Kemp’s Ridley sea turtles (Lepidochelys kempii) are the smallest species of sea turtles, classified within the family Cheloniidae, a group of marine reptiles [15, 17]. Adults typically measure 21.6–27.6 inches (55–70 cm) and weigh up to 119 lbs (54 kg) [15, 16].
This critically endangered species inhabits the Gulf of Mexico and the western Atlantic Ocean, where it primarily consumes crustaceans [8, 20]. Their movements are seasonal, following shifts in water temperature to find optimal foraging grounds [1, 9]. The species’ status is a direct result of historical population declines and ongoing threats [7, 19].
This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth biological overview, detailing the species’ unique physical characteristics, specific habitat, and their distinctive behaviors. We will examine everything from their specialized diet and migratory patterns to their world-renowned arribada nesting events. Understanding their classification and physical features is the first step in appreciating the complexities of this reptile.

What Is Kemp’s Ridley Sea Turtle?
Kemp’s Ridley sea turtle is a critically endangered marine reptile of the family Cheloniidae, native to the Gulf of Mexico and the western Atlantic Ocean, recognized for their unique synchronized nesting behavior [17, 19]. This species belongs to the class Reptilia and the order Testudines, a lineage that includes all turtles and tortoises [15].
Its scientific classification is Lepidochelys kempii, and it is a close relative of the Olive Ridley sea turtle (Lepidochelys olivacea). The species was first formally described by Samuel Garman in 1880 [3], but it remained a rare sight until its major nesting ground was rediscovered in Mexico in the 1960s [1]. It is also known by alternative names such as the Atlantic Ridley or simply the Ridley turtle [19].
