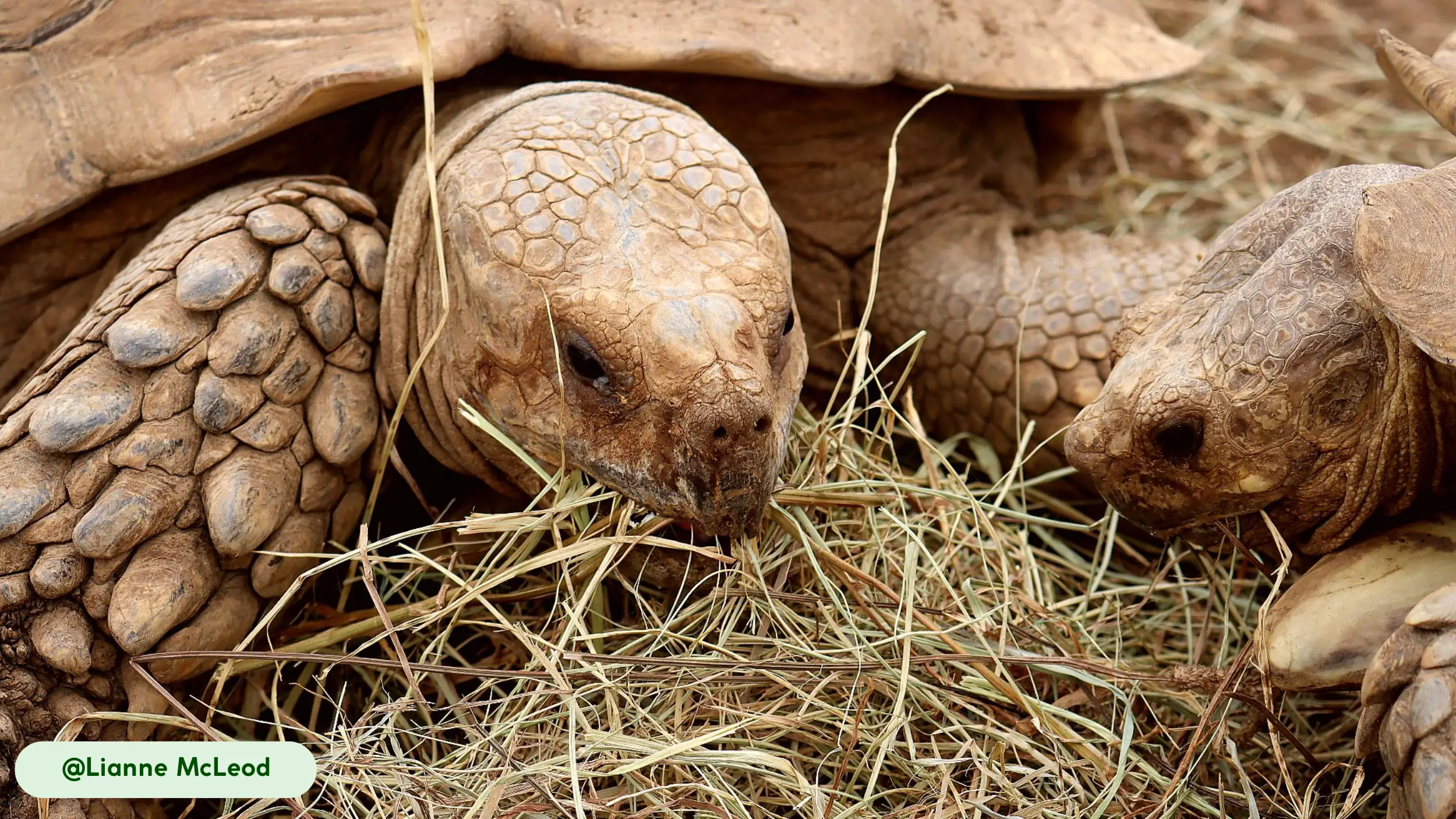
African spurred tortoises (Centrochelys sulcata), commonly known as sulcata tortoises, are one of the world’s largest terrestrial tortoise species and the third largest overall. These strong reptiles belong to the Testudinidae family and are native to the arid Sahel region of Africa. Their physical attributes include a large, heavy build, a broad carapace, and specialized hind-leg spurs used for locomotion and defense [11].
As herbivorous species, they sustain themselves on grasses and herbs, while their slow, deliberate movements enable efficient energy conservation across their vast home ranges. Despite their resilience, the species is classified as Vulnerable (VU) by the IUCN Red List, facing threats from habitat degradation and overexploitation [12].
This guide explores the African spurred tortoise’s unique characteristics, encompassing its scientific classification, physical appearance, and key behaviors. We will examine the distinct features that define this species and its vital ecological role, providing a comprehensive understanding of its biology and conservation status. How are these animals classified, and what do their names signify?

