Most Popular Animals Start With F
The animal kingdom is filled with fascinating creatures, and today we’re spotlighting animals that start with the letter ‘F.’ From the cunning fox to the colorful flamingo, these species demonstrate the incredible variety of life on Earth. Whether you’re a wildlife enthusiast, a student, or simply curious, this collection of animals starting with ‘F’ will inspire your love for nature and its remarkable creations!
| Ferret | Flying Squirrel | Finch |
| Flamingo | Fox | Frog |
| Fennec Fox | Field Mouse | Fur Seal |
1. Ferret
The Ferret (Mustela putorius furo), a member of the Mustelidae family, is a domesticated carnivore originally native to Europe. Measuring 14–18 inches (36–45 cm) and weighing 1.5–4 pounds (0.7–1.8 kg), they have slender, elongated bodies, bushy tails, and small triangular faces with rounded ears. Their fur varies in color, including sable, black, white, and albino, often with distinctive masks.
Ferrets are crepuscular, active during dusk and dawn, alternating energetic play with long naps. Carnivorous by nature, they hunt small mammals and birds in the wild, while domesticated ferrets eat high-protein commercial foods. Jills (females) give birth to 6–8 kits after a 42-day gestation, nursing them until weaning at 6–8 weeks.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 14–18 inches (36–45 cm) |
| Weight | 1.5–4 lbs (0.7–1.8 kg) |
| Lifespan | 5–10 years |
| Habitat | Grasslands, forests, and domestic environments |
| Diet | Carnivorous; small mammals, birds, and insects |
| Social Structure | Solitary or small family groups |
| Conservation | Domesticated |
Fun fact: Ferrets can sleep up to 18 hours a day and often enter a limp, deep rest called “ferret dead sleep,” which can alarm new owners!
2. Flying Squirrel
Flying squirrels are a group of small to medium-sized nocturnal rodents from the Sciuridae family. They are found in various habitats across Asia, Europe, and North America. They prefer coniferous forests, particularly those dominated by spruce, fir, and pine trees. Flying squirrels are small to medium-sized rodents, with a body length ranging from about 9 to 15 inches (23 to 38 cm), excluding their tails. They have a flattened tail that acts as a stabilizer during glides. One of their most distinguishing features is the patagium, a fold of skin that stretches from their wrists to their ankles, allowing them to glide between trees.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 9 to 15 inches (23 to 38 cm) |
| Weight | 2 to 6 ounces (55 to 170 grams) |
| Lifespan | 5 to 10 years |
| Habitat | Forests, woodlands, and areas with abundant trees. |
| Diet | Nuts, seeds, fruits, fungi, and sometimes insects or small animals. |
| Social Structure | Social animals, often living in small family groups. |
| Conservation | Not evaluated |
Fun fact: Flying squirrels have even been recorded gliding for over 300 feet (90 meters).
3. Finch
Finches are small, colorful birds belonging to the Fringillidae family, known for their cheerful songs and lively behavior. They typically range in size from 3 to 6 inches (8 to 15 cm) in length, with a stout, conical beak perfectly adapted for cracking seeds. Found in various habitats worldwide, finches are admired for their vibrant plumage, diversity of species, and adaptability to different environments.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 3–6 inches (8–15 cm), depending on species |
| Weight | 0.3–1 oz (8–28 grams) |
| Lifespan | 4–7 years in the wild; up to 10 years in captivity |
| Habitat | Forests, grasslands, shrublands, and urban areas worldwide |
| Diet | Primarily seeds, with some insects and fruits |
| Social Structure | Social; often found in flocks |
| Conservation | Varies by species; many are Least Concern |
Fun fact: Some species, like the zebra finch, are known for their impressive ability to mimic sounds! Male zebra finches, for instance, can learn and mimic songs from their environment, including sounds from other bird species or even human-made noises.
4. Flamingo
Flamingos are elegant, wading birds known for their striking pink or reddish plumage, long legs, and S-shaped necks, which make their size reach 3.3 to 4.6 feet (1 to 1.4 meters), and weigh 4.4 to 8.8 pounds (2 to 4 kilograms). They inhabit wetlands, lagoons, and shallow lakes in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide.