The unique biological and behavioral traits of the Kemp’s Ridley, from their taxonomic lineage to their specific feeding habits, provide a foundation for understanding their place in marine ecosystems. This knowledge is fundamental to understanding their physical features and what makes them a distinct species. From their taxonomic classification, we can gain a better understanding of their physical features. We will now examine the unique physical characteristics that distinguish the Kemp’s Ridley.

What Do Kemp’s Ridley Sea Turtles Look Like?
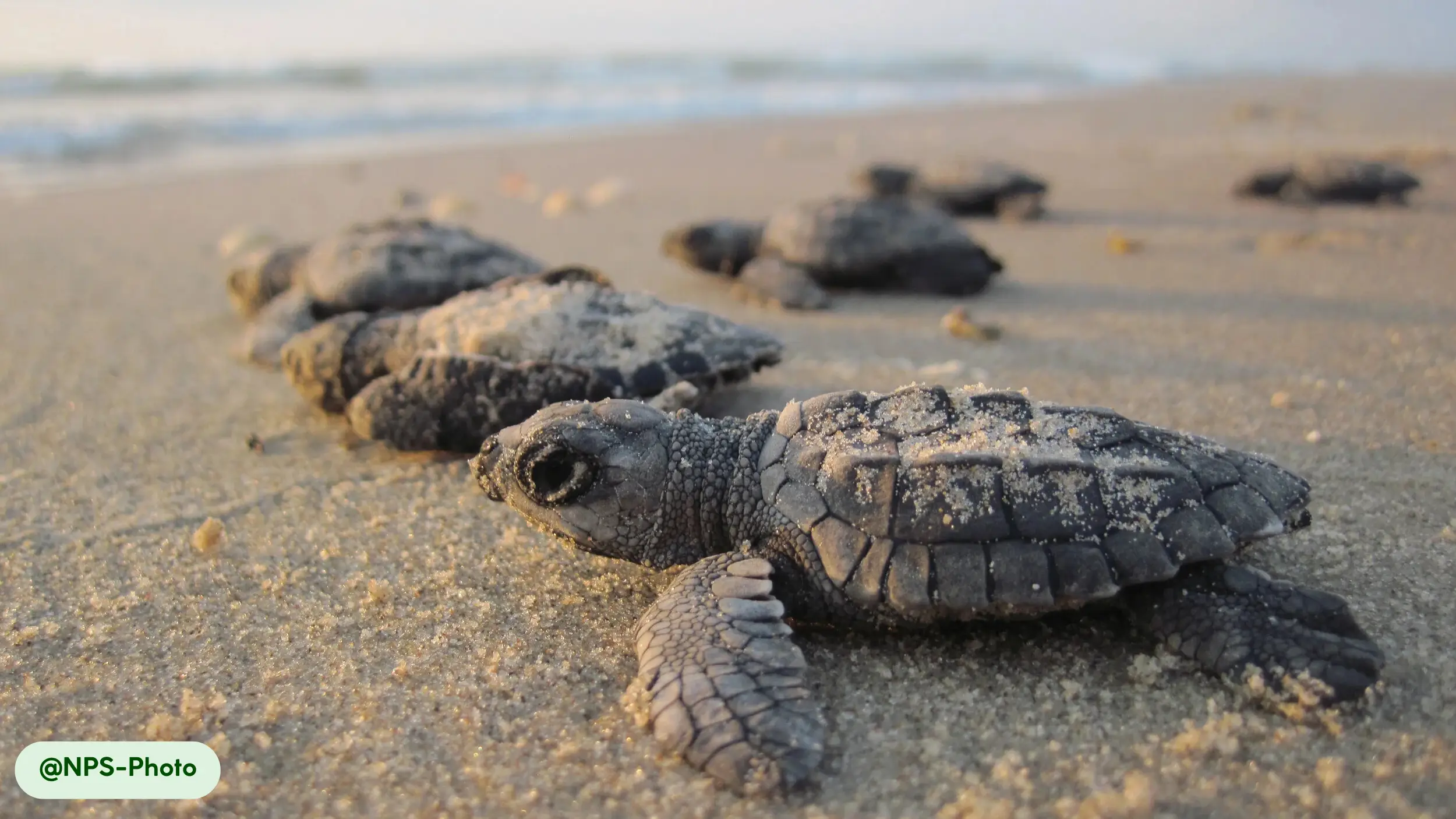
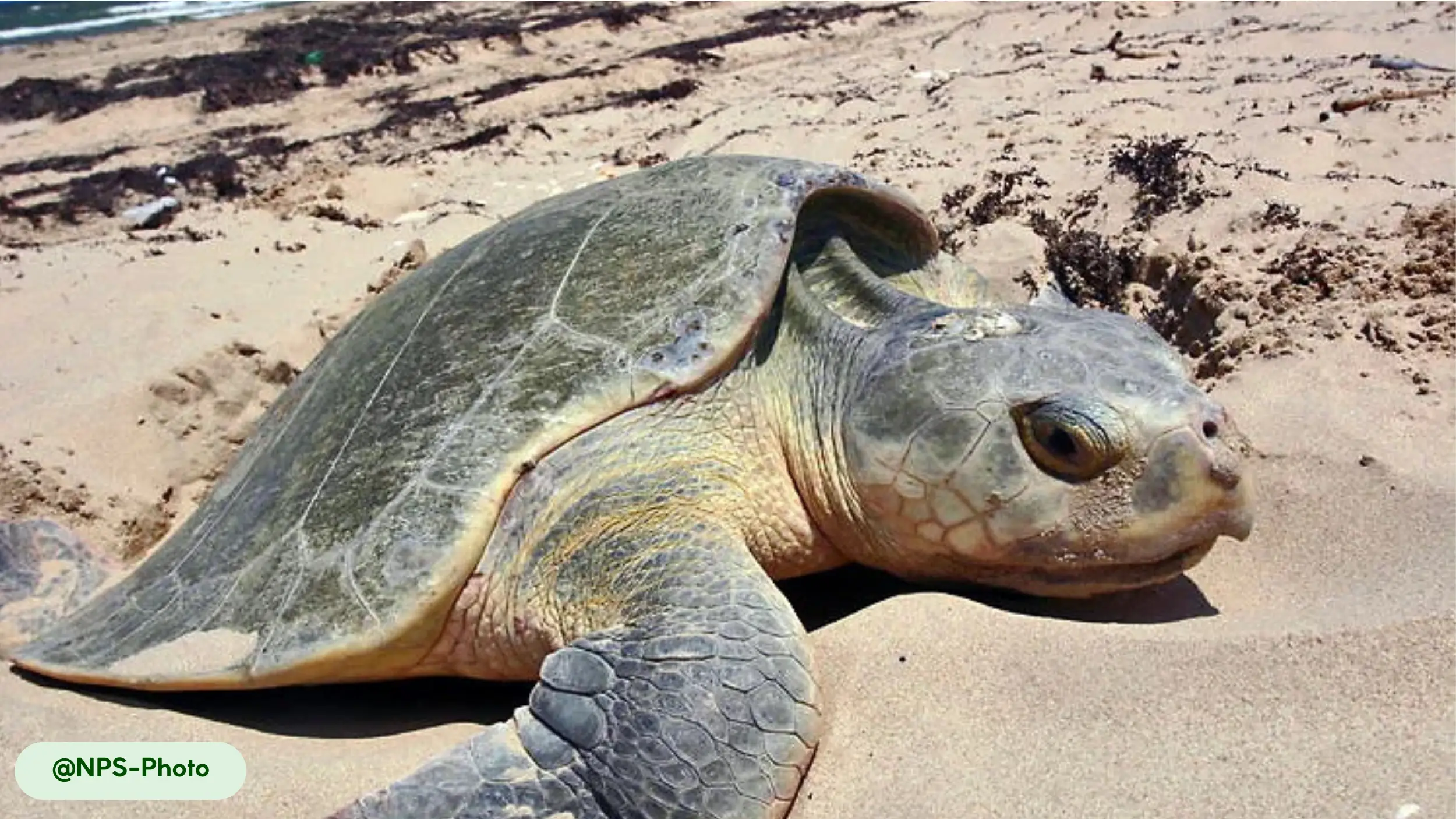
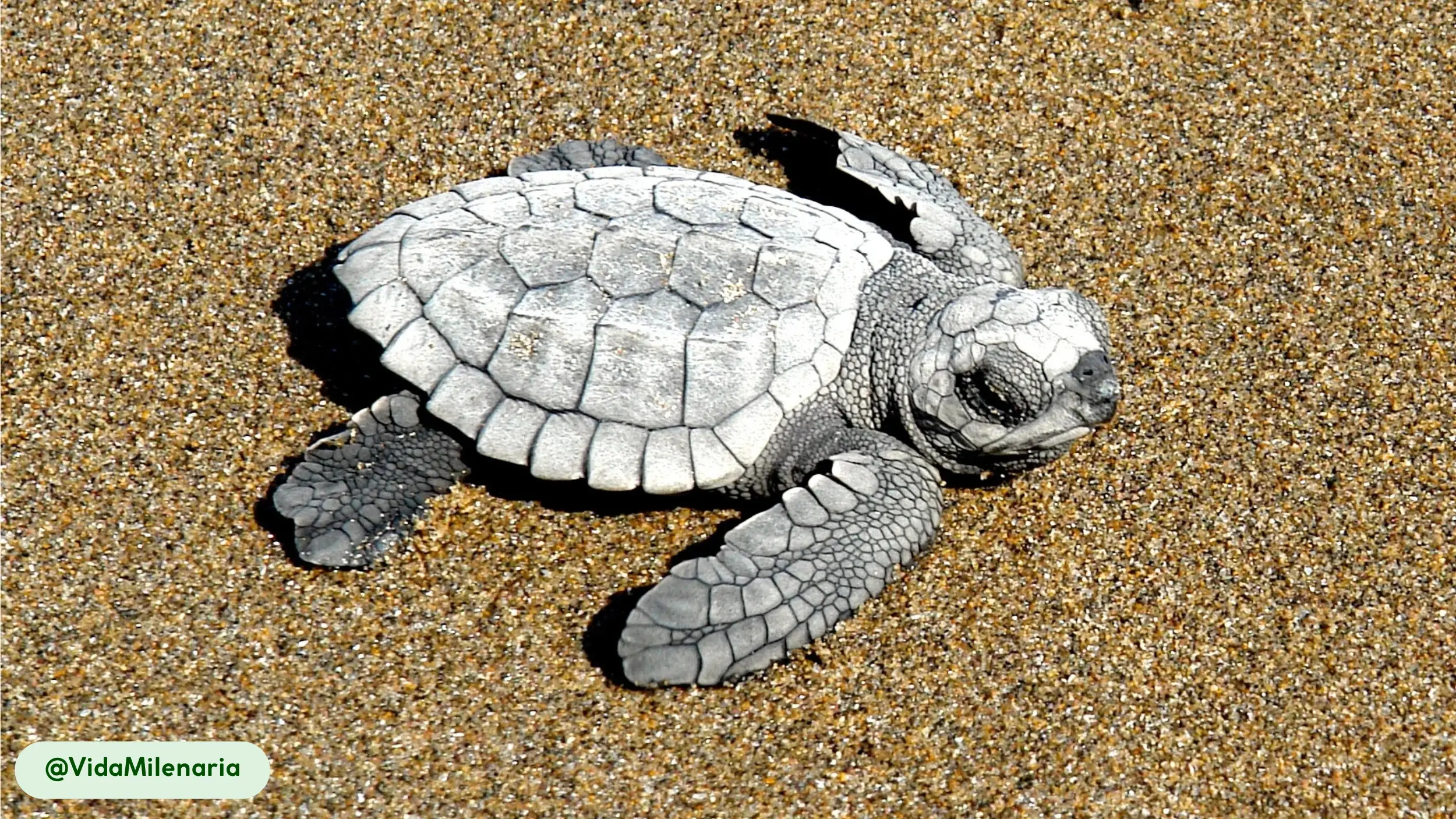
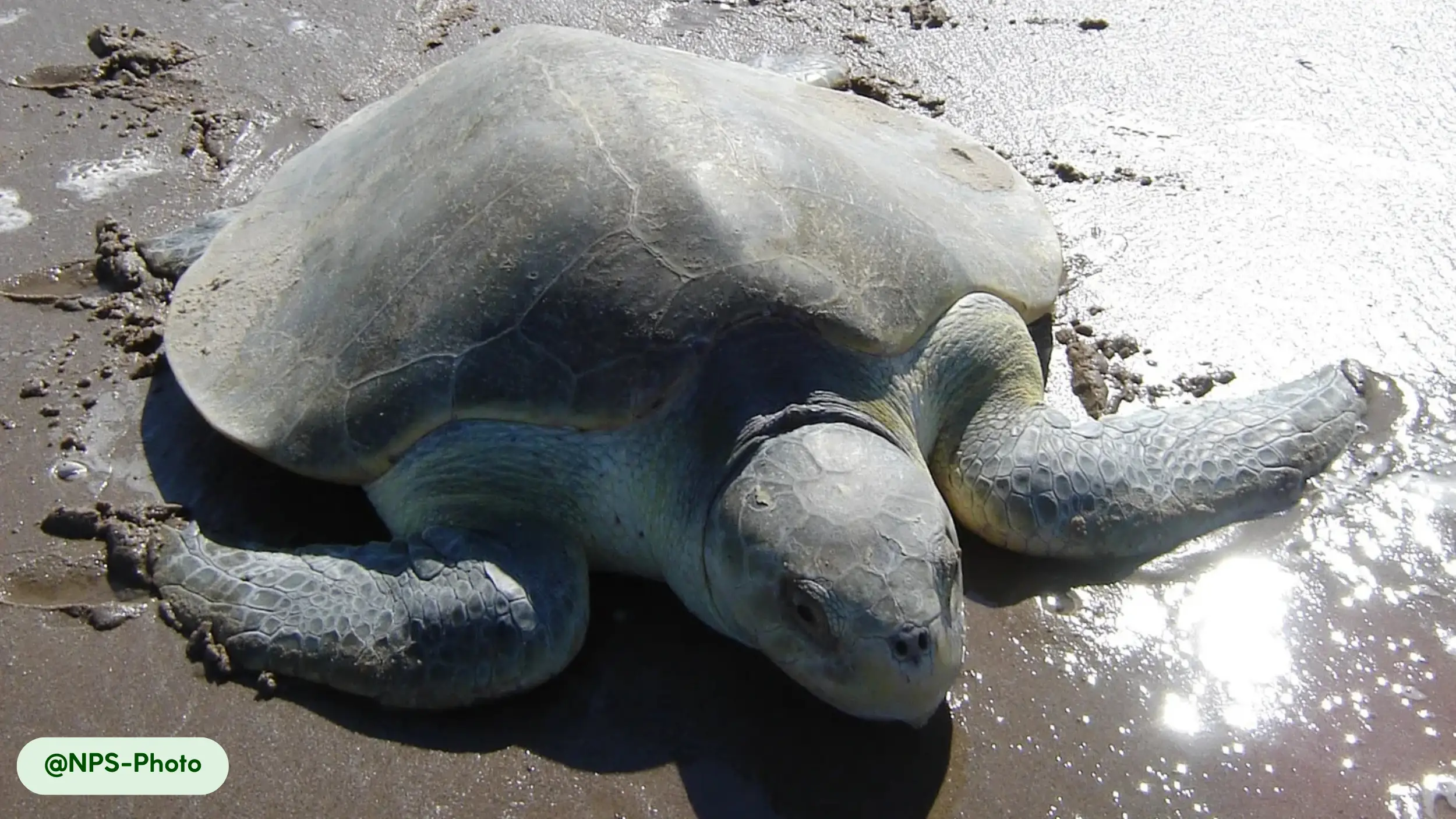
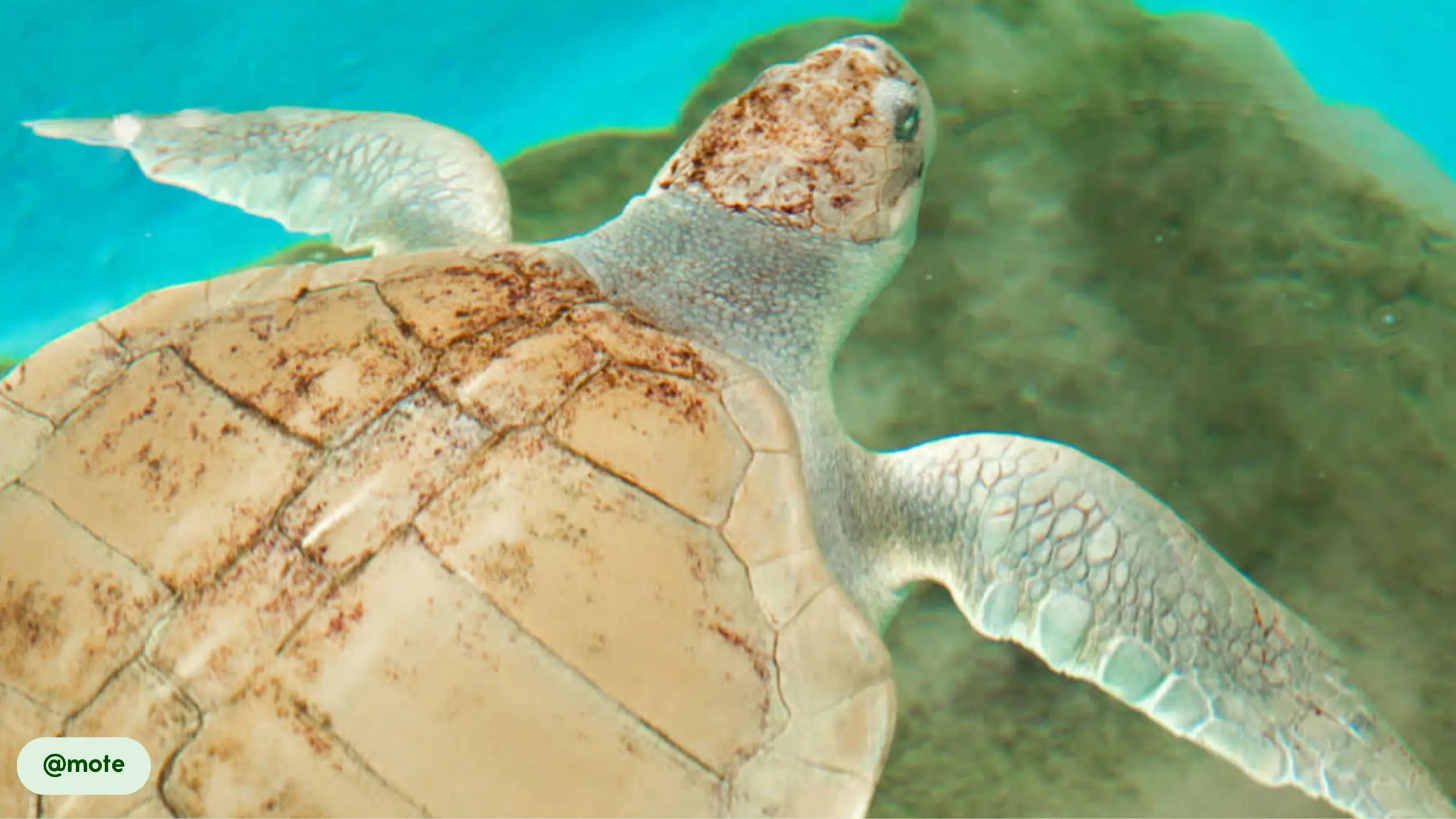
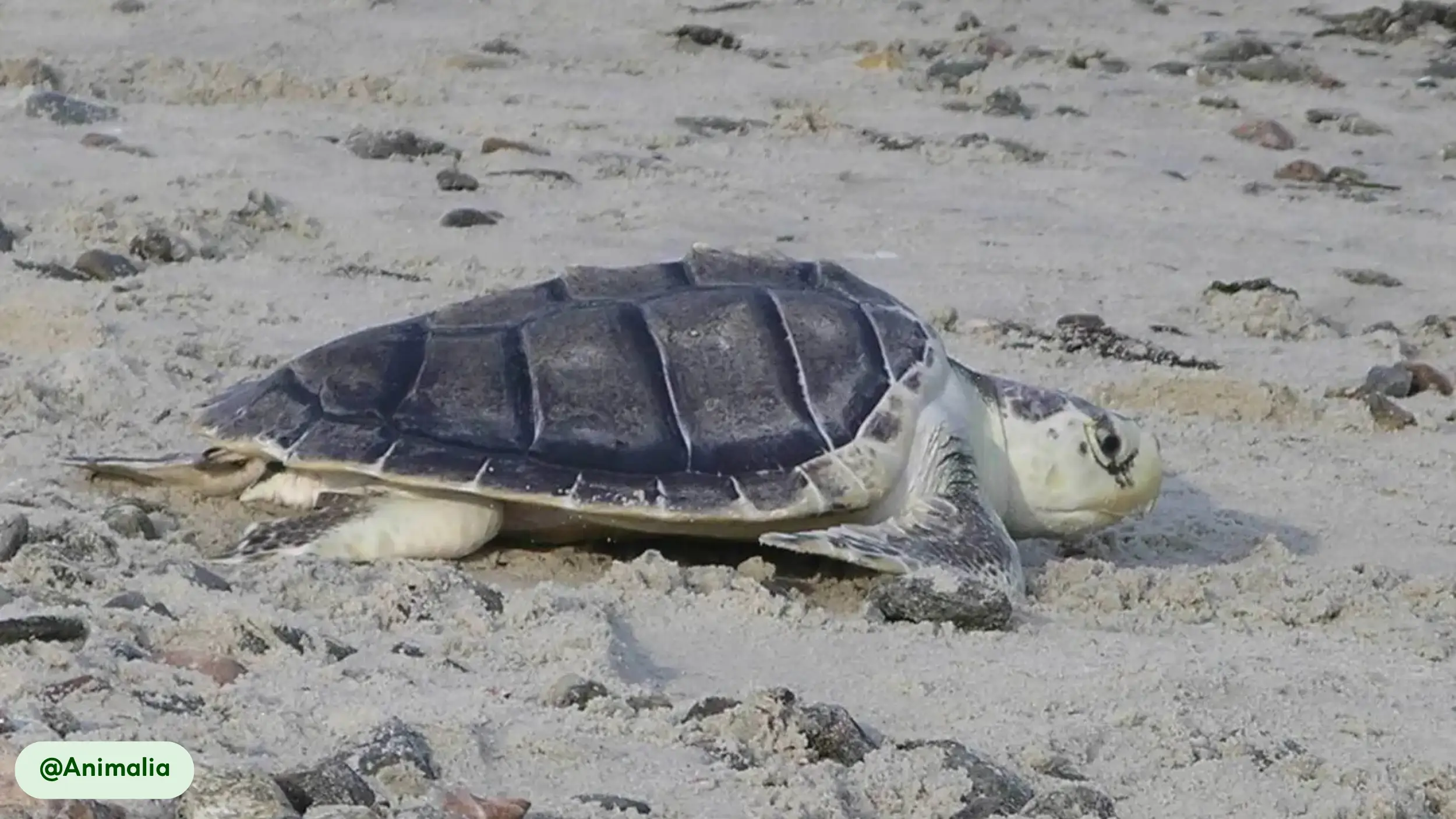
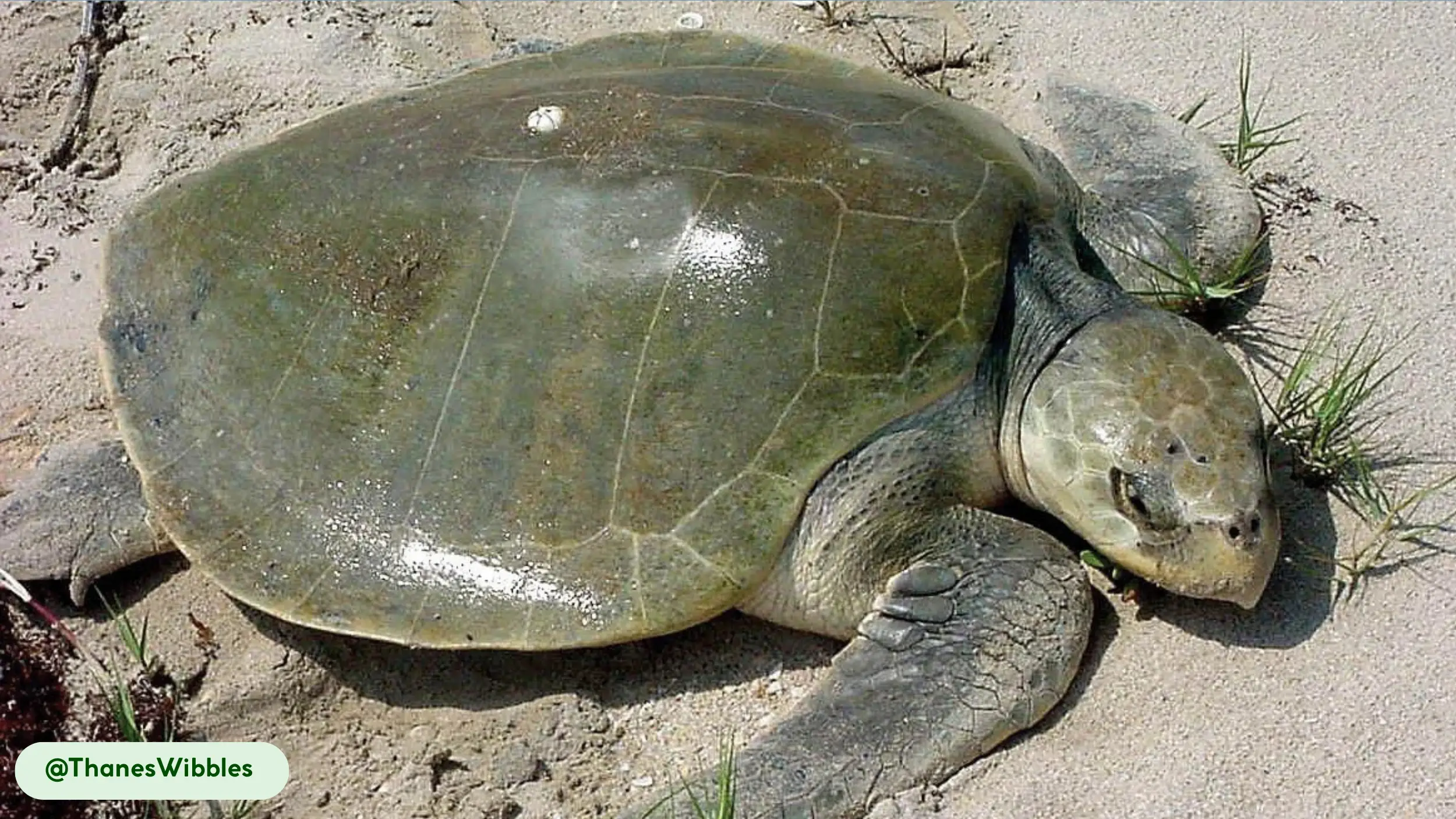
Kemp’s Ridley sea turtles possess a distinctive physical appearance that suits their marine lifestyle, characterized by a compact, oval body and a unique coloration pattern. The carapace, or upper shell, is a smooth, olive-green or gray, while the plastron, the underside, maintains a pale yellow hue [8, 10, 17].