What Is a Sulcata Tortoise?
Sulcata tortoise (Centrochelys sulcata) is a large terrestrial chelonian native to the hot, arid Sahel region of Africa, known for their powerful burrowing abilities and sturdy physical structure [11, 15]. Scientifically, this species is classified within the kingdom Animalia, the phylum Chordata, the class Reptilia, and the order Testudines, belonging to the family Testudinidae [15, 21].
While commonly called the African spurred tortoise or sulcata tortoise, other names include grooved tortoise, Sahel tortoise, and the French term, tortue sillonnée, all referencing its geographical range or physical attributes [21]. There is debate over its taxonomic status: older scientific literature often placed the species in the genus Geochelone, whereas contemporary genetic analyses support its placement in the monotypic genus Centrochelys [11].
To better understand these tortoises, one must observe their physical characteristics. With their size and durability, what exactly defines the Sulcata tortoise’s appearance?

What Do Sulcata Tortoises Look Like?
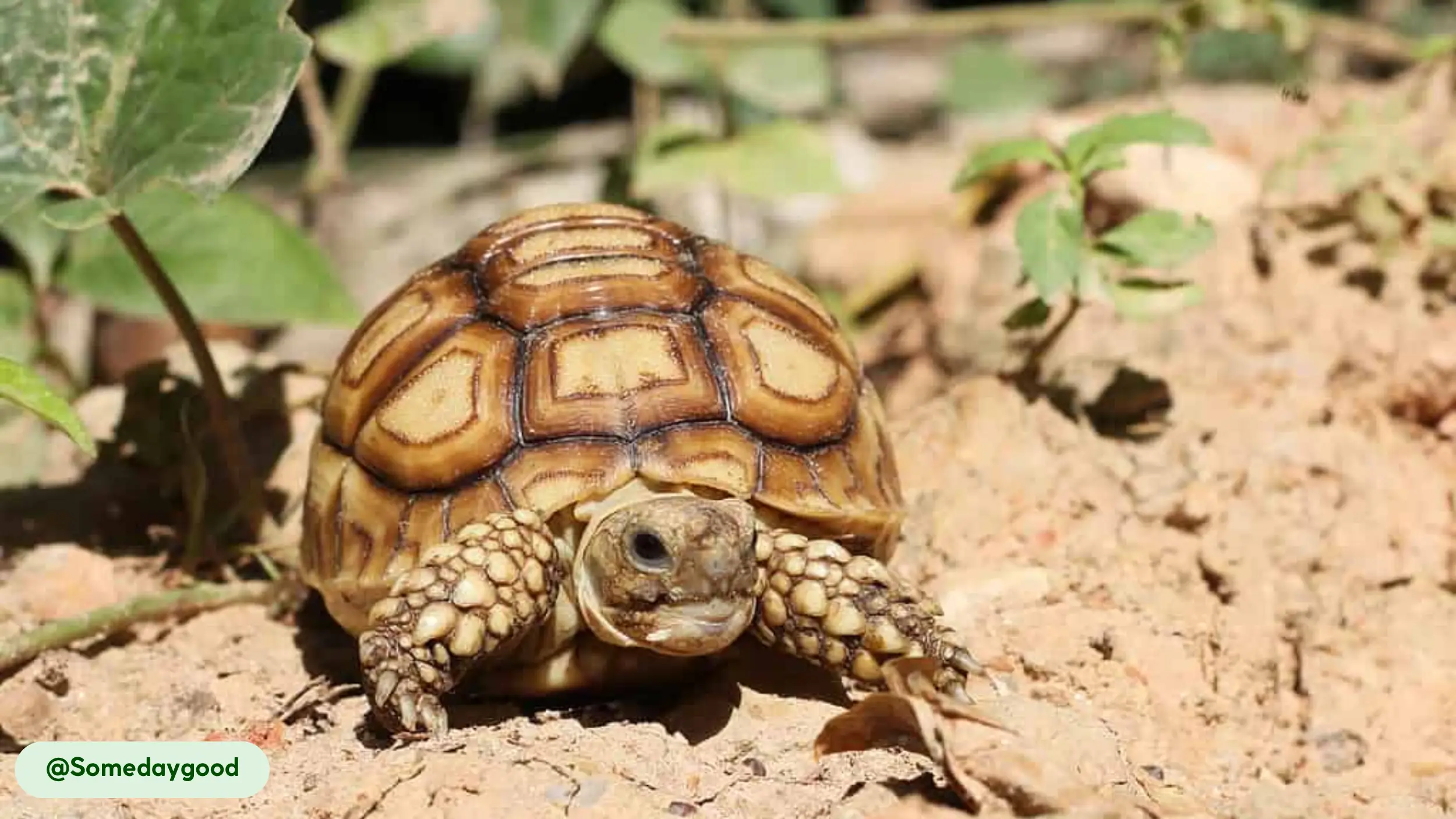
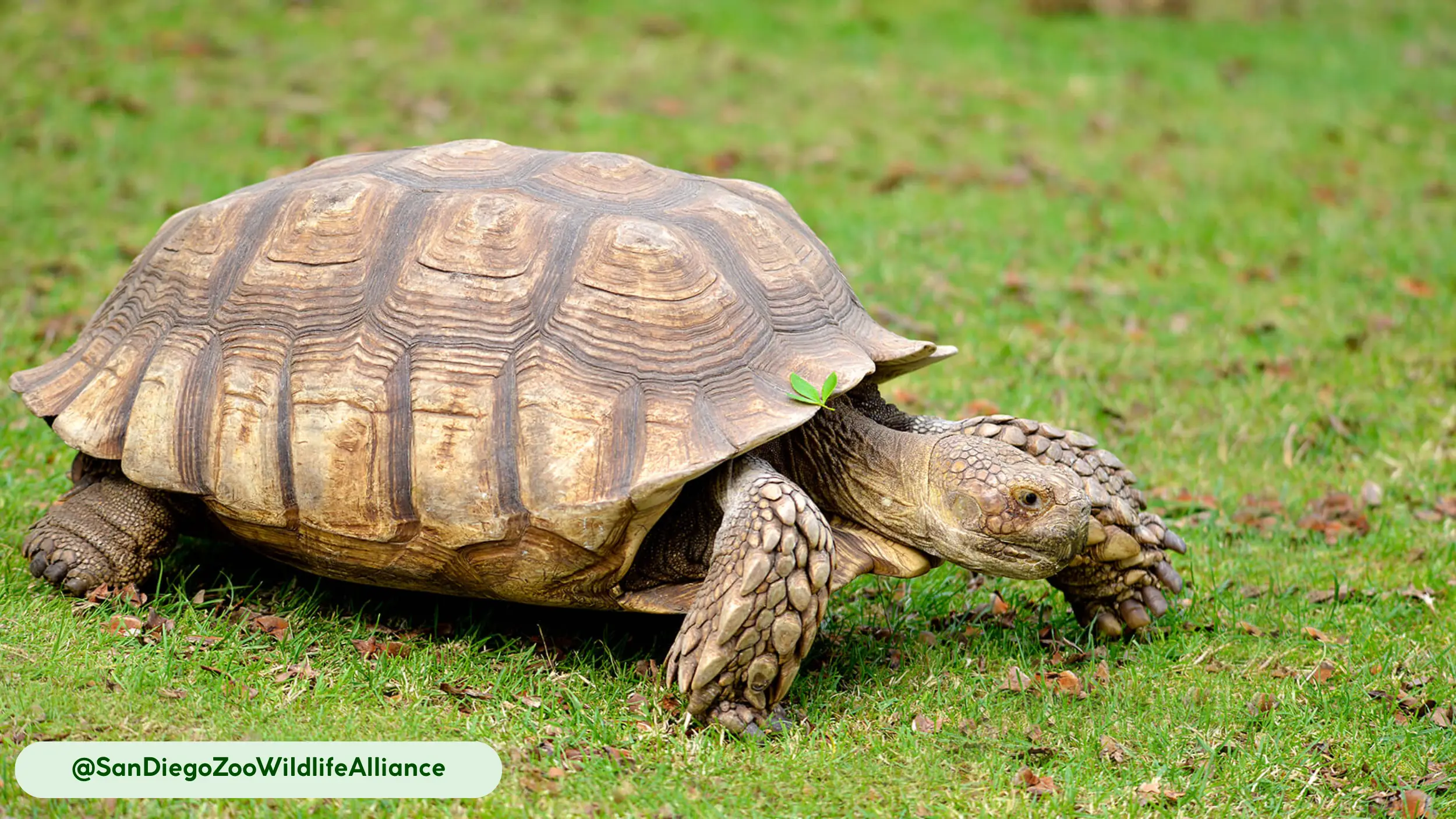
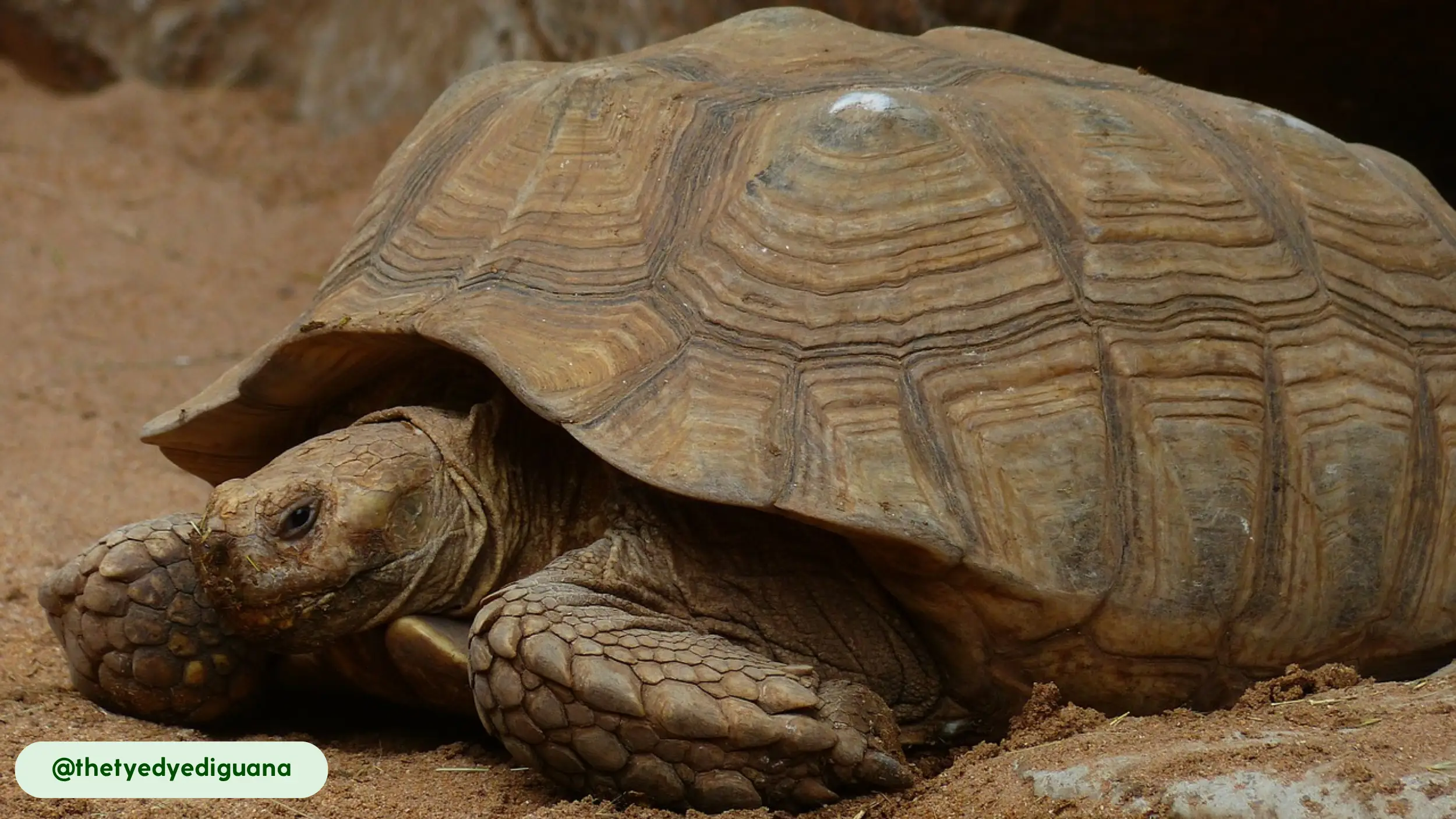
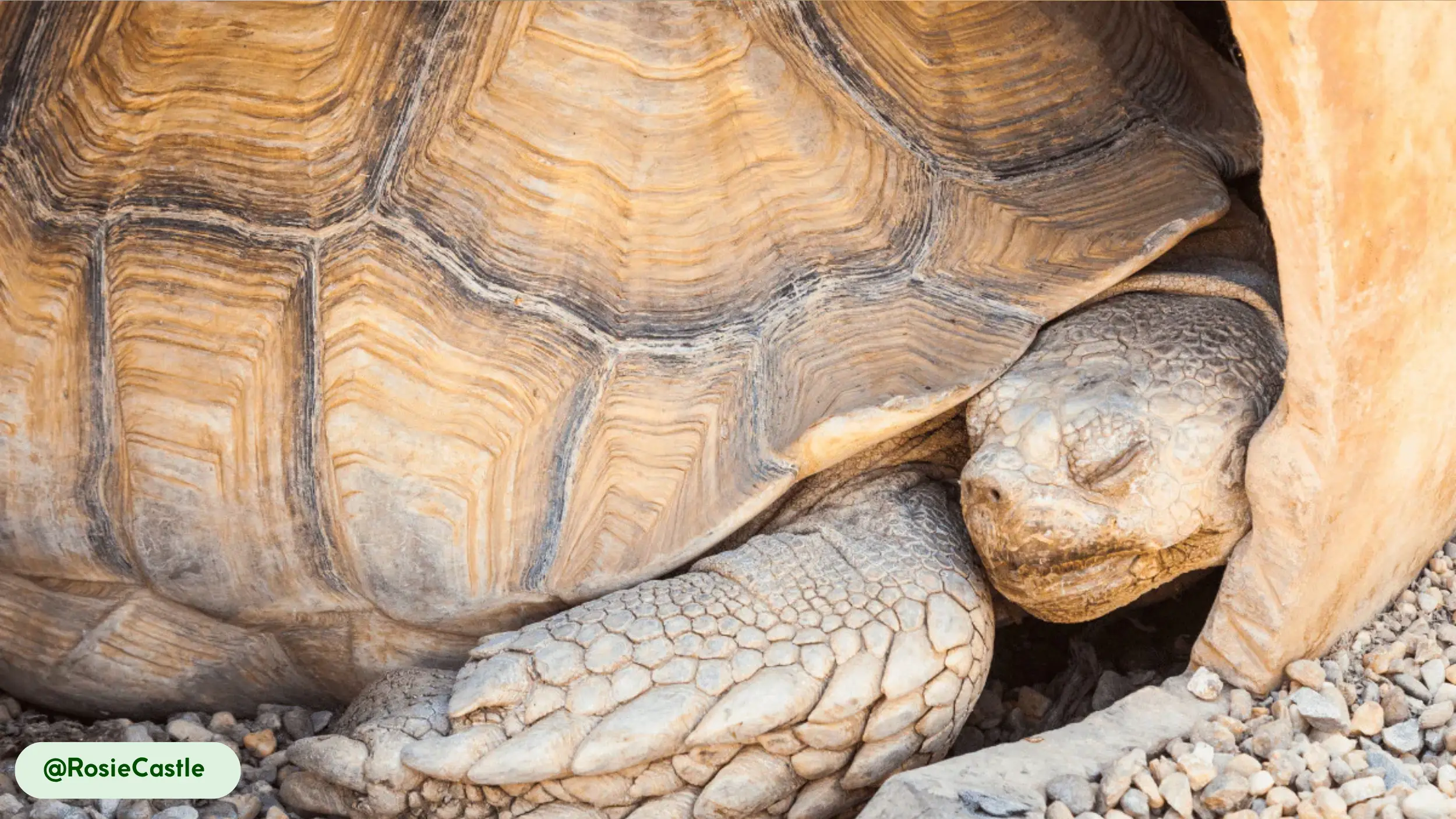
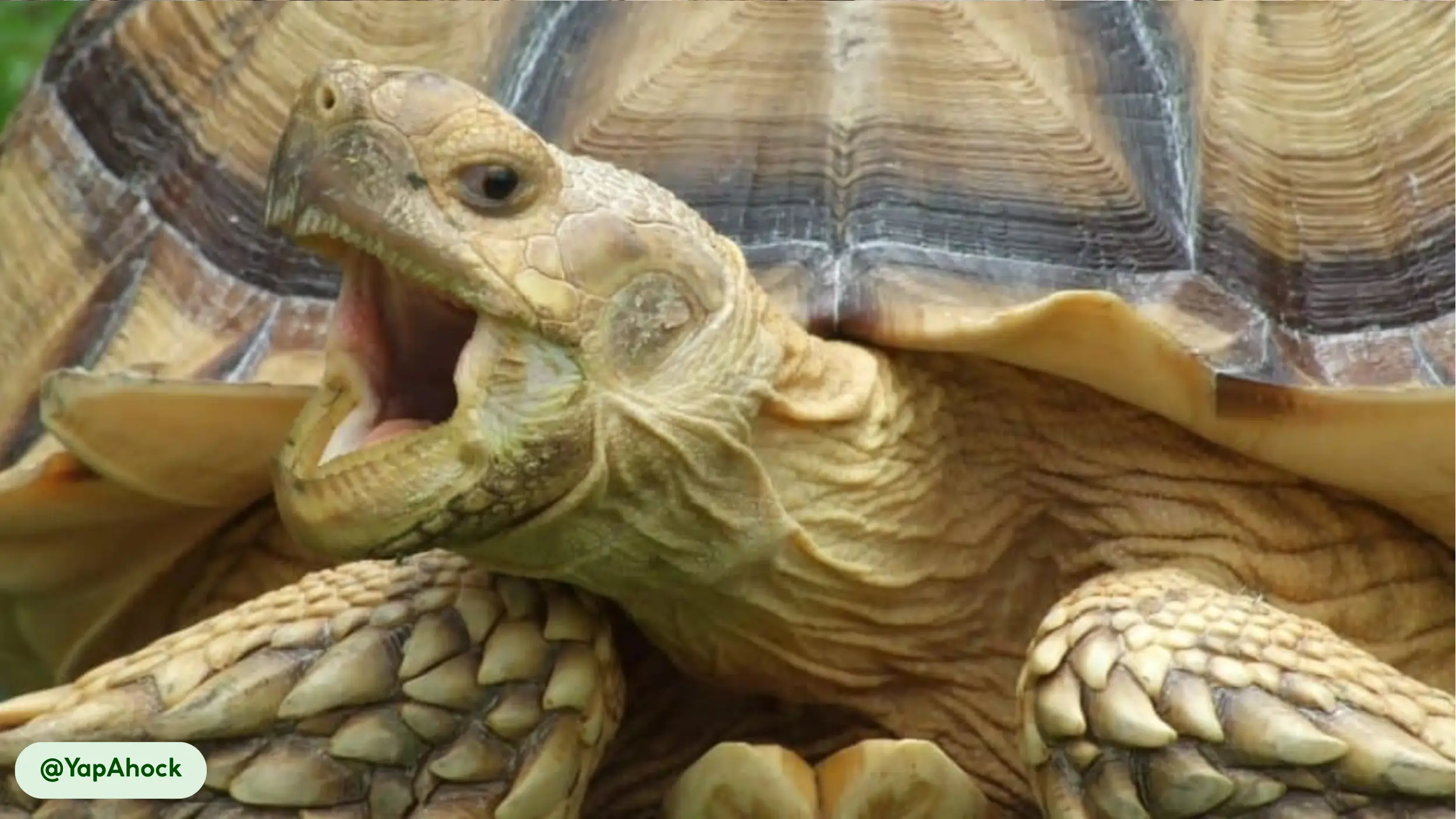
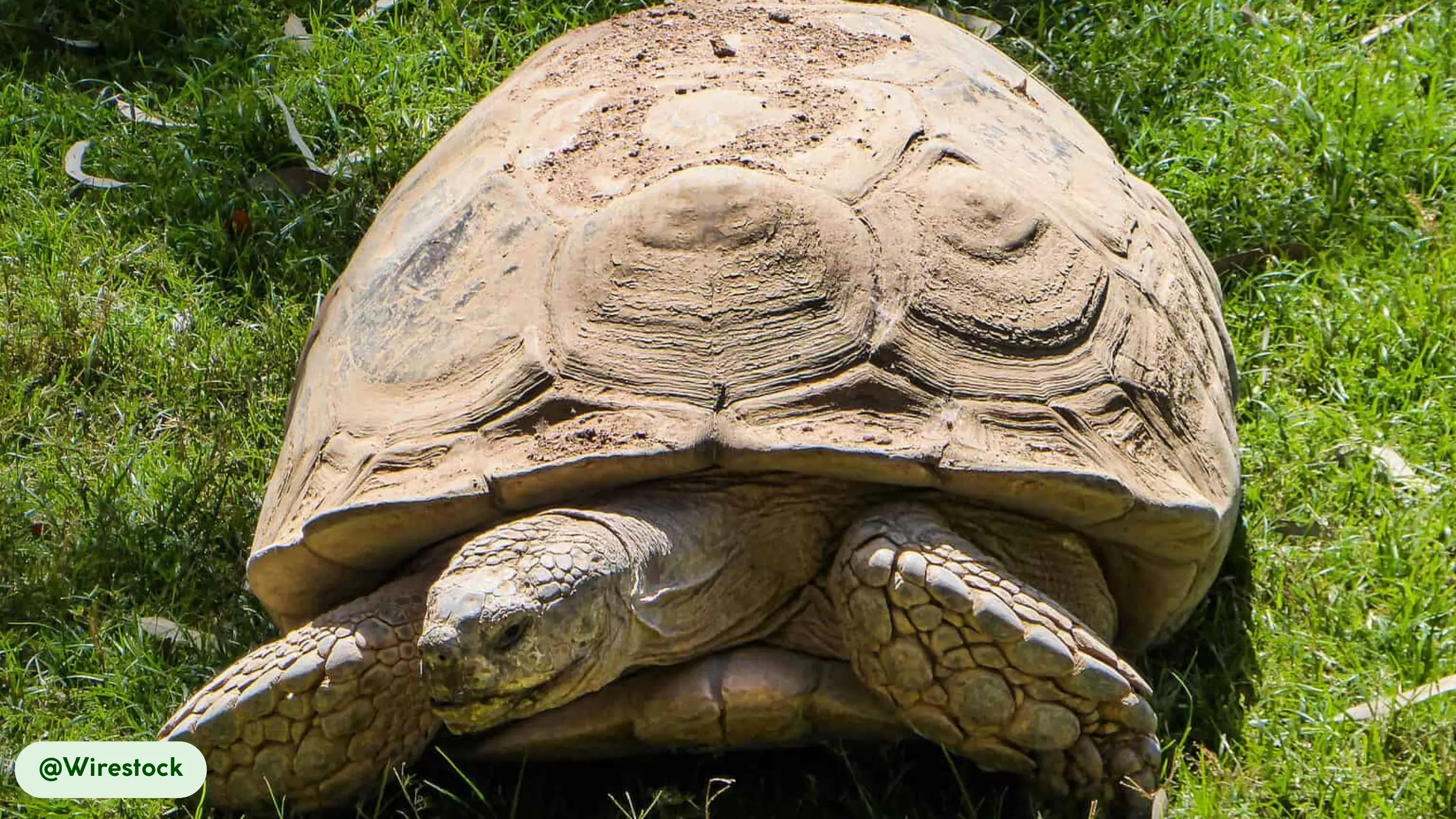
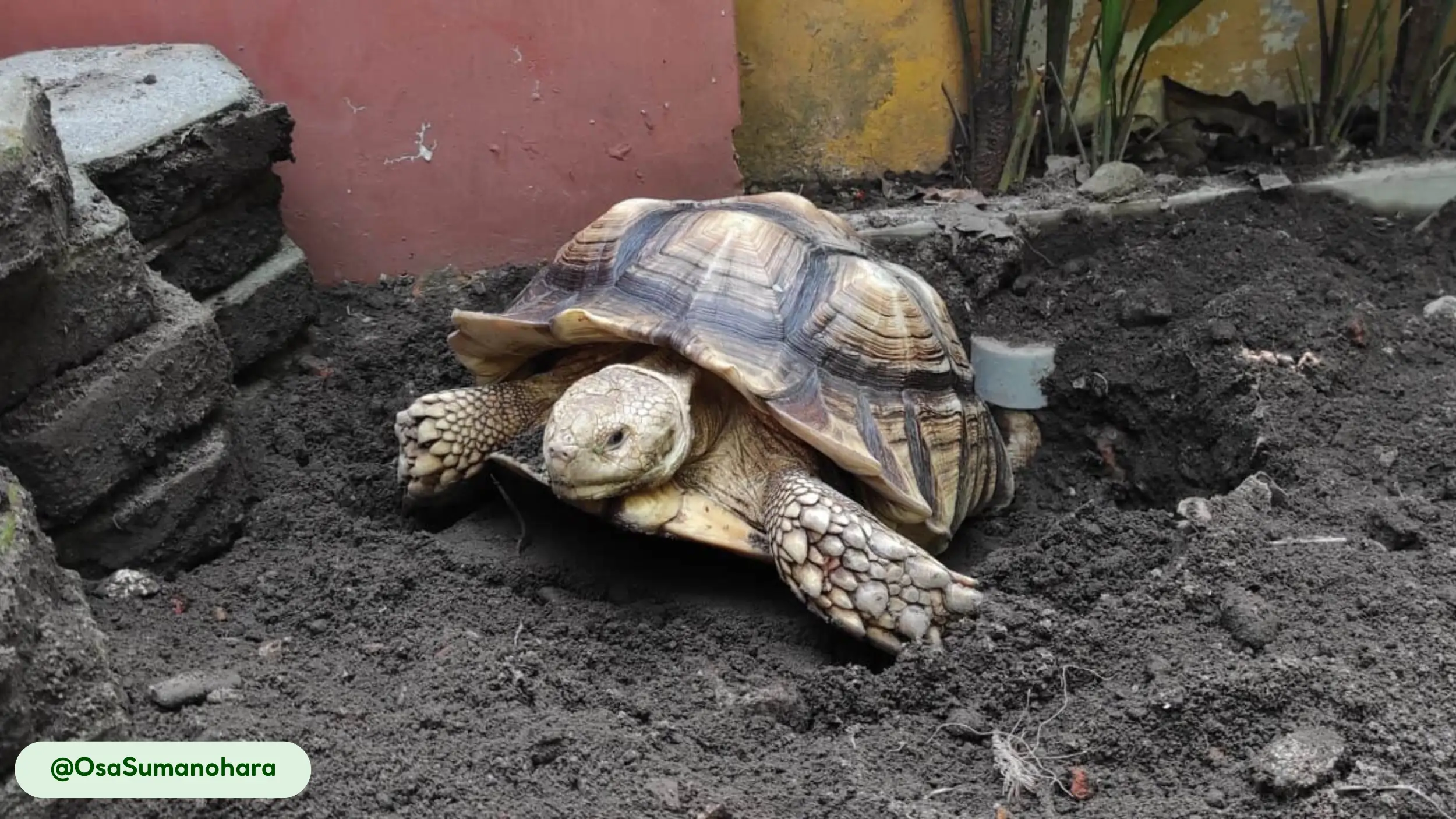
African spurred tortoises are characterized by their rugged appearance and massive, durable shells, which serve as their primary defense against predators. The carapace is broad and oval, with a color spectrum ranging from tan to yellow-brown, which provides camouflage in its desert home [11].
Each scute, or plate on the shell, features concentric rings known as annuli. These rings, while sometimes used to estimate age, are more accurately a record of growth spurts and can be inconsistent due to environmental factors like diet and temperature. The skin is thick and scaly, with a wrinkled texture that helps retain moisture, and its coloration often matches that of the shell.
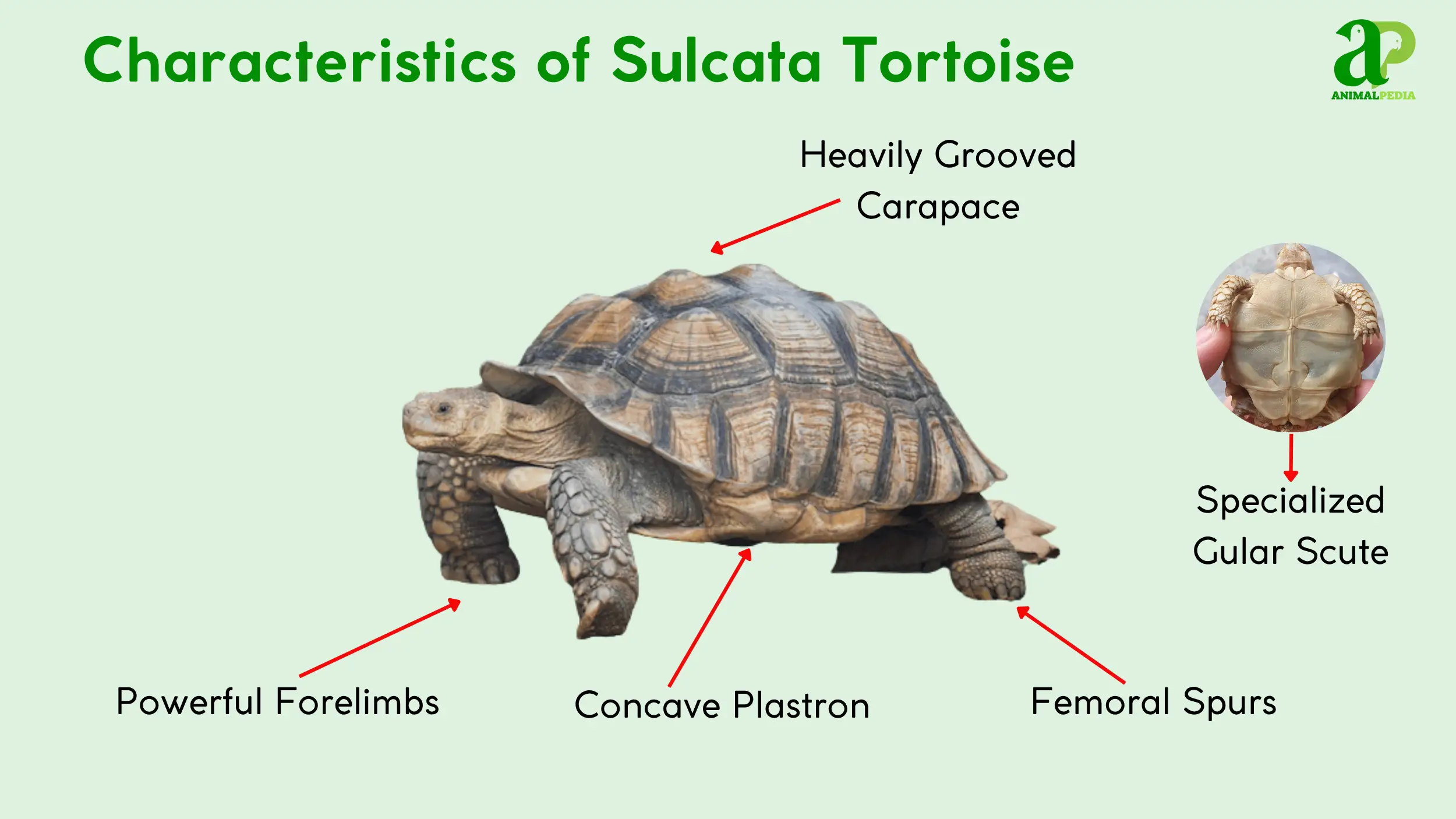
The tortoise’s distinctive morphology includes five distinct characteristics that set it apart from other chelonians. Each of these features serves a purpose in its arid environment.
- Prominent Femoral Spurs: The most notable feature of this species is the conical spurs located on the rear thighs, which gave the tortoise its name. These spurs provide traction for movement across sandy soils and help navigate obstacles.
- Heavily Grooved Carapace: The deeply ridged scutes give the shell a weathered look. This texture enhances camouflage and provides additional structural rigidity to the shell [11].
- Sturdy, Powerful Forelimbs: The front legs are thick and muscular, with flattened claws adapted for digging. These limbs are essential for excavating the extensive burrows that provide refuge from the Sahel’s heat [11].
- Concave Plastron: Males exhibit a concave plastron, the underside of the shell. This indentation serves a purpose during reproduction, fitting over the female’s rounded carapace during mating [11].
- Specialized Gular Scute: The tortoises have a long, forked projection at the front of their plastron. This structure is used in territorial conflicts between males, in which they ram each other forcefully to flip opponents onto their backs [18].