Their unique coloration comes from a diet rich in algae and small crustaceans. Flamingos are social creatures, living in large colonies that offer protection and aid in breeding. They are a symbol of grace and beauty, but some species face threats from habitat loss and environmental changes, making conservation efforts crucial for their survival.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 3.3 to 4.6 feet (1 to 1.4 meters) |
| Weight | 4.4 to 8.8 pounds (2 to 4 kilograms) |
| Lifespan | 20 to 30 years, but in captivity, with proper care, they can live up to 50 years |
| Habitat | Wetlands, including lagoons and shallow lakes. Found in tropical and subtropical regions of Africa, South America and parts of southern Europe |
| Diet | Algae, small crustaceans, and invertebrates. |
| Social Structure | Highly social birds and live in large colonies |
| Conservation | Not evaluated |
5. Fox
Foxes are small to medium-sized mammals that are members of the Canidae family. They normally weigh from 6 to 24 pounds and are 18 to 35 inches long. They are distinguished by their pointed ears, bushy tail, and slender body. Diverse habitats, such as deserts, grasslands, woods, and cities, are home to these incredibly adaptive animals.
Foxes eat a variety of foods, including fruits, insects, and small mammals. They are agile hunters, usually living alone, and rely on their sharp senses to stay alive. The conservation of certain fox species, such as Darwin’s fox, is threatened by habitat loss and other factors, whereas the majority, like the red fox, are widespread and common.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 18 to 35 inches (46 to 90 cm) |
| Weight | 6 to 24 pounds (2.7 to 11 kg) |
| Lifespan | 2 to 6 years |
| Habitat | Forests and even urban areas. They are found on every continent except Antarctica. |
| Diet | Small mammals, birds, insects, fruits, berries, and carrion. |
| Social Structure | Primarily solitary animals but form small family groups. |
| Conservation | Data Deficient |
Fun fact: Foxes are skilled jumpers and can leap over obstacles as high as 6 feet (1.8 meters) to escape predators or access food sources.
6. Frog
Frogs, members of the order Anura, include over 7,000 species found in diverse habitats like wetlands, forests, and deserts worldwide. Ranging from 0.4–12 inches (1–30 cm) in length and weighing 0.1 ounces to 6.6 pounds (3 g–3 kg), their appearance varies greatly. Some are dull-colored for camouflage, while others display bright colors to warn predators of their toxicity. Frogs are known for their compact bodies, long hind legs for jumping, webbed feet for swimming, and large, protruding eyes that offer excellent vision.
Carnivorous by nature, frogs use their sticky, extendable tongues to catch insects, worms, and even small fish. They breed in water, laying eggs that hatch into tadpoles, which later metamorphose into adults. While most frogs lack parental care, some species, like poison dart frogs, guard their young or transport tadpoles to water.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 0.4–12 inches (1–30 cm) |
| Weight | 0.1 oz–6.6 lbs (3 grams–3 kg) |
| Lifespan | 1–20 years, depending on species |
| Habitat | Freshwater wetlands, forests, grasslands, and deserts worldwide |
| Diet | Carnivorous; insects, spider and other invertebrates |
| Social Structure | Solitary, except during breeding seasons |
| Conservation | Least Concern |
Fun fact: Frogs absorb water and oxygen through their skin, making them sensitive to environmental changes and valuable indicators of ecosystem health!
7. Fennec Fox
The Fennec Fox (Vulpes zerda) is a small desert-dwelling fox known for its adorable appearance and unique adaptations. Fennec Foxes are found in the Sahara Desert and other arid regions of North Africa. They are well adapted to desert life and are known to inhabit sandy deserts and rocky desert outcrops. The fennec fox is the smallest species of fox, typically weighing between 0.8 to 1.5 kg (1.8 to 3.3 lbs). It has a distinctive appearance with large, bat-like ears that can grow up to 6 inches (15 centimeters) long.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 24 to 41 cm (9.5 to 16 inches) |
| Weight | 0.8 to 1.5 kg (1.8 to 3.3 lbs) |
| Lifespan | 10 to 14 years |
| Habitat | Native to the deserts of North Africa, including the Sahara |
| Diet | Small mammals, birds, insects, eggs, and plants. |
| Social Structure | Live in small family groups. |
| Conservation | Least concern |
Fun fact: The Fennec Fox large ears help dissipate heat and regulate their body temperature in the hot desert environment.
8. Field Mouse
Field Mice (Apodemus spp.), part of the Muridae family, are small rodents found in grasslands, forests, fields, and even near human settlements worldwide. Measuring 2.5–4 inches (6–10 cm) in body length, with a 2–3 inch (5–8 cm) tail, they weigh just 0.5–1 ounce (15–30 grams). Their fur is typically brown or gray on the back with a lighter underbelly, and they have large, rounded ears and sensitive whiskers for navigating in low light.