This streamlined body shape reduces drag and supports efficient swimming in coastal environments [10, 15]. The turtle’s appearance changes over its lifespan; hatchlings are a solid, glossy black, which provides camouflage on the beach before they enter the water [8]. A mature Kemp’s Ridley is easily distinguished from other sea turtles by its smaller size and the specific shape and color of its shell.
This species has six defining characteristics. These include a triangular head, a hooked beak, four flipper-like limbs, a smooth carapace, and a pale yellow plastron. These features serve specific purposes, from foraging for food to evading predators [5, 10, 17].
- Triangular head and powerful jaws: The head’s triangular shape supports a robust jaw structure, lending it a powerful bite. This strong jaw and a hooked, keratinized beak are designed for crushing the hard shells of crabs, their main food source [5, 17].
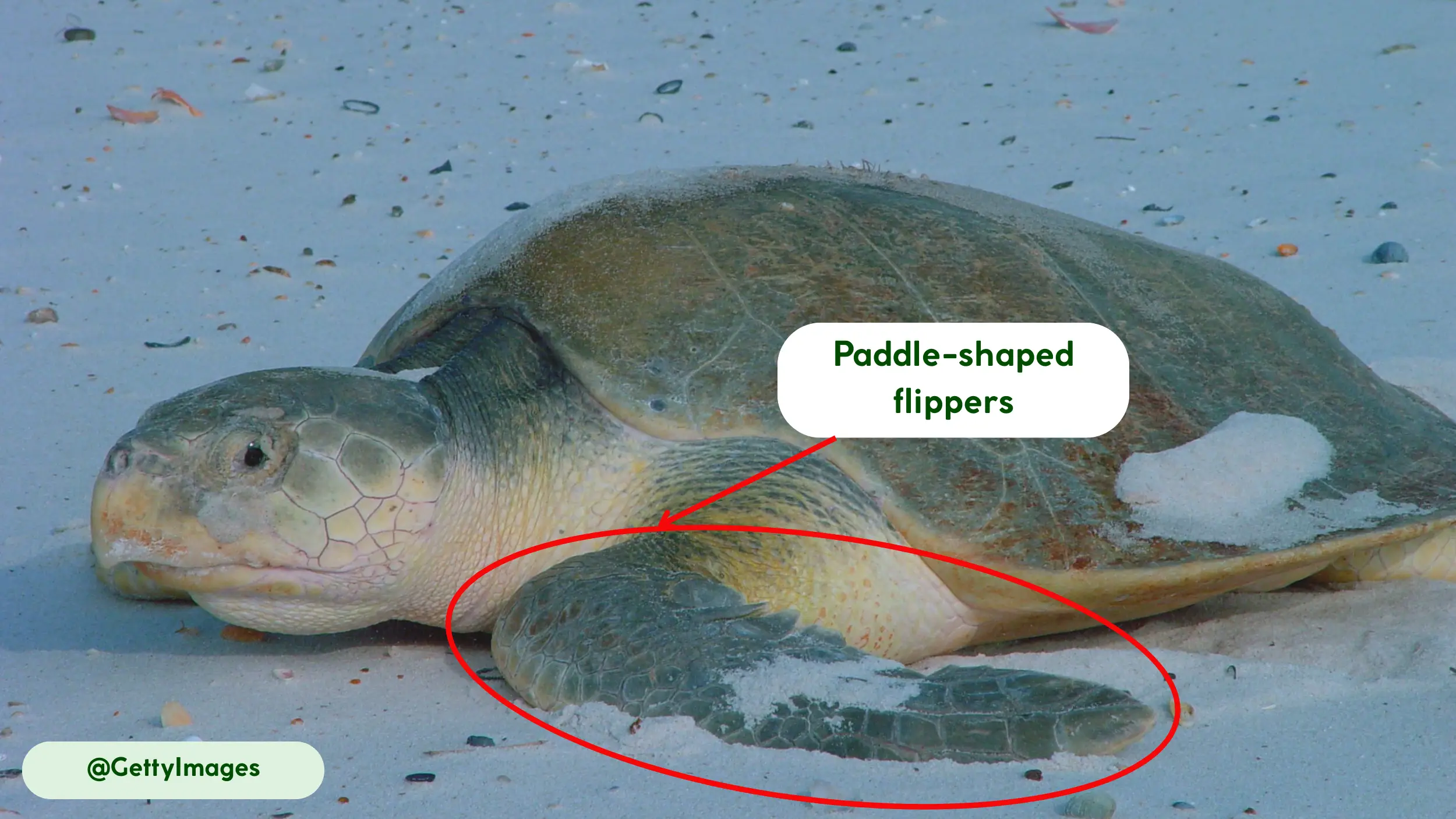
- Paddle-shaped flippers: The turtle has four flippers, each resembling a limb. The two foreflippers are particularly large and paddle-shaped, acting as the primary source of propulsion in water [10]. They are powerful enough to push the turtle through strong currents and for long-distance migrations [15].
- Unique carapace: The carapace is smooth and hard, serving as a protective shield against threats. Its circular, streamlined shape contributes to the turtle’s hydrodynamic efficiency, allowing it to move easily through water [8, 15]. Unlike many other sea turtles, the Kemp’s Ridley has a carapace that is wider than it is long [10].
- Distinctive coloration: The contrast between the olive-green or grayish carapace and the pale yellow plastron helps camouflage the turtle in different marine settings. This pattern is consistent across all mature individuals [8].
- Sexual dimorphism: There are subtle differences in physical appearance between males and females. Mature males have a longer, thicker tail that extends past the end of their shell, and their claws on the foreflippers are more curved than those of females. These adaptations assist in mating [5, 10, 15].
Beyond their appearance, the compact size of this reptile is a defining trait. A closer look at their measurements reveals why they hold the title of the world’s smallest sea turtle.

How Big Are Kemp’s Ridley Sea Turtles?
The Kemp’s Ridley Sea Turtle is the smallest species of sea turtle in the world. Adult individuals average a carapace length of 21.6–27.6 inches (55–70 cm) and weigh between 55 -119 lbs (25–54 kg) [15, 16]. Their size remains compact compared to other sea turtle species.
| Feature | Male | Female |
| Length | 21.6–27.6 in (55–70 cm) | 21.6–27.6 in (55–70 cm) |
| Weight | 55–119 lbs (25–54 kg) | 55–119 lbs (25–54 kg) |
Hatchlings begin life at a size of 1.65–1.89 inches (4.2–4.8 cm) and weigh 0.53–0.71 oz (15–20 g) [8, 17]. Juveniles grow to 10–20 inches (25–50 cm) and vary in weight from 2–20 lbs (1–9 kg) [17]. Their adult size is comparable to a large car tire or a medium-sized suitcase.

The size of this turtle is closely related to its chosen habitats. Next, we’ll explore their geographic distribution and the specific marine environments they call home.
Where Do Kemp’s Ridley Sea Turtles Live?