Beyond these defining features, sexual dimorphism is evident in their physical form. Males are typically larger and possess a more elongated, pointed tail, while females have a shorter, blunter tail and a flat plastron [11, 15]. This distinction in body shape is important for reproduction and can be observed in mature individuals.
With all their defining features, just how large can these impressive reptiles become?
How Big Are Sulcata Tortoises?
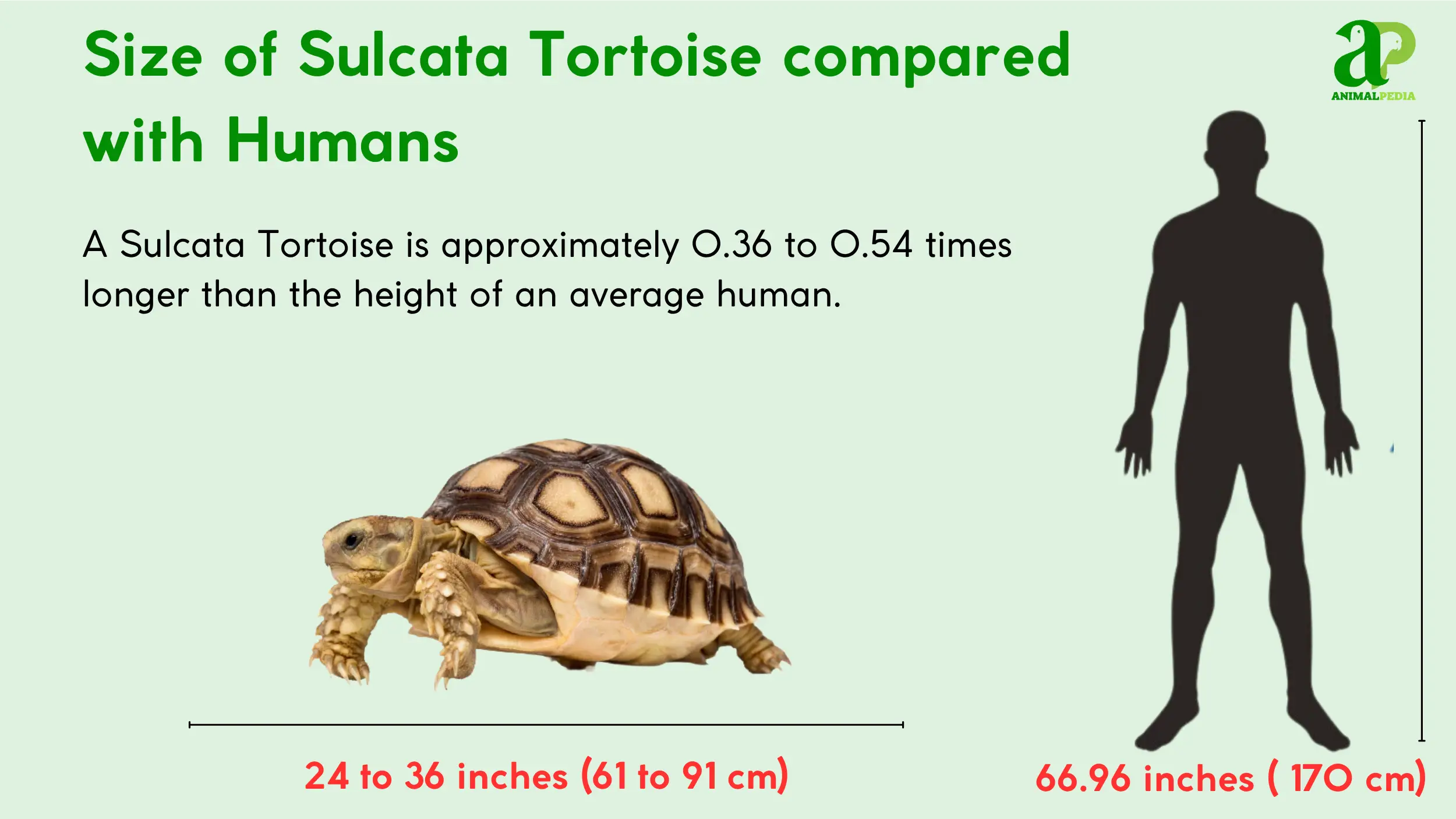
Sulcata tortoises are among the largest of their kind, with adult sizes showing significant variation based on sex. An average adult male can grow to a length of 24 to 36 inches (61 to 91 cm) and weigh between 100 to 220 pounds (45 to 100 kg), while females are generally smaller. A sulcata tortoise’s growth trajectory begins with its size at birth.
Hatchlings are small, measuring approximately 1.5 to 2.5 inches (4 to 6 cm) in length and weighing less than 0.05 pounds (25 g). They grow rapidly, often reaching a significant size within their first few years [13]. Their adult size can be compared to the size of a large car tire or a small refrigerator, a visual that helps illustrate their considerable mass [11].
| Category | Male | Female |
| Length | 24 – 36 inches (61 – 91 cm) | 20 – 26 inches (50 – 66 cm) |
| Weight | 100 – 220 lbs (45 – 100 kg) | 70 – 110 lbs (32 – 50 kg) |
| Record Size | 232 lbs (105 kg) [11, 21] | N/A |
Now that we have a better sense of their physical scale, it’s time to explore their natural home. Where on the African continent do these creatures thrive?
Where Do Sulcata Tortoises Live?
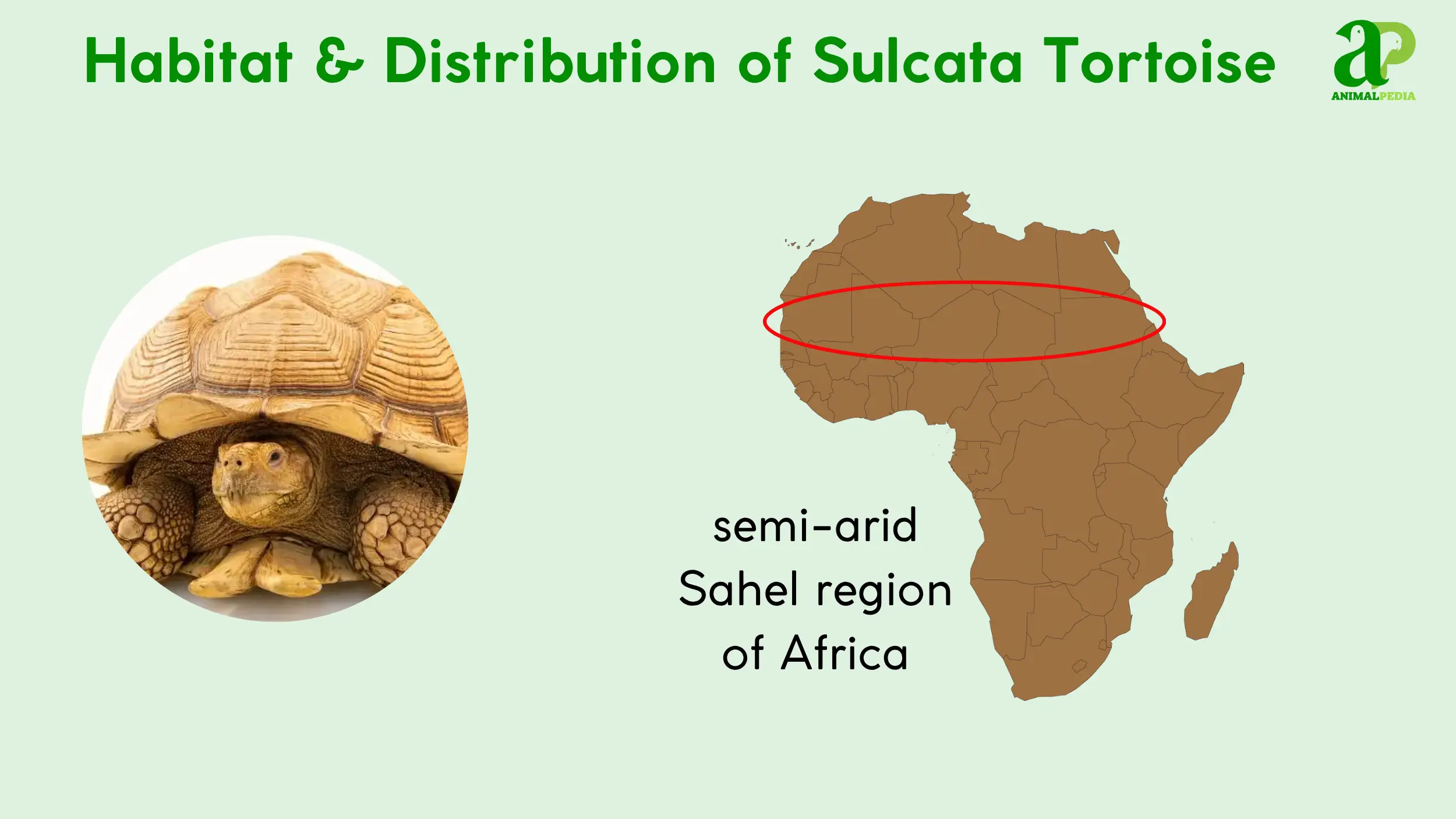
Sulcata tortoises inhabit the semi-arid Sahel region of Africa, a broad, transitional strip of land south of the Sahara Desert. This geographic distribution spans from Mauritania and Senegal eastward through Mali, Niger, Chad, and Sudan, extending to Ethiopia and Eritrea on the Red Sea coast [6, 9, 10, 11].