These nocturnal creatures forage at night for seeds, grains, fruits, roots, and insects, adapting to available food sources. Females breed frequently, producing up to 10 litters annually, with young becoming independent within weeks. Field Mice rest in burrows or nests during the day, often forming small groups in colder months.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 2.5–4 inches (6–10 cm) (body length); tail adds 2–3 inches (5–8 cm) |
| Weight | 0.5–1 oz (15–30 grams) |
| Lifespan | 1–2 years in the wild; up to 4 years in captivity |
| Habitat | Grasslands, forests, fields, and human environments worldwide |
| Diet | Omnivorous; seeds, grains, insects, fruits, and roots |
| Social Structure | Solitary or small groups, especially in nests |
| Conservation | Least Concern |
Fun fact: Field Mice are excellent jumpers, allowing them to escape predators and navigate uneven terrain with ease!
9. Fur Seal
Fur Seals (Arctocephalinae), part of the Otariidae family, are marine mammals found along coastal waters, rocky shores, and islands in temperate and subpolar regions of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Southern Oceans. Ranging from 4–7 feet (1.2–2.1 meters) in length and weighing 60–660 pounds (27–300 kg), males are significantly larger than females. Their dense, waterproof fur, with nearly 300,000 hairs per square inch, provides warmth and buoyancy.
Carnivorous by nature, Fur Seals dive up to 600 feet (180 meters) to hunt fish, squid, and crustaceans. Highly social, they form large colonies during breeding seasons, where males establish territories and mate with multiple females. Pups nurse for several months, with mothers alternating between foraging at sea and caring for their young on land.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 4–7 feet (1.2–2.1 m) |
| Weight | 60–660 lbs (27–300 kg) |
| Lifespan | 12–30 years, depending on species |
| Habitat | Coastal waters, rocky shores, and islands in temperate |
| Diet | Carnivorous; fish, squid, and other marine organisms |
| Social Structure | Highly social; forms large colonies |
| Conservation | Least Concern |
Fun fact: Fur Seals spend up to 70% of their time underwater, using their sensitive whiskers to detect prey in dark or murky conditions! After exploring the most popular animals starting with ‘F,’ let’s narrow our focus to mammals. These warm-blooded creatures offer fascinating insights into survival and adaptability in diverse habitats.
Mammals that start with F
Mammals beginning with ‘F’ showcase the incredible adaptability of this class. From the playful ferret to the majestic fossa, these species inhabit diverse ecosystems worldwide.
| Fainting Goat | Fisher | Fox Squirrel |
| Fallow Deer | Fairy Armadillo | Fossa |
| Fruit Bat | Florida Panther | Fijian Monkey-faced Bat |
10. Fainting Goat
The Fainting Goat (the Tennessee Fainting Goat or Myotonic Goat) is a unique breed of domestic goat known for its distinctive response to sudden movements or loud noises. When startled or excited, these goats exhibit a temporary muscle stiffness or “fainting” response, which can cause them to lose their ability to move briefly. Adult Fainting Goats are typically small to medium-sized. They stand between 17 to 25 inches (43 to 64 cm) at the shoulder and weigh between 60 to 175 pounds (27 to 79 kg), depending on the specific breed line.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 17–25 in (43–64 cm) at the shoulder |
| Weight | 60–175 lbs (27–79 kg), varies by breed and sex |
| Lifespan | 10–15 years |
| Habitat | Domesticated; adaptable to various environments |
| Diet | Herbivorous; primarily grasses, hay, and grains |
| Social Structure | Highly social; thrives in herds |
| Conservation | Domesticated |
Fun fact: Fainting Goats are known to be playful and curious. They enjoy exploring their surroundings and interacting with both humans and other animals.