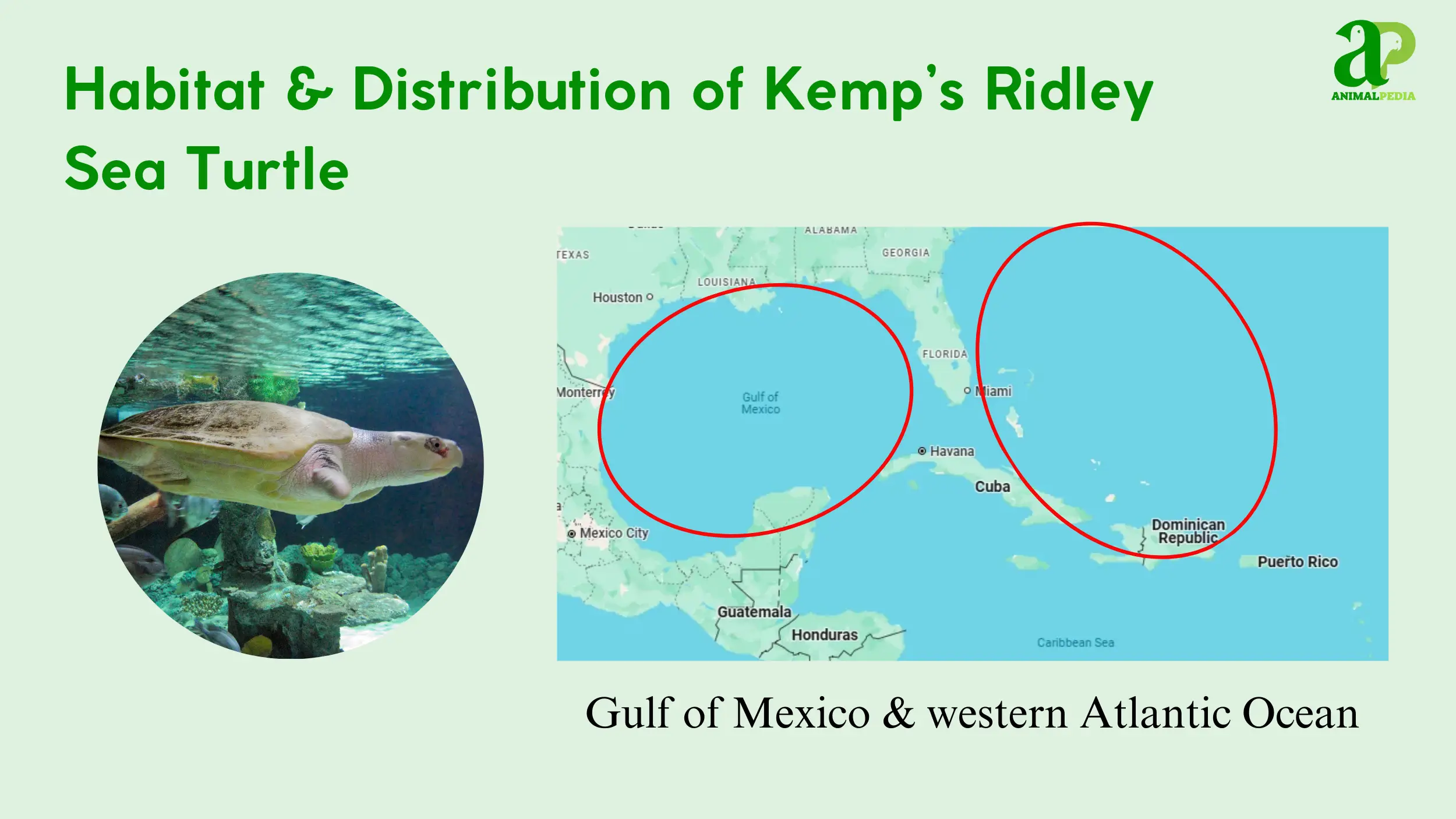
Kemp’s Ridley Sea Turtles inhabit the warm, temperate waters of the Gulf of Mexico and the western Atlantic Ocean, favoring coastal areas with sandy or muddy bottoms [1, 9, 15]. Their geographic distribution includes the northern coasts of the Gulf of Mexico, with major nesting sites in Tamaulipas, Veracruz, and Texas [1, 9, 17].
These turtles are not territorial and prefer nearshore waters, estuaries, and other coastal habitats at depths of up to 164 feet (50 m) [1, 15]. Their movements are seasonal, following shifts in water temperature to stay within their preferred range of 68–86°F (20–30°C) [1, 9]. While they do not defend specific areas, they aggregate during nesting events.
The turtle’s habitat preferences influence a wide array of behaviors. We will now explore their daily habits, from their feeding patterns to their seasonal migrations.
How Do Kemp’s Ridley Sea Turtles Behave?
Kemp’s Ridley sea turtles exhibit a range of behaviors that facilitate survival in their coastal habitats, from their specialized feeding to their synchronized mass nesting events. The species’ behavioral repertoire includes specific feeding habits, powerful aquatic movements, and predictable daily and seasonal patterns [1, 5, 15].
- Diet and Feeding: This species primarily consumes crustaceans, utilizing their powerful jaws and beaks to crush hard-shelled prey on the seafloor.
- Movement and Abilities: Kemp’s Ridleys are strong swimmers, using their flippers for propulsion through both nearshore waters and open ocean currents.
- Daily/Seasonal Patterns: Their activity is a mix of diurnal and nocturnal, with behaviors shifting between foraging and resting in response to environmental conditions and seasonal needs.
These behaviors are critical to the turtle’s life history. To fully appreciate their daily lives, it is helpful to examine the specifics of their diet, physical activity, and seasonal patterns. These are the details that truly define the species’ behavior.
Diet and Feeding
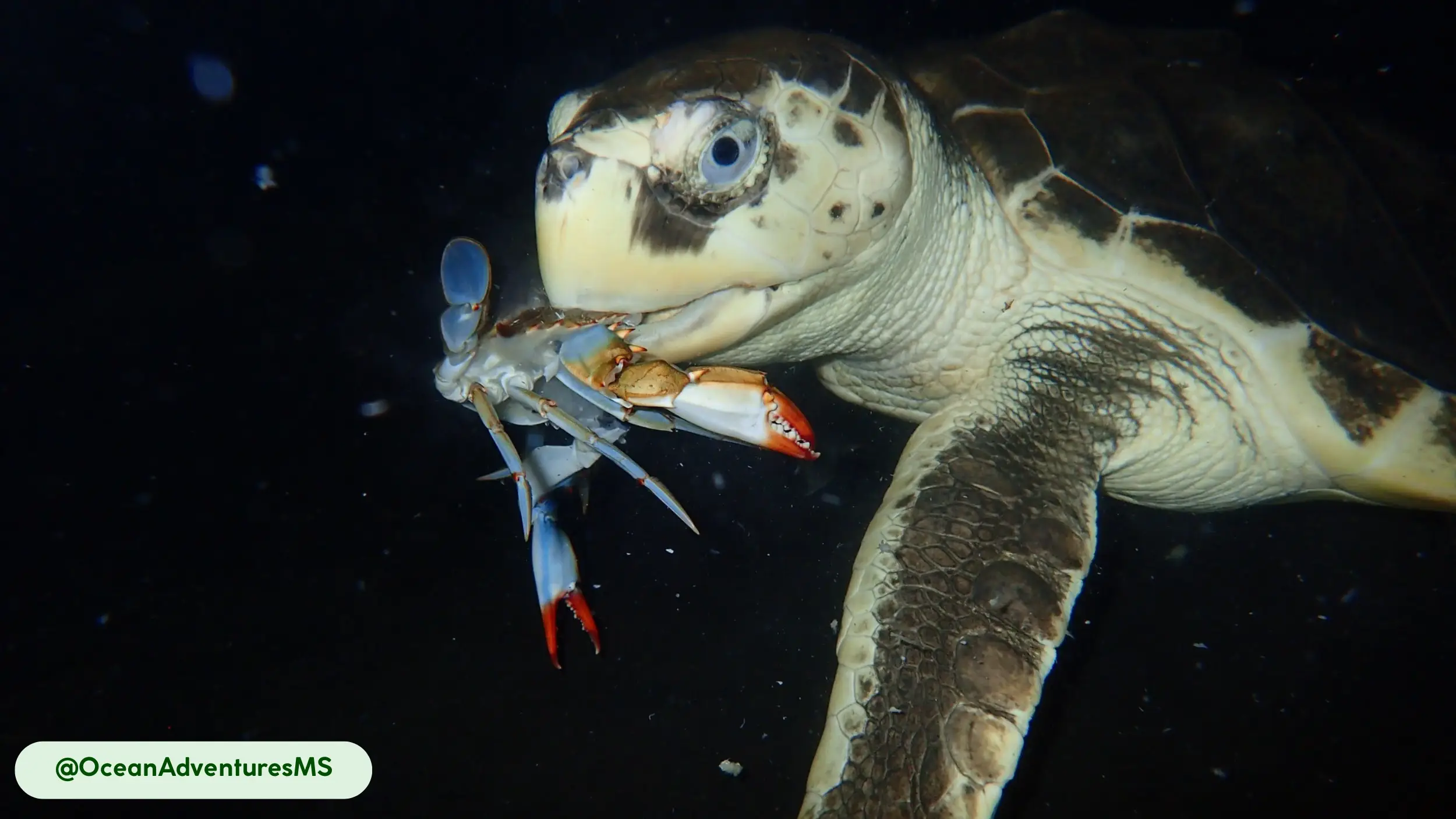
Kemp’s Ridley sea turtles are carnivores that consume a specialized diet, primarily composed of crustaceans [5, 20]. They are classified as benthivores, as they find their prey on the seafloor [20, 21]. Their diet is almost entirely crustaceans, with up to 90% of their intake consisting of crabs like the blue crab [20].
They may also consume other bottom-dwelling invertebrates, including mollusks, fish, and jellyfish, though these are secondary food sources [20]. Kemp’s Ridleys are opportunistic foragers. They use their powerful jaws to crush the hard exoskeletons of their prey [5, 20]. Their feeding patterns are tidal; they often forage in nearshore waters during high tide, moving to deeper habitats during low tide [21].
The Kemp’s Ridley’s specialized diet is directly related to its impressive movement capabilities. They are highly efficient navigators in their marine environment.

Movement and Abilities
Kemp’s Ridley sea turtles move with a combination of powerful aquatic locomotion and passive transport via ocean currents [1, 12]. In water, they use their large foreflippers to propel themselves with strong, deliberate strokes. Juveniles often rely on ocean currents, such as the Loop Current and Gulf Stream, to travel long distances, a strategy that conserves energy [12, 22].
This species can achieve bursts of speed to escape predators, reaching speeds of up to 15 miles per hour (24 km/h), although their sustained cruising speed is significantly slower [23].
The Kemp’s Ridley possesses an exceptional sense of direction, which aids in its long-distance migration and helps it find its way back to specific nesting beaches [1, 18]. Their powerful foreflippers, which are used for swimming, also enable them to haul their bodies up onto land for nesting, a physically demanding task [5, 18].
Daily/Seasonal Patterns
The daily activity of Kemp’s Ridley sea turtles is variable, with active periods for foraging occurring both day and night [21, 24]. Their behavior is often tied to the tides. During the day, turtles often feed in shallow waters during high tides. Their activity can extend into the night, but they may also rest on the seafloor or in sheltered areas [24].