The species is adapted to thrive in harsh environments, including arid grasslands, dry savannas, and thorny scrub habitats [9, 10]. They are typically found at elevations up to 1,600 feet (488 meters). Their survival in these extreme conditions is directly linked to their ability to excavate burrows, which provide a stable, cooler microclimate that offers refuge from the intense heat and dry winds of the day and the cold temperatures of the night [11].
The species demonstrates territorial behavior, with male tortoises defending their home ranges, especially during the breeding season. The burrows themselves are a central feature of these territories, as they represent a critical resource for survival and are often vigorously protected from rivals [18]. This aggressive territoriality, involving ramming and pushing with the gular scutes, is a defining characteristic of male sulcata behavior.
Their home is a rugged environment, and their actions are a direct response to it. How do these tortoises behave to survive in such a challenging climate?
How Do Sulcata Tortoises Behave?
Sulcata tortoises exhibit a behavioral repertoire defined by adaptations to their arid environment, with a primary focus on resource acquisition and temperature regulation. These behaviors are essential for survival in the Sahel’s challenging climate. Their daily and seasonal patterns are dictated by the need to conserve moisture and avoid overheating, while their diet and movement reflect their role as a large herbivore.
- Diet and Feeding: Sulcata tortoises are herbivorous grazers that feed primarily on tough grasses and weeds. Their feeding behavior is methodical and consistent, ensuring they obtain sufficient nutrients from a low-quality diet.
- Movement and Abilities: They can walk slowly and deliberately, but their most notable ability is digging. The tortoises use their powerful limbs and spurs to construct extensive burrow systems.
- Daily/Seasonal Patterns: The tortoises are most active during cooler parts of the day, seeking shelter in their burrows during intense heat. They also enter a period of dormancy during the hottest, driest months.
Understanding these foundational behaviors provides a framework for examining the specifics of their life in the wild. As we consider their existence, it’s important to understand how they bring new life into the world. How do these tortoises reproduce?
Diet and Feeding
The sulcata tortoise is a strict herbivore, classified as a grazer, with a diet composed almost entirely of vegetation from arid landscapes [11]. Their primary food source is grass, which makes up about 90% of their diet in the wild. The tortoises also consume a range of other plants, including fibrous weeds and leaves from thorny shrubs, which provide essential moisture and nutrients.
They are not predators; instead, they forage methodically, using their powerful jaws to tear and grind tough, low-nutrient grasses [11]. This consistent grazing is vital for maintaining their gut health and preventing the buildup of toxins. Their digestive system is specifically adapted to process high-fiber, low-protein vegetation, extracting maximum hydration and energy from sparse resources.

Movement and Abilities
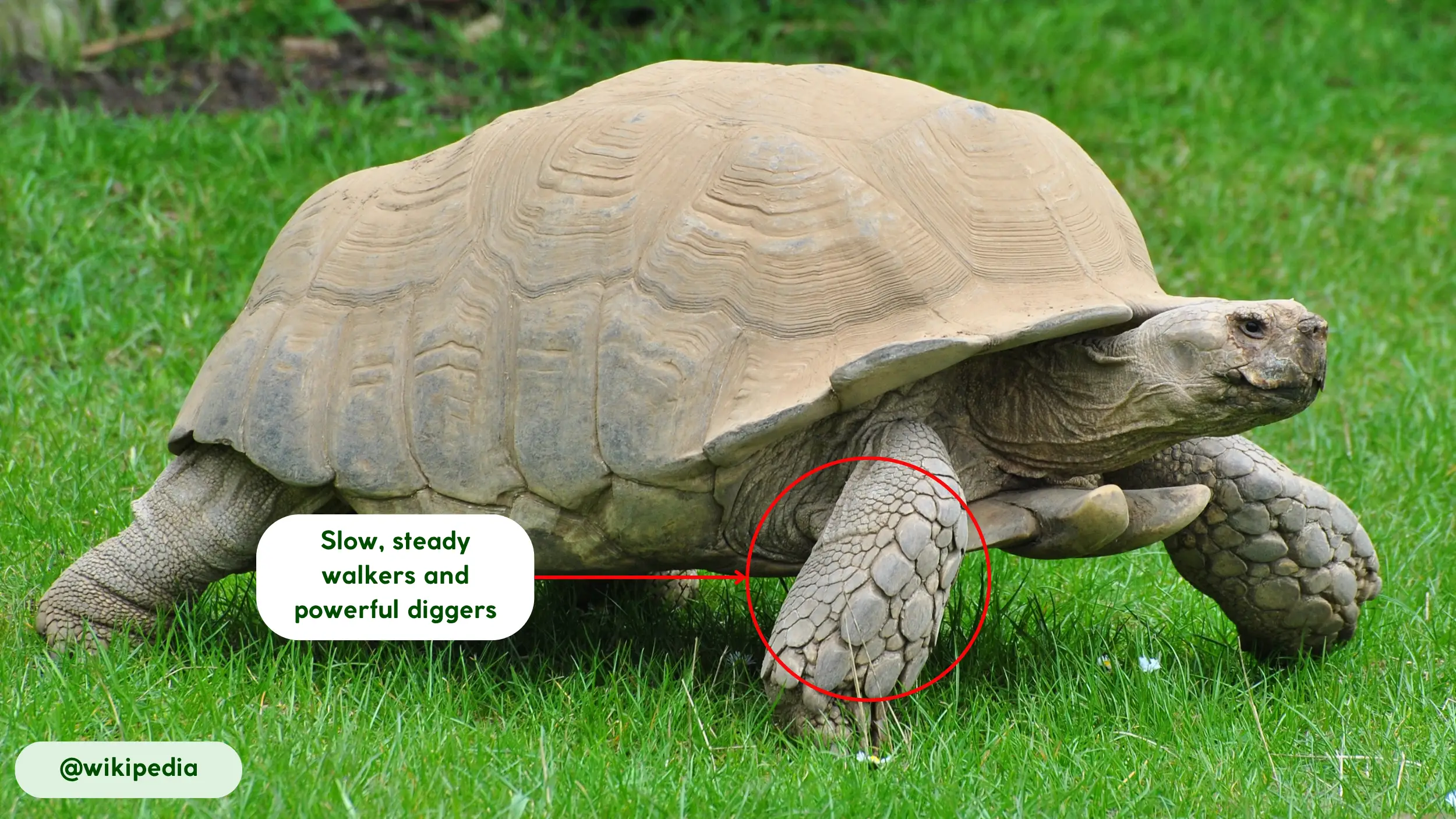
Sulcata tortoises are primarily terrestrial movers, navigating their environment with a slow, deliberate gait. While not built for speed, their movement is consistent and energy-efficient, a critical adaptation for survival in their vast, resource-scarce habitats. While a specific top speed is not widely documented in scientific literature, their locomotion prioritizes conservation. Their most important physical capabilities are related to digging and defense.
- Locomotion: The tortoises walk slowly and ploddingly, their heavy shells making them appear cumbersome. Their strong legs and feet, however, provide solid traction on loose, sandy soils.
- Burrowing: Their most specialized ability is excavation. Using their strong forelimbs and shovel-like claws, they can dig extensive burrow systems that can extend up to 30 feet (9 meters) long and 10 feet (3 meters) deep. These burrows are their primary shelter.
- Defensive Abilities: When threatened, sulcata tortoises can retract their limbs and head into their shell, presenting a durable, nearly impenetrable shield. Their size and powerful build are significant deterrents to many potential predators [11].
Daily/Seasonal Patterns
Sulcata tortoises are diurnal, with a daily activity cycle that is highly regulated by environmental temperatures. They are most active in the morning and late afternoon, when temperatures are moderate. During the hottest part of the day, typically between noon and 4 PM, they retreat into their burrows to escape the extreme heat [11, 18]. This behavioral pattern allows them to maintain a stable body temperature and avoid dehydration. The burrows provide a cooler, humid microclimate that is far more hospitable than the surface.
Their seasonal patterns are defined by the cycle of wet and dry seasons in the Sahel. During the dry season, which can last for several months, food and water become scarce. To survive, the tortoises can enter a state of dormancy known as aestivation, reducing their metabolic rate and conserving energy until conditions improve [11]. This period is distinct from hibernation, as it is a response to heat and drought rather than cold temperatures. Aestivation is a vital survival mechanism that allows them to endure periods of extreme environmental stress. Migration is not a typical behavior for this species; instead, they rely on their burrow systems and home ranges for long-term survival.
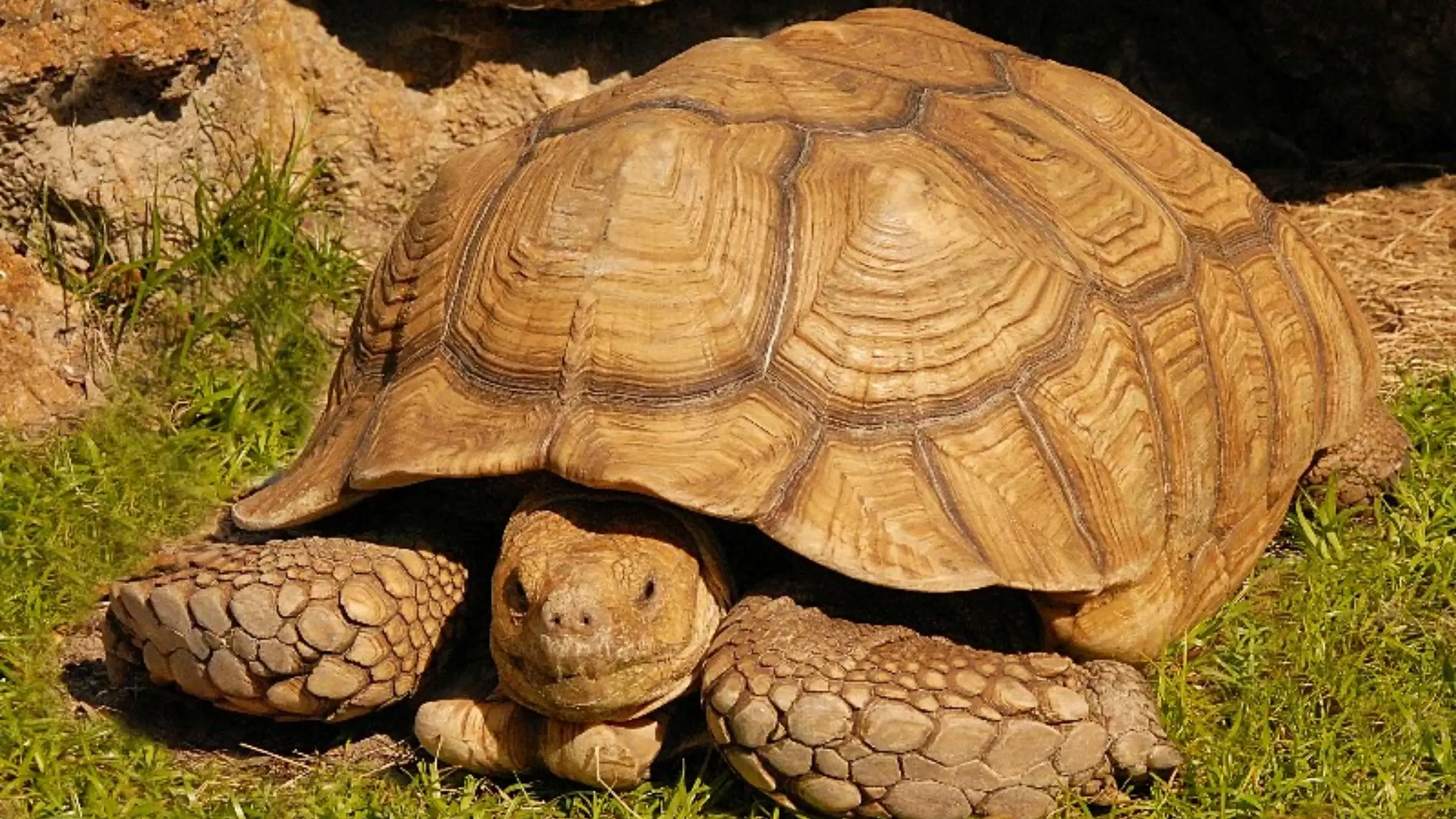

How Do Sulcata Tortoises Reproduce?
Sulcata tortoises are oviparous, meaning they reproduce by laying eggs [2]. Mating typically occurs after the rainy season, from September to November, when males engage in aggressive courtship rituals. Male tortoises use their gular scutes to ram and flip rivals during conflicts for dominance [18].
Following successful mating, a female can retain sperm for several years, though she usually lays one or more clutches of eggs 15 to 60 days later. Each clutch contains 15-30 eggs, and the incubation period lasts 100-200 days, with temperature dictating the sex of the hatchlings [2]. There is no parental care once the eggs have been laid.

Understanding their reproductive cycle makes us wonder about the length of their existence. How long can these creatures live, and what factors contribute to their lifespan?
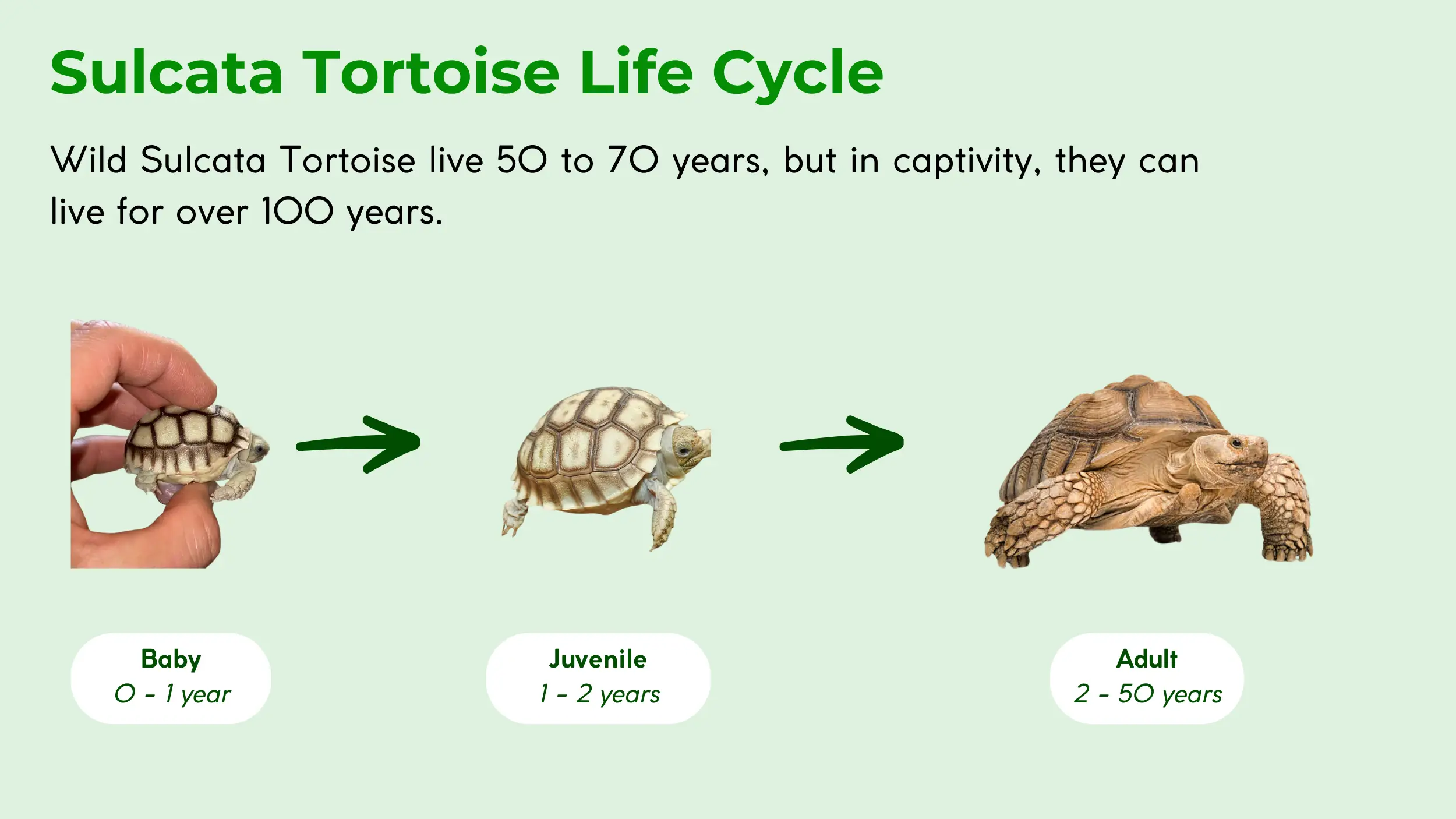
How Long Do Sulcata Tortoises Live?
African spurred tortoises have a long lifespan, averaging 50 to 70 years in the wild. In captivity, with proper care and nutrition, these tortoises can live significantly longer, with some individuals surpassing 100 years [16]. Their longevity is shaped by factors such as a high-fiber diet, habitat quality, and human impact.
They reach sexual maturity at a relatively late age, with males generally maturing around 15 years and females around 20 years [16]. The slow rate of maturity contributes to their long life, but also makes them vulnerable to population decline in the face of environmental pressures.
Their durability and longevity have made them popular, but in what ways are they beneficial to humans?
Are Sulcata Tortoises Beneficial to Humans?
Sulcata tortoises are beneficial to humans, primarily through their roles in the pet trade and as educational animals. They are a popular species in the exotic pet market due to their unique appearance and durable nature [14]. Their presence in zoos and conservation centers provides an opportunity for public education.
These tortoises serve as ambassadors for their species, helping to raise public awareness about reptiles, their ecosystems, and the importance of conservation efforts in the Sahel region of Africa. Their popularity helps fund conservation projects and promotes an appreciation for natural life.