11. Fisher
The fisher (Pekania pennanti) is a medium-sized mammal native to North America. They prefer mature forests with dense vegetation and areas near water sources. Fishers are excellent climbers well adapted to arboreal habitats, spending much of their time in trees. Fishers have robust and elongated bodies, short legs, and a long, bushy tail. Fishers typically weigh between 3 to 12 pounds (1.4 to 5.4 kilograms), with males being larger and heavier than females. They have dark brown or black fur that is coarse and glossy, often with a lighter patch on their chest. Fishers have sharp, retractable claws and semi-retractable claws.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 30-47 inches (76-120 cm) in length, including their tail |
| Weight | 3 to 12 pounds (1.4 to 5.4 kg) |
| Lifespan | 7-10 years |
| Habitat | Mature forests, including deciduous, coniferous, and mixed woodlands |
| Diet | Small mammals like squirrels, rabbits, and birds. They also hunt larger animals like porcupines |
| Social Structure | Solitary animals and are usually found alone |
| Conservation | Least concern |
12. Fox Squirrel
The Fox Squirrel (Sciurus niger) is a species of tree squirrel native to North America. It is one of North America’s largest squirrels known for its striking reddish-brown fur and bushy tail. The Fox Squirrel is found across various habitats, including woodlands, parks, suburban areas, and urban environments. Fox Squirrels have a distinctive appearance. They are larger than many other squirrel species, with adults typically measuring 18–29 inches (46–73 cm) in length, including their tails. Their fur can vary in color, but their reddish-brown coat often recognizes them, although some may have gray or black fur.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 18–29 in (46–73 cm) including tail |
| Weight | 1.1–2.2 lbs (0.5–1 kg) |
| Lifespan | 6–12 years in the wild; up to 18 years in captivity |
| Habitat | Deciduous forests, woodlands, and urban areas in North America |
| Diet | Omnivorous; feeds on nuts, seeds, fruits, fungi, and occasionally insects and bird eggs |
| Social Structure | Solitary, though may gather in groups during feeding or nesting |
| Conservation | Least Concern |
13. Fallow deer
The Fallow deer (Dama dama) is a species native to Eurasia. It is a medium-sized deer known for its distinctive coat coloration and impressive antlers in males. Fallow deer have a striking coat with various color variations, including standard, melanistic (black), and albino. The typical coloration features a light brown coat with white spots during the summer and a grayish-brown coat during the winter. Males (bucks) typically have antlers with broad, flattened palms, while females (does) do not have antlers. Adult Fallow deer are medium-sized, with males standing about 3–5 feet (90–150 cm) tall at the shoulder and weighing between 65–220 lbs (30–100 kg).

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 3–5 feet (90–150 cm) in body length, with a shoulder height of 2.5–3 feet (75–95 cm) |
| Weight | 65–220 lbs (30–100 kg) |
| Lifespan | 12–16 years in the wild |
| Habitat | Woodlands, grasslands, and open fields, o |
| Diet | Herbivorous, feeding on grasses and acorns |
| Social Structure | Lives in herds, with males forming bachelor groups outside of the breeding season |
| Conservation | Least Concern |
14. Fairy armadillo
The fairy armadillo (the Pink Fairy Armadillo or the Pichiciego) is a unique and fascinating creature native to central Argentina. It is typically found in sandy habitats, including sandy plains, dunes, and grasslands. The fairy armadillo is the smallest species of armadillo, measuring only about 4 to 6 inches (10 to 13 centimeters) in length. It has a distinct pinkish or pale yellow shell, which is flexible and covered in fine, dense hair. The shell covers the creature’s back and head, while its underside is covered in soft, pale fur.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 4–6 inches (10–15 cm) |
| Weight | Approximately 3.5–4.2 oz (100–120 grams) |
| Lifespan | 5–10 years in the wild (estimated) |
| Habitat | Sandy plains, scrublands, and grasslands in central Argentina |
| Diet | Insectivorous, feeding on ants, larvae, and plant material |
| Social Structure | Solitary |
| Conservation | Near Threatened |
Fun fact: Their burrows can be up to 20 inches (50 centimeters) deep and protect them from predators and the elements.