Kemp’s Ridleys exhibit distinct seasonal behaviors tied to migration and reproduction [1, 9, 18]. During spring, they migrate to northern feeding grounds along the U.S. coast, returning to the Gulf of Mexico in the fall as water temperatures drop [1, 9]. This species is known for its migratory journeys. Adult females undertake long-distance migrations from their foraging grounds to the primary nesting beaches in Rancho Nuevo, Tamaulipas, Mexico [1, 18]. This annual migration is a critical part of their reproductive cycle.

Reproduction is a critical part of their life cycle, but survival depends on longevity. We will now discuss their estimated lifespan and the factors that influence it.
How Do Kemp’s Ridley Sea Turtles Reproduce?
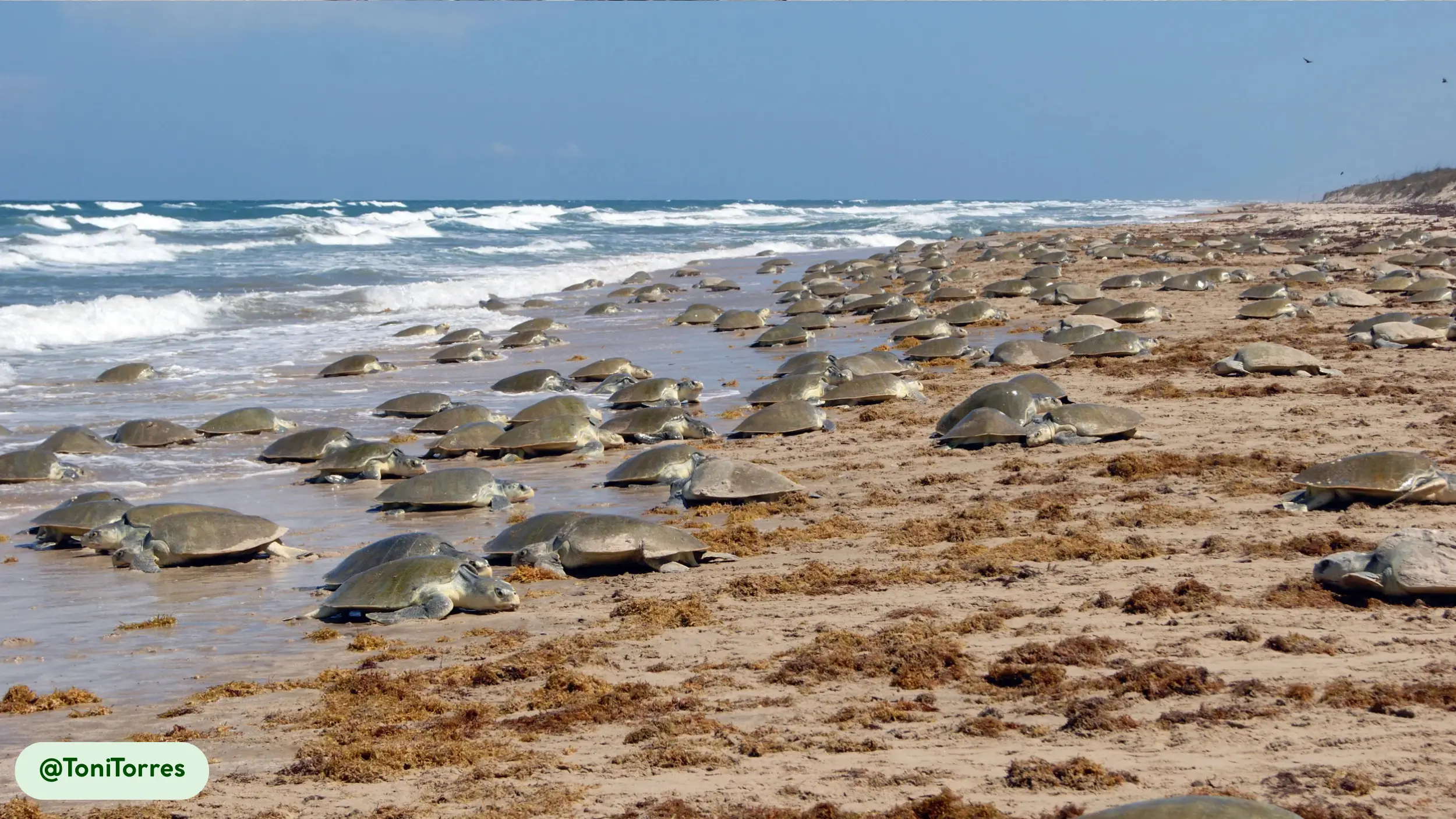
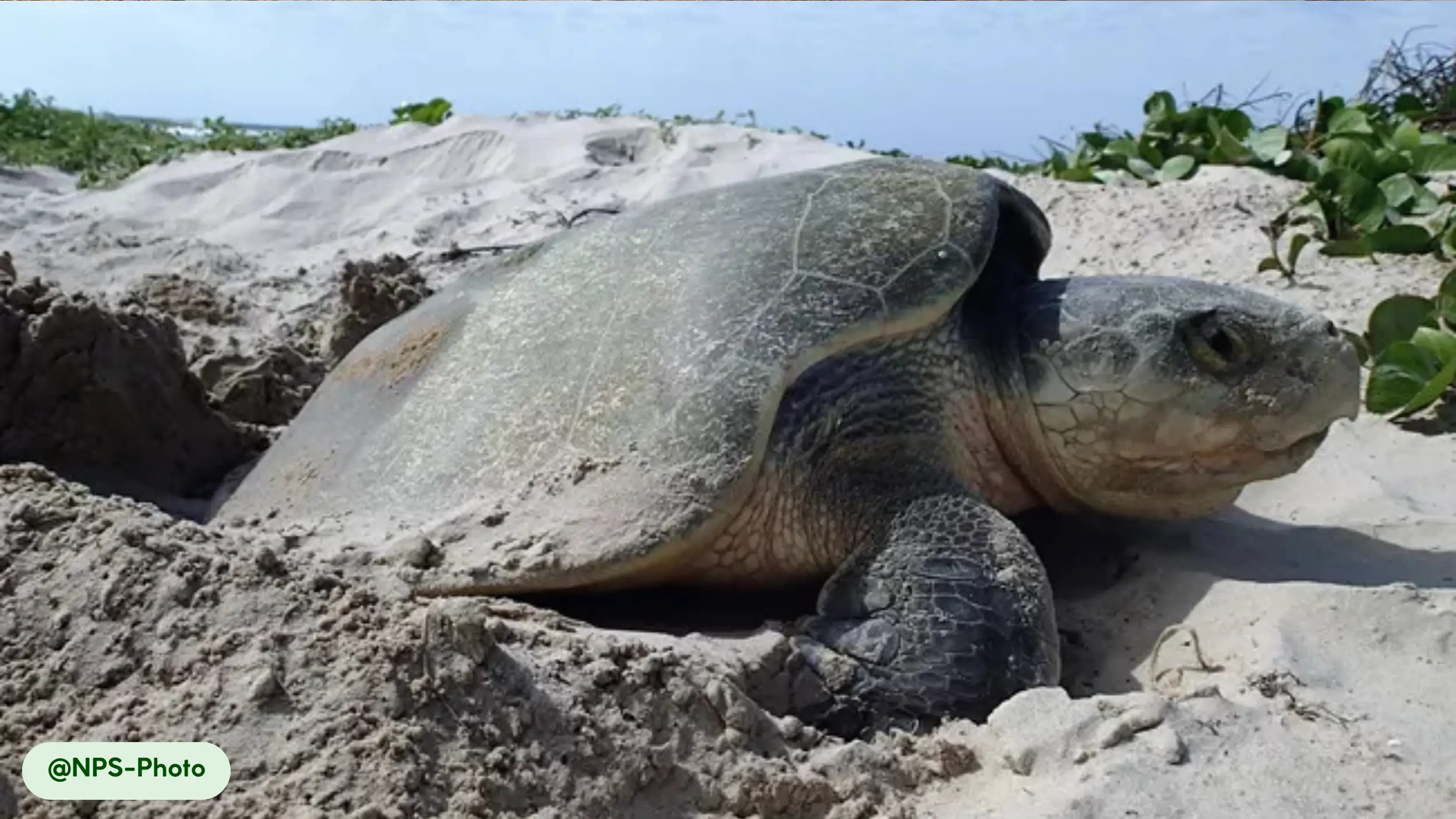
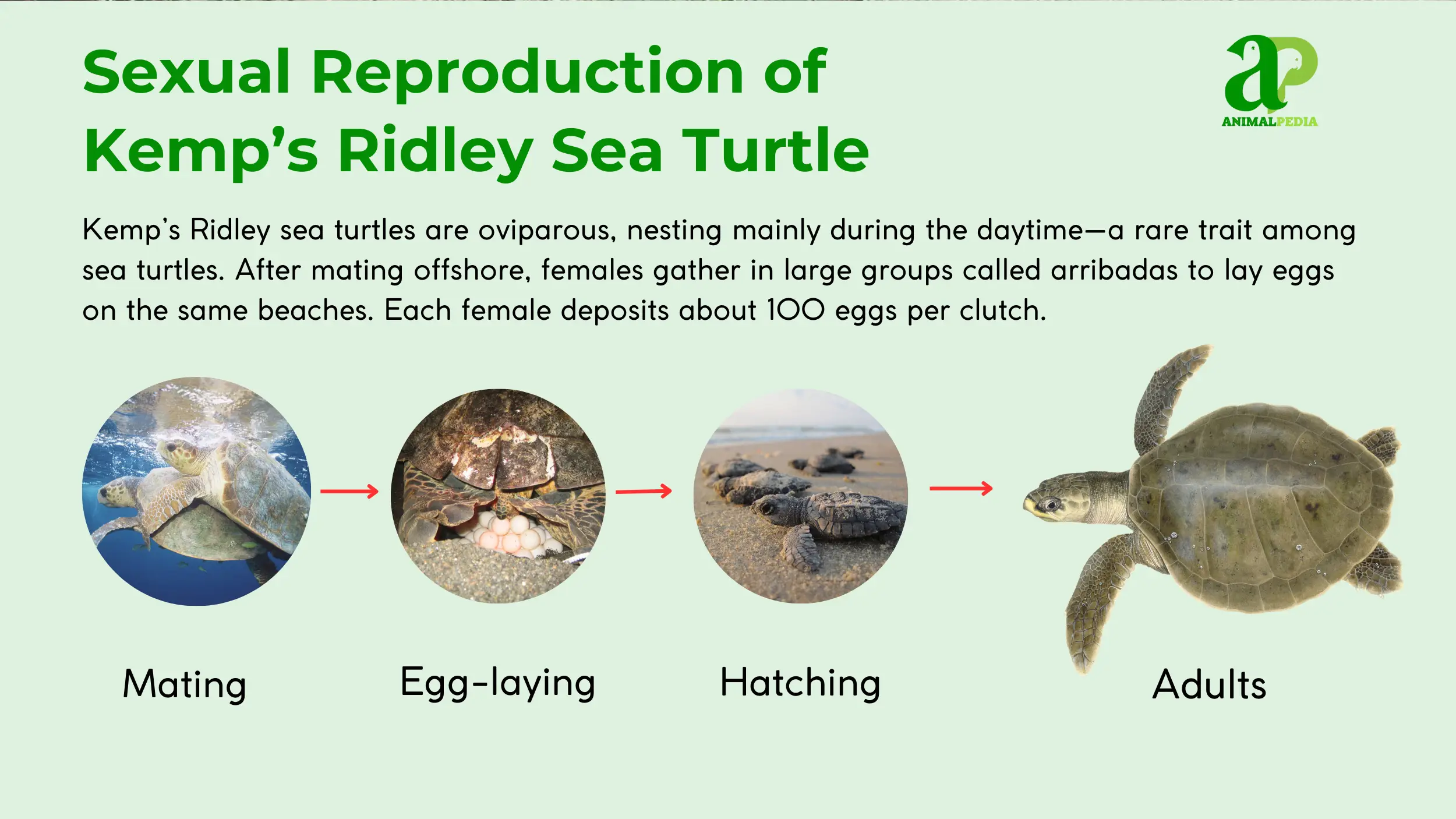
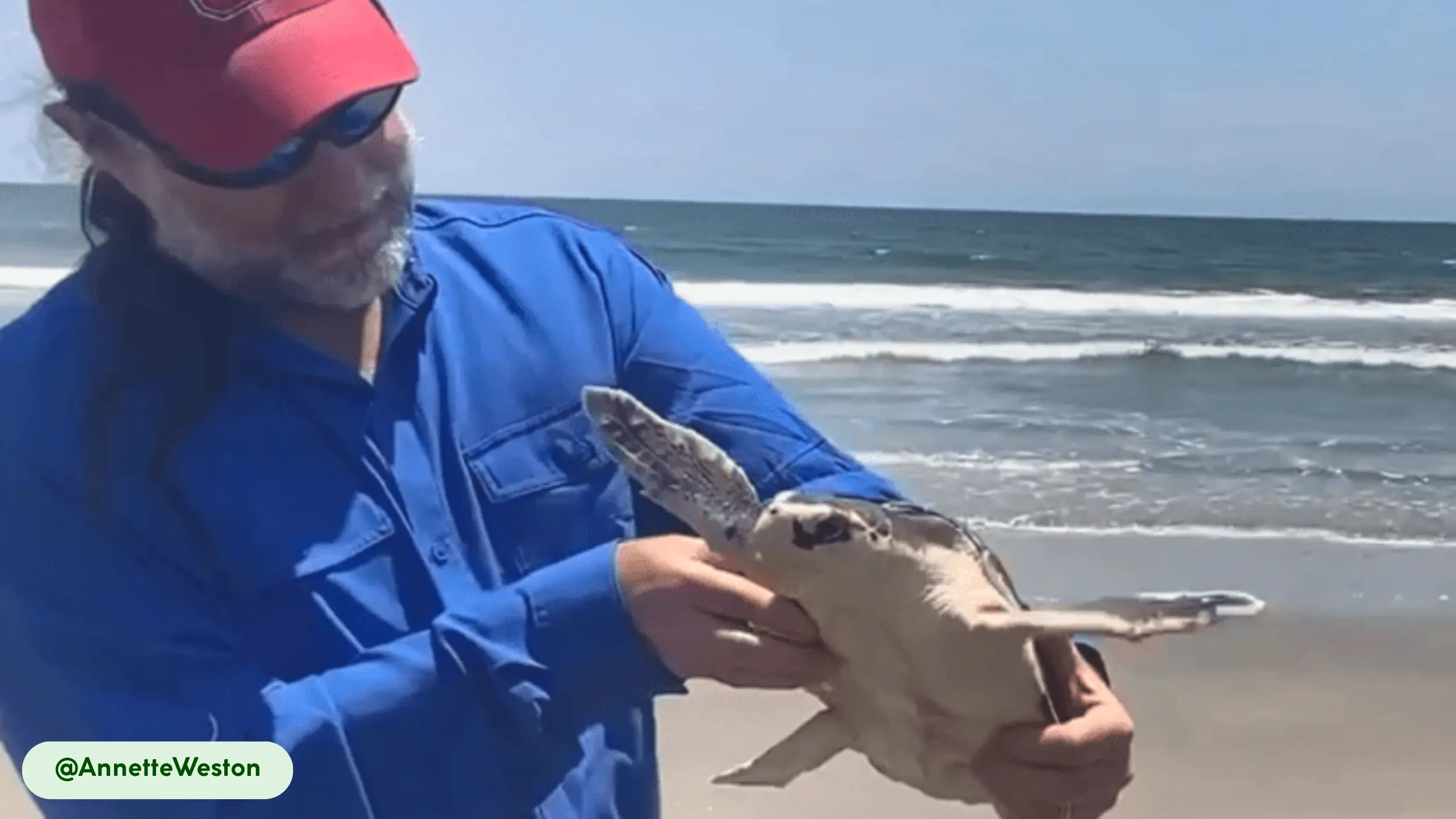
Kemp’s Ridley sea turtles are oviparous, meaning they lay eggs that develop outside the mother’s body. Mating occurs in the coastal waters of the Gulf of Mexico, beginning in