoid handling them to prevent the musky spray and a possible bite. They contribute to their ecosystem by consuming decaying matter and controlling populations of aquatic invertebrates (3, 11).
The musk turtle’s defensive habits are a natural part of its existence. Its overall survival is a matter of conservation. We can now examine their conservation status and the efforts to protect their habitats.

Are Musk Turtles Endangered?
The Common Musk Turtle is not endangered, holding a conservation status of Least Concern on the IUCN Red List (3). Despite this status, the species faces threats from habitat loss due to wetland draining and pollution (15). The pet trade also poses a risk, as many are collected from the wild (15). These turtles play an important role in their ecosystem, controlling populations of snails and insects, and serving as a food source for larger animals (3, 11). Individuals can help by protecting wetland habitats, avoiding their removal from the wild, and driving carefully near bodies of water to prevent road mortality.
The musk turtle’s conservation status shows its resilience in the wild. Its story holds many surprising details. We can now explore some of the most captivating facts about this small but resilient reptile.

Frequently Asked Questions About Musk Turtles
Why Do Musk Turtles Sometimes Bask On Branches Above Water?
Musk turtles bask on branches to regulate their body temperature. This behavior, known as thermoregulation, is essential for their metabolism, digestion, and overall health (4, 11). They climb out of the water to absorb heat from the sun and then return to the water to cool down.
How Do Musk Turtles Communicate With Each Other?
Musk turtles primarily communicate through chemical signals and tactile contact. They use scents to identify mates and territorial boundaries. During courtship, males use physical contact and biting to initiate interaction (4). Vocalizations are rare and are not a primary form of communication (13).
Can Musk Turtles Survive In Brackish Water?
Yes, musk turtles can survive in brackish water, although they prefer freshwater habitats. Their physiology allows them to tolerate some level of salinity, and populations have been found in coastal estuaries and tidal areas (14).
Do Musk Turtles Migrate Seasonally?
No, musk turtles do not undertake long-distance migrations. Their movements are usually confined to a small home range. They may undertake brief terrestrial trips to find a new habitat or lay eggs, but they stay within a localized area (4).
How Do Musk Turtles Avoid Predation on Their Nests?
Musk turtles avoid nest predation by using camouflage and concealment. Females lay their eggs in small, well-hidden nests under leaf litter, soil, or logs (4, 11). The small clutch size also reduces the overall loss if a single nest is discovered.
The common musk turtle’s resilience and unique features make it a truly fascinating species. Its ability to thrive in various freshwater habitats, along with its surprising climbing skills, highlights its adaptability. By understanding its biology and behavior, we can better appreciate its role in the ecosystem. Animal Pedia is committed to providing comprehensive, scientifically accurate information about the animal kingdom. We invite you to explore our extensive digital encyclopedia for more in-depth knowledge and discover other amazing species that call our planet home.