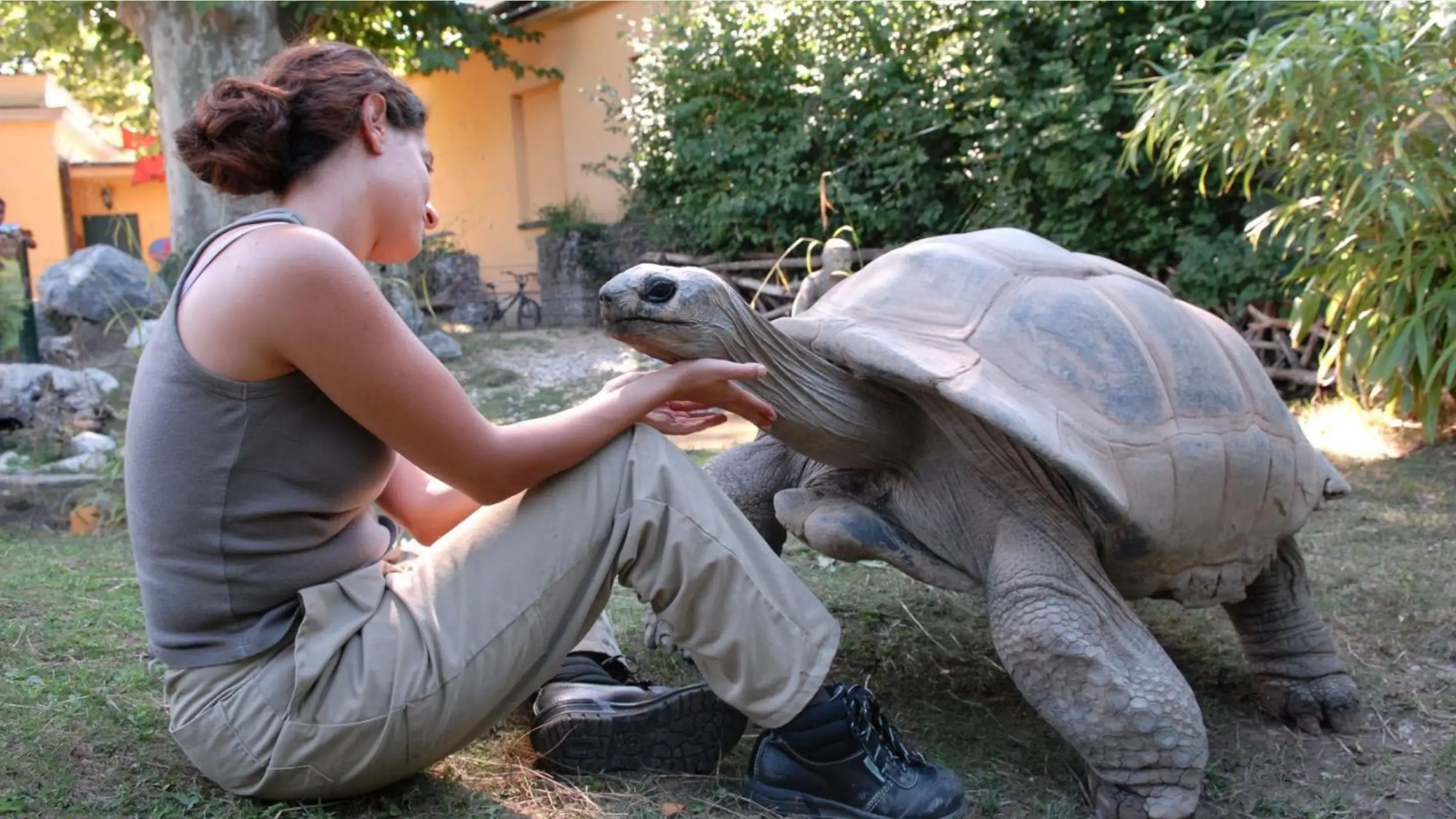

Despite their positive interactions with humans, their wild populations remain under threat. So, what is their current conservation status, and are they in danger?
Are Sulcata Tortoises Endangered?
Sulcata tortoises are not currently endangered but are classified as Vulnerable (VU) by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) [12]. The primary threats to their survival are habitat destruction and the illegal collection for the pet trade. Their slow reproductive rate and long time to reach maturity make them particularly susceptible to population decline from these pressures.
Several organizations and international conventions, such as CITES, work to protect the species [1]. Efforts include monitoring wild populations, combating illegal trade, and supporting captive breeding programs to reduce pressure on wild tortoises. Their ecological importance in their native arid landscape is in their role as ecosystem engineers, with their burrows providing shelter for many other species.

After learning so much about their wild existence, it’s natural to have more practical questions. The following section provides quick answers to common inquiries about sulcata tortoises, from their suitability as pets to their specific care needs.
Frequently Asked Questions About Sulcata Tortoises
Is A Sulcata Tortoise A Good Pet?
A sulcata tortoise can be a good pet for experienced keepers with sufficient space. Their immense size, long lifespan, and specialized dietary and environmental needs demand a serious, long-term commitment that most individuals cannot provide [14].
Are Sulcata Tortoises Friendly To Humans?
They are not affectionate in the traditional sense. Sulcatas can grow accustomed to human presence and may show curiosity, but their behavior is driven by instincts, not emotions. They are solitary and can become aggressive, especially males [18].
How Quickly Do Sulcata Tortoises Grow?
Sulcata tortoises have a rapid growth rate, particularly during their first five years. A hatchling weighing less than 0.1 pounds (45 grams) can reach 10 pounds (4.5 kg) within its first year and can double in weight annually for several years with proper care [13].
What Issues Do Sulcata Tortoises Have?
Common issues include metabolic bone disease from improper diet, respiratory infections from inadequate humidity, and digestive impaction from ingesting substrate. They require a high-fiber, low-protein diet to avoid shell pyramiding and maintain digestive health [22].
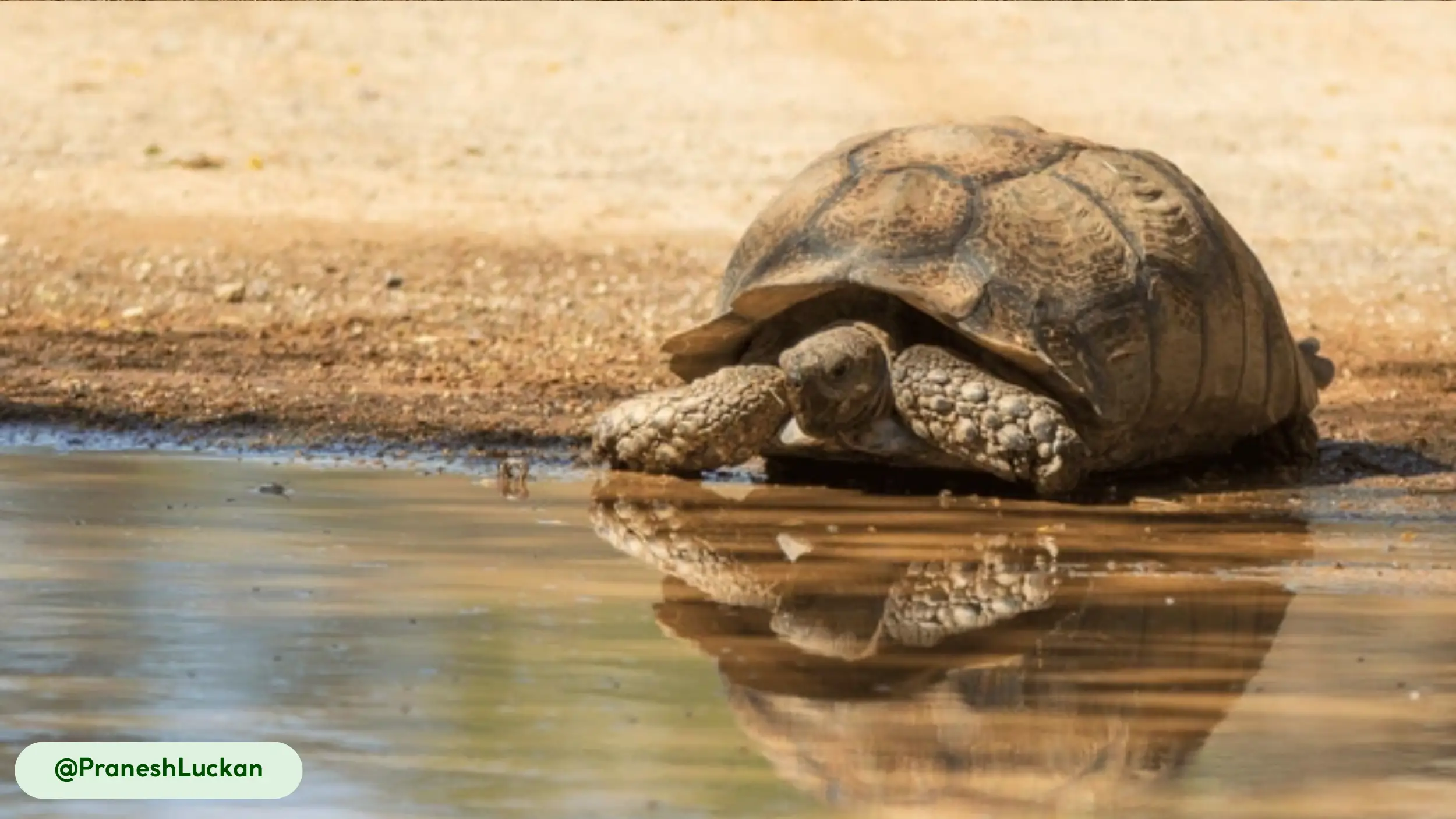
How Often Do Sulcata Tortoises Need Water?
Sulcata tortoises are adapted to dry climates and can get hydration from their food. However, they should always have access to a shallow water dish for soaking and drinking. Providing water is especially important in hot weather to prevent dehydration [14].
Conclusion
This comprehensive guide has provided an in-depth look at the African spurred tortoise, exploring its unique physical attributes, habitat, behavior, and conservation status. From their impressive size and powerful digging abilities to their adaptations for survival in arid environments, these reptiles are a true wonder of the animal kingdom. Understanding these characteristics highlights the importance of preserving this vulnerable species and its fragile ecosystem.
Animal Pedia is committed to delivering accurate and detailed information to help you understand the incredible diversity of animal life. For more detailed guides and fascinating facts about other species, continue to explore our resources and embark on your own journey of discovery.