late winter [4, 18]. Courtship involves males pursuing females, with copulation occurring at the water’s surface [17]. Females migrate to specific nesting beaches, primarily in Tamaulipas, Mexico, to lay eggs in what is known as an “arribada” [1, 18].
During these synchronized events, thousands of females come ashore to lay their eggs [18]. Each female lays a clutch of approximately 100 eggs in a nest dug in the sand [16, 24]. The incubation period averages 50 to 60 days, influenced by ambient temperature, which also determines the sex of the hatchlings [16]. Parental care ends when the eggs are laid [18].
How Long Do Kemp’s Ridley Sea Turtles Live?
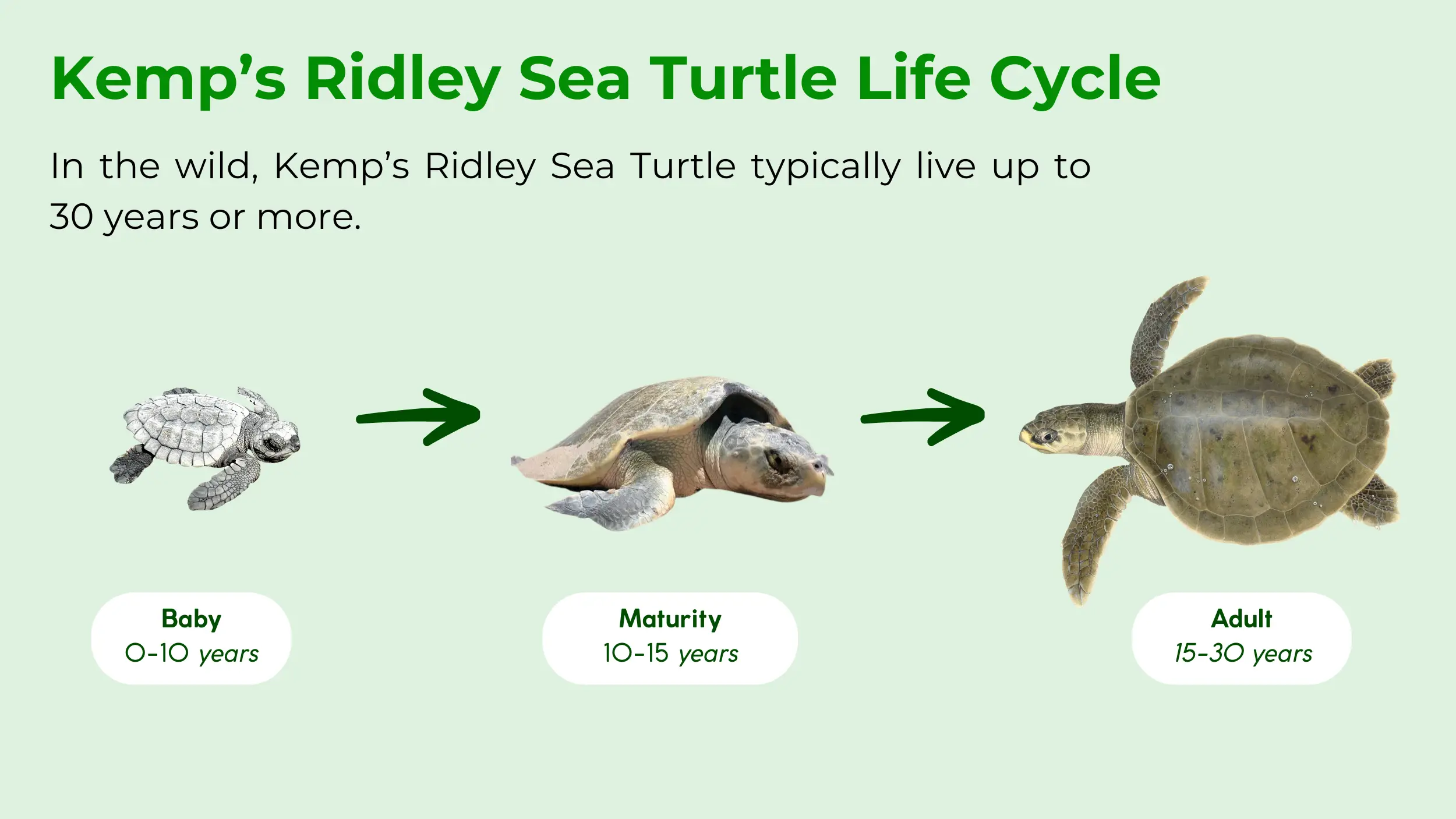
The average lifespan of a Kemp’s Ridley sea turtle is difficult to determine, but scientists estimate they can live up to 30 years or more in the wild [15, 19]. This longevity is impacted by numerous factors, including habitat quality, predation, and human activities. The age of sexual maturity is a significant milestone, with females reaching it between 10 and 15 years [15].