15. Fossa
The Fossa (Cryptoprocta ferox) is a unique and elusive carnivore from Madagascar. It is the largest carnivorous mammal on the island, known for its slender, cat-like appearance. The Fossa has a long, slender body with short, reddish-brown fur. It has a pointed snout, sharp claws, and a long, bushy tail. Its body length can range from about 28–31 in (70–80 cm) body, with an additional 26–28 in (66–71 cm) of tail length. Fossas are currently listed as “Vulnerable” by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 28–31 in (70–80 cm) body; tail 26–28 in (66–71 cm) |
| Weight | 12–19 lbs (5.5–8.5 kg) |
| Lifespan | 15–20 years in captivity; slightly less in the wild |
| Habitat | Forests of Madagascar, including rainforests, dry forests, and spiny forests |
| Diet | Carnivorous; preys on lemurs, birds, reptiles, and small mammals |
| Social Structure | Solitary, except during mating season |
| Conservation | Vulnerable |
16. Fruit Bat
The fruit bat is a mammal in the family Pteropodidae distributed throughout tropical and subtropical regions, inhabiting forests, woodlands, and urban areas. The distribution of fruit bats is diverse, encompassing regions in Africa, Asia, Australia, and the Pacific Islands. Fruit bats are among the largest bat species in the world. Their size can vary depending on the species, but they generally have a wingspan ranging from 0.5 to 1.5 meters (about 1.6 to 4.9 feet). Some individuals can weigh up to 2.2 pounds (1 kilogram). Fruit bats possess a long snout, large eyes, and a well-developed sense of smell.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 0.5 to 1.5 meters (about 1.6 to 4.9 feet) |
| Weight | 0.5 to 1.5 kg (1.1 to 3.3 lbs) |
| Lifespan | 10–30 years |
| Habitat | Forests, woodlands, and urban areas in tropical and subtropical regions across Africa, Asia, Australia, and the Pacific Islands |
| Diet | Fruits, nectar, and flowers. Some species may occasionally consume leaves |
| Social Structure | Highly social and often live in large colonies |
| Conservation | Vulnerable |
17. Florida Panther
The Florida Panther (Puma concolor coryi, Cougar or mountain lion) is a large wild cat native to the southeastern United States, particularly Florida. It is one of the most endangered mammals in North America, with a critically low population estimated to be fewer than 200 individuals. Florida Panthers are similar in appearance to other cougars. They have a sleek, tawny coat with a slightly reddish hue and typically weigh between 60 to 160 pounds (27 to 73 kilograms). They stand about 3.25 to 5.25 feet (1 to 1.6 meters) tall at the shoulder and can be up to 7 feet (2.1 meters) long, including the tail.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 3.25 to 5.25 feet (1 to 1.6 meters) |
| Weight | Male: 100 to 160 pounds (45 to 73 kg); Female: 60 to 100 pounds (27 to 45 kg) |
| Lifespan | 10 to 15 years |
| Habitat | Forests and wetlands of southern Florida, specifically within the Everglades ecosystem |
| Diet | White-tailed deer, wild hogs, and smaller mammals such as raccoons and armadillos. |
| Social Structure | Solitary animals |
| Conservation | Endangered |
18. Fijian Monkey-faced Bat
The Fijian monkey-faced bat (Mirimiri acrodonta) is a unique and critically endangered bat species native to the islands of Fiji in the South Pacific Ocean. There are only 6 individuals of this species in the world. The Fijian monkey-faced bat is characterized by its large, expressive eyes, which give it a monkey-like appearance, hence its name. It has a wingspan of approximately 8.5–9 inches (21–23 cm) and a body length of around 3-3.5 inches (8-9 centimeters). The fur of this bat is generally reddish-brown or greyish-brown in color, and it has a distinctive white patch on its throat.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 8.5–9 inches (21–23 cm) in wingspan |
| Weight | Approximately 0.7–1.2 lbs (300–550 grams) |
| Lifespan | Unknown, but similar species live 10–15 years |
| Habitat | Lowland and montane tropical forests in Fiji, particularly in caves and hollow trees |
| Diet | Frugivorous, feeding on fruits, nectar, and flowers |
| Social Structure | Likely small groups or solitary, limited data available |
| Conservation | Critically Endangered |
Fun fact: Fijian monkey-faced bats emit high-frequency sounds that bounce off objects and return to the bat, providing information about their surroundings.
Reptiles that start with F
Reptiles starting with ‘F’ include some lesser-known yet fascinating species. Their cold-blooded nature and ancient lineage make them critical players in ecosystems.
| Flying Snake | False Water Cobra | Fer-de-lance Snake |
| Fire Ball Python | Frilled Lizard | False Cobra |
| False Coral Snake | Freshwater Crocodile | Forest Cobra |
| Fierce Snake | Flat-tailed Tortoise |
19. Flying Snake
The Flying Snake (Chrysopelea) is a reptile known for its unique ability to glide through the air. Flying Snakes are native to Southeast Asia and are commonly found in tropical rainforests and lowland forests. Flying Snakes are relatively slender and can grow to lengths ranging from 3.3 to 5 feet (1 to 1.5 meters). They have elongated bodies with a distinctive triangular-shaped head. Their bodies are flattened dorsoventrally, which aids in gliding. They are skilled climbers and can move through trees with agility, using their prehensile tails to aid in gripping branches. Flying snakes are mainly active during the day and are known for their shy and non-aggressive behavior.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 1 to 1.5 meters (3.3 to 5 feet) |
| Weight | 200 to 500 grams (0.4 to 1.1 pounds) |
| Lifespan | 5 to 7 years |
| Habitat | Tropical regions of South and Southeast Asia, including countries like India, Sri Lanka, Thailand, and Malaysia. They typically inhabit forests, woodlands, and jungle areas |
| Diet | Small vertebrates, including lizards, frogs, birds, and eggs. |
| Social Structure | Solitary creatures |
| Conservation | Not evaluated |
20. False Water Cobra
The False Water Cobra (Hydrodynastes gigas) is a non-venomous snake species native to South America. It primarily inhabits tropical and subtropical regions, favoring wetlands, marshes, and forested areas near bodies of water, such as swamps, rivers, and lakes. Although non-venomous, the False Water Cobra can display aggressive behavior when threatened. It may raise its forebody from the ground, spread its neck, and hiss loudly. The False Water Cobra is a giant snake, with adults typically reaching lengths between 4.5 to 6 feet (1.4 to 1.8 meters). It has a slender body, a distinct neck, and a slightly flattened head.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 4.5 to 6 feet (1.4 to 1.8 meters) |
| Weight | 1 to 3 kg (2.2 to 6.6 pounds) |
| Lifespan | Up to 20 years |
| Habitat | Tropical rainforests, wetlands, and marshes |
| Diet | Small mammals like squirrels, rabbits, and birds. They also hunt larger animals like porcupines and sometimes feed on fruits, nuts, and carrion |
| Social Structure | Solitary creatures |
| Conservation | Not evaluated |
21. Fer-de-lance Snake
The Fer-de-lance snake (Bothrops asper) is highly venomous in Central and South America. It thrives in tropical rainforests, moist and wet forests, cloud forests, lowland swamps, and agricultural areas. The Fer-de-lance snake is a giant and robust snake, with adult individuals typically ranging from 5 to 8 feet (1.5 to 2.5 meters) in length. They have a triangular-shaped head and prominent, heat-sensitive pits between their eyes and nostrils, which aid in detecting prey. The coloration of the Fer-de-lance snake varies, but they typically have a brown or yellowish-brown body with dark, diamond-shaped patterns along their back.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 5 to 8 feet (1.5 to 2.5 meters) in length, with some individuals reaching up to 3 meters (10 feet) |
| Weight | 2 to 3 kg (4.4 to 6.6 lbs) |
| Lifespan | 15 to 20 years |
| Habitat | Tropical rainforests, forest edges, agricultural areas |
| Diet | Small mammals (like rodents), birds, amphibians, lizards |
| Social Structure | Solitary |
| Conservation | Not evaluated |
22. Fire Ball Python
The Fire Ball Python is a specific morph or color variation of the Ball Python (Python regius), a popular and widely kept python species in the reptile pet trade. In the wild, Ball Pythons are native to sub-Saharan Africa, where they inhabit grasslands, savannas, and the edges of forests. Like all Ball Pythons, Fire morphs have a distinctive pattern of irregular blotches or “balls” that run down their back and sides. The pattern is often less distinct in Fire morphs due to the intensity of their coloration. They are a medium-sized python species, with adult Fire Ball Pythons typically reaching lengths of 3 to 5 feet (0.9 to 1.5 meters).

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 3 to 5 feet (0.9 to 1.5 meters) |
| Weight | 2 to 5 pounds (0.9 to 2.3 kg) |
| Lifespan | 20 to 30 years |
| Habitat | Grasslands, savannas, and forests |
| Diet | Small mammals, such as rodents, as well as birds |
| Social Structure | Solitary animals |
| Conservation | Not evaluated |
23. Frilled Lizard
The frilled lizard (Chlamydosaurus kingii) is a unique reptile native to northern Australia and southern New Guinea. Frilled lizards inhabit tropical and subtropical forests, savannas, and woodlands. One of the most distinctive features of the frilled lizard is the large frill around its neck. The frill is composed of thin skin supported by elongated spines or cartilage, and it can be brightly colored, featuring shades of red, orange, and yellow. Frilled lizards are relatively giant compared to other lizards. They can grow up to 2 feet (60 centimeters) in length, with males slightly larger than females.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | Up to 2 feet (60 centimeters), including the tail |
| Weight | 300–500 grams (10–18 ounces) |
| Lifespan | In the wild: Around 10–15 years; In captivity: Up to 20 years with proper care |
| Habitat | Native to northern Australia and southern New Guinea; Found in tropical and warm temperate forests, woodlands, and savannas |
| Diet | Carnivorous, ants, spiders, beetles, and small vertebrates like mice and other lizards |
| Social Structure | Solitary creatures |
| Conservation | Least Concern |
24. False Cobra
The False Cobra (Malpolon moilensis) is a non-venomous snake species native to parts of Africa and the Middle East. It belongs to the colubrid family and is named for its cobra-like appearance and behavior when threatened. Despite its name, the False Cobra is not a true cobra and lacks venomous fangs. The False Cobra has a slender and elongated body, reaching lengths of 3–4 ft (90–120 cm) or more. It is typically olive-green or brownish, with dark markings along its back and sides. The head is somewhat flattened and resembles a true cobra, with a distinct neck spread when threatened.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 3–4 ft (90–120 cm) |
| Weight | Approximately 1–2 lbs (0.5–0.9 kg) |
| Lifespan | 10–15 years |
| Habitat | Dry grasslands, scrublands, and rocky areas in the Middle East and North Africa |
| Diet | Small mammals, birds, and reptiles |
| Social Structure | Solitary |
| Conservation | Least Concern |
Fun fact: The coloration and pattern of the False Cobra’s skin provide excellent camouflage in its natural habitat, helping it blend in with the surrounding vegetation and rocky terrain.