In comparison, sea turtles in captivity often live longer due to the controlled environment and the absence of predators or threats from human activities [21]. A turtle’s ability to survive its first year and avoid human-related threats, such as entanglement in fishing gear, is a major factor in its long-term survival [1, 25].
Beyond their individual lifespans, the species plays a role in the broader ecosystem. Their presence benefits not only the marine environment but also humans.
Are Kemp’s Ridley Sea Turtles Beneficial to Humans?
Kemp’s Ridley sea turtles are beneficial to humans through their significant role in marine ecosystems and their cultural importance [6, 25]. As benthivores, they help maintain the health of seagrass beds by preying on invertebrates that might otherwise overgraze the grasses, promoting biodiversity [5, 6]. Healthy seagrass beds are vital for coastal ecosystems, serving as nurseries for various fish species important to commercial fisheries [6].
The turtle’s presence as a charismatic species also supports ecotourism, particularly in areas with nesting beaches, which contributes to local economies [22]. Their synchronized nesting events have become a symbol of conservation, inspiring international efforts and public engagement [18]. By protecting these turtles, we are also preserving a critical part of the marine environment and its natural resources [25].

Despite their ecological importance, the species faces serious threats. We will now examine their critically endangered status and the conservation efforts underway to protect them.
Are Kemp’s Ridley Sea Turtles Endangered?
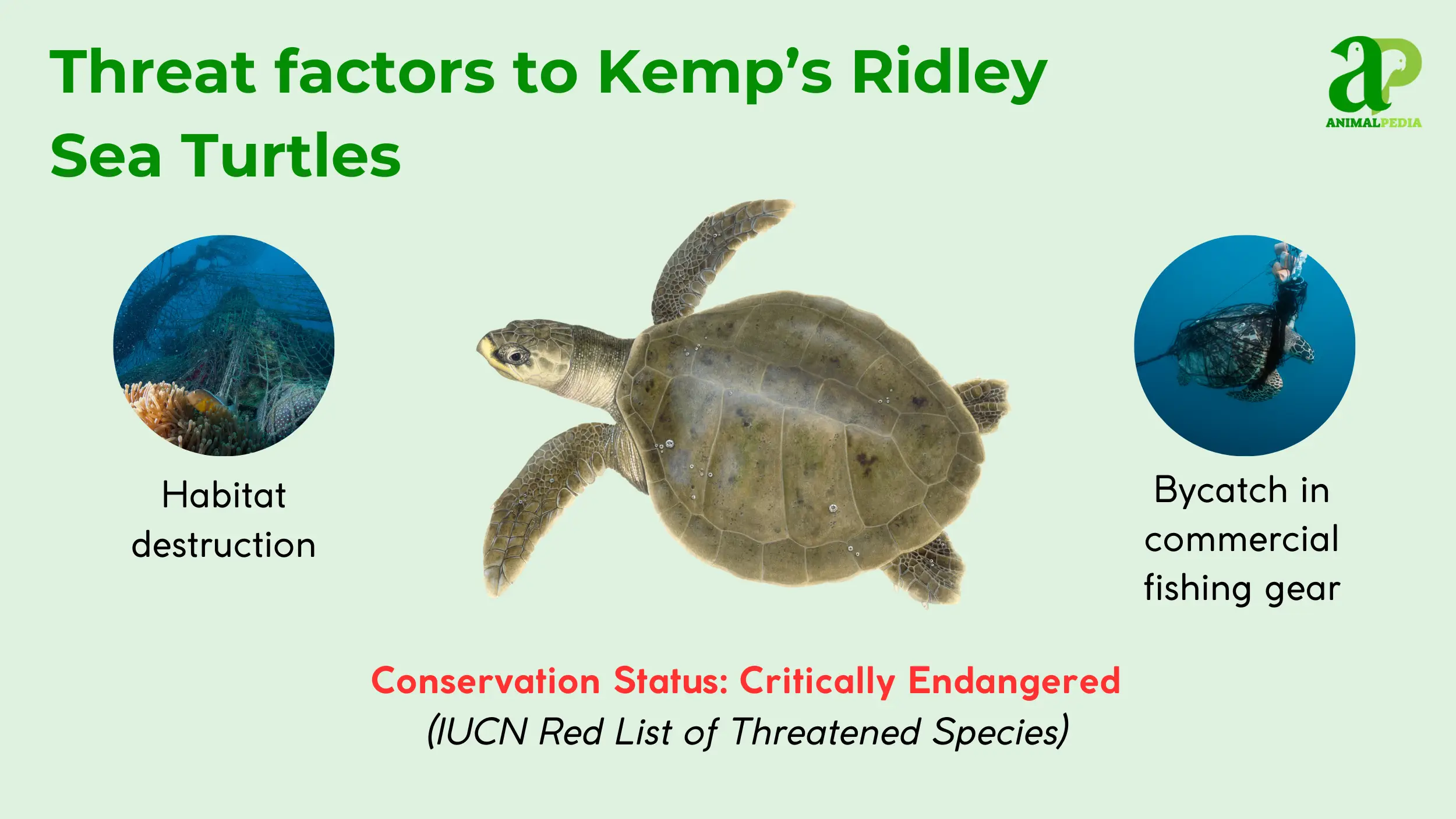
Kemp’s Ridley sea turtles are critically endangered, a status designated by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) [7]. The species experienced a severe population decline in the mid-20th century, resulting in a 99% reduction from historical estimates [7, 19]. Primary threats to their survival include bycatch in commercial fishing gear, direct harvesting of turtles and eggs, habitat loss due to coastal development, and marine pollution [1, 25].
Oil spills, such as the Deepwater Horizon disaster, have also posed a major threat to the Gulf of Mexico habitat [1, 25]. Conservation efforts have shown success; for instance, the number of nests has increased in recent years, a positive trend attributed to international protection programs [18]. Public support for conservation programs, including the use of Turtle Excluder Devices (TEDs) in fishing nets, remains a key factor in the species’ recovery [25].
Frequently Asked Questions About Kemp’s Ridley Sea Turtles
What are the adaptations of the Kemp’s Ridley sea turtle?
Kemp’s Ridley sea turtles have specific physical adaptations that enable their unique feeding and movement behaviors. Their powerful jaws and hooked beak are adapted for crushing the hard exoskeletons of their primary food source, crabs [5, 17]. Their strong, paddle-shaped flippers allow for efficient swimming and migration over long distances [10, 15].
How to identify Kemp’s Ridley sea turtle?
The Kemp’s Ridley sea turtle can be identified by its small, compact size, its smooth, olive-green or grayish carapace, and a pale yellow plastron [8, 10]. It is the smallest of all sea turtles. A key identifier is the carapace, which is typically wider than it is long and has a distinctive oval shape [10].
What color is the Kemp’s Ridley sea turtle?
The carapace, or upper shell, of a mature Kemp’s Ridley sea turtle is a smooth, solid olive-green or gray [8, 10]. The plastron, or underside, is a pale yellow [8]. Hatchlings of this species are a uniform, glossy black, which helps them blend in on the beach before they enter the water [8].
Conclusion
The Kemp’s Ridley sea turtle stands as a testament to both the fragility and resilience of marine life. From their unique arribada nesting behavior to their critical role in maintaining healthy coastal ecosystems, this species highlights the interconnectedness of our planet’s biodiversity.
Their critically endangered status serves as a poignant reminder of the threats facing our oceans, but their recent population recovery offers a powerful message of hope through targeted conservation efforts.
Animal Pedia provides comprehensive, scientifically accurate content to foster a deeper understanding of these incredible animals. We encourage you to explore our extensive library and continue your journey into the fascinating world of Earth’s diverse fauna.

