25. False coral snake
The False Coral Snake (the Lampropeltis genus) is a non-venomous snake species in North and Central America. It is often mistaken for the venomous Coral Snake due to its similar coloration, but it has distinct differences in its pattern. The False Coral Snake is a member of the family Colubridae and is known for its vibrant and striking coloration, which serves as a form of mimicry. They are slender and can grow from 1–3 ft (30–90 cm), depending on the specific species.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 1–3 ft (30–90 cm), depending on species |
| Weight | Less than 1 lb (under 0.5 kg) |
| Lifespan | 10–15 years in the wild |
| Habitat | Forests, grasslands, and scrublands in Central and South America |
| Diet | Small reptiles, amphibians, and insects |
| Social Structure | Solitary |
| Conservation | Least Concern |
Fun fact: The rhyme “Red touch yellow, kill a fellow; red touch black, friend of Jack” helps people distinguish the deadly Coral Snake from the False Coral Snake.
26. Freshwater Crocodile
The freshwater crocodile (Crocodylus johnstoni) is a reptile species native to northern Australia, parts of Indonesia, and Papua New Guinea. Freshwater crocodiles inhabit various aquatic habitats, particularly freshwater environments such as rivers, creeks, billabongs, and freshwater swamps. It is a smaller crocodile species than its larger relative, the saltwater crocodile. Freshwater crocodiles typically have a slender and elongated body shape. They are smaller than saltwater crocodiles, with males reaching an average length of 8 to 10 feet (2 to 3 meters) and females slightly smaller. However, some individuals can grow up to 13 feet (4 meters) in length.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 8.2 feet (2.5 meters) in length |
| Weight | 50 to 100 kilograms (110 to 220 pounds) |
| Lifespan | 50 to 60 years |
| Habitat | Freshwater rivers, lakes, and estuaries of northern Australia, New Guinea |
| Diet | Small to medium-sized fish, crustaceans, amphibians, and birds, or reptiles |
| Social Structure | Solitary animals |
| Conservation | Least Concern |
27. Forest Cobra
The Forest Cobra (Naja melanoleuca) is a venomous snake native to central and western Africa’s rainforests and wooded areas. It is one of the most giant cobras in the world and is known for its striking appearance and potent venom. Forest Cobras are giant, slender snakes with a highly variable coloration. They range from dark brown to nearly black; some may have pale yellow or cream-colored bands or speckles. Adult Forest Cobras can reach lengths of 6–10 ft (1.8–3 m), with females generally slightly smaller than males.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 6–10 ft (1.8–3 m) |
| Weight | 3–10 lbs (1.4–4.5 kg) |
| Lifespan | 20–25 years in captivity; slightly less in the wild |
| Habitat | Forests, savannas, and agricultural areas in sub-Saharan Africa |
| Diet | Carnivorous; preys on small mammals, birds, reptiles, and amphibians |
| Social Structure | Solitary |
| Conservation | Least Concern |
28. Fierce Snake
The Fierce Snake (the Inland Taipan or Oxyuranus microlepidotus) is the most venomous snake in the world. The Fierce Snake is native to central Australia’s arid and semi-arid regions. The Fierce Snake is a relatively small and slender snake, with adults typically measuring around 6.5–8.8 feet (2–2.7 meters) in length. It has a light brown to olive coloration, often with a darker head and a lighter belly. The scales are smooth and glossy, and the snake’s overall appearance helps it blend effectively into its arid surroundings.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 6.5–8.8 feet (2–2.7 meters) |
| Weight | Approximately 4–6.6 lbs (1.8–3 kg) |
| Lifespan | 10–15 years in the wild |
| Habitat | Semi-arid regions, clay plains, and grasslands of central Australia |
| Diet | Small mammals such as rodents and occasionally birds |
| Social Structure | Solitary |
| Conservation | Least Concern |
Fun fact: The Fierce Snake holds the Guinness World Record for the highest venom yield of any snake, which is approximately 110 milligrams of venom in one extraction. Leaving behind the world of reptiles, we ascend to the skies. Birds starting with ‘F’ captivate us with their vibrant plumage and remarkable adaptability.
29. Flat-tailed Tortoise
The flat-backed spider tortoise (Pyxis planicauda) is a tortoise species native to the island of Madagascar. As the name suggests, the flat-backed spider tortoise has a flattened carapace (shell) compared to other tortoise species. The carapace is typically dark brown to black and features a raised ridge down the center. The tortoise has long limbs and a domed, oval-shaped carapace. Adult flat-backed spider tortoises can reach around 4–5 inches (10–13 cm). The flat-backed spider tortoise is listed as “Critically Endangered” on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 4–5 inches (10–13 cm) |
| Weight | 0.5–1 lb (200–500 grams) |
| Lifespan | 30–50 years |
| Habitat | Dry deciduous forests and sandy areas in Madagascar |
| Diet | Herbivorous, feeding on fallen leaves, fruits, and flowers |
| Social Structure | Mostly solitary, interacting during breeding season |
| Conservation | Critically Endangered |
Fun fact: Their distinctive flattened carapace is an adaptation to its arid habitat, allowing it to maneuver through tight spaces and burrow into the sandy soil more easily.
Birds that start with F
Birds like the flamingo and falcon epitomize grace and power. These avian species, starting with ‘F,’ showcase the splendor of life in flight and on land.
| Frizzle Chicken | Flycatcher | Fairy-Wren |
| Ferruginous Hawk | Frigatebird |
30. Frizzle Chicken
The Frizzle chicken is a unique and visually striking breed of domestic chicken known for its distinctive feather structure. The defining characteristic of Frizzle chickens is their curly or frizzled feathers. The feathers are twisted and turned outward, creating a fluffy and tousled appearance. Unlike most chickens, whose feathers lie flat against their bodies, the feathers of Frizzles curve outward, giving them a unique and striking look. Its color variations include black, white, buff, blue, and partridge. Adult Frizzle chickens typically weigh between 4.5 to 8 pounds (2 to 3.6 kilograms).

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | Generally medium-sized |
| Weight | Male Frizzles usually weigh around 6–7 pounds (2.7–3.2 kg); Female Frizzles generally weigh between 4–5 pounds (1.8–2.3 kg) |
| Lifespan | 5–10 years |
| Habitat | Safe, sheltered area |
| Diet | Primarily consisting of grains, seeds, insects, and vegetation |
| Social Structure | Social creatures, and they thrive in groups |
| Conservation | Domestics |
31. Flycatcher
Flycatcher is a type of bird belonging to the family Tyrannidae. This species is quite small with 4 to 8 inches (10 to 20 cm) length.
Flycatchers encompass many species, with over 400 recognized species worldwide. Different species of flycatchers can be found in other regions worldwide, including the Americas, Africa, Europe, and Asia. While flycatchers come in various shapes and sizes, they generally have a compact body with a relatively large head and a short neck. Their plumage can vary greatly depending on the species, ranging from dull browns and grays to vibrant yellows, blues, and oranges. Many flycatchers have distinctive facial markings, such as eye rings or bold streaks.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 4 to 8 inches (10 to 20 cm) |
| Weight | 10 to 30 grams (0.35 to 1 ounce) |
| Lifespan | 3 to 5 years |
| Habitat | Forests, woodlands, wetlands, and open fields. |
| Diet | Insects, such as flies, beetles, and moths |
| Social Structure | Generally solitary, especially during the breeding season |
| Conservation | Not evaluated |
Fun fact: Male flycatchers engage in elaborate courtship displays during the breeding season to attract females, involving aerial acrobatics and singing.
32. Fairy-Wren
Fairy-wrens are a group of small, brightly colored birds native to Australia and nearby regions. They belong to Maluridae and are known for their striking plumage and lively behavior. There are several species of fairy-wrens, but one of the most well-known is the Superb Fairy-wren (Malurus cyaneus). Fairy-wrens are small birds, with an average length ranging from about 5–6 in (12–15 cm). Male adults have vibrant blue and black feathers on their heads, wings, and tails, while their bodies are primarily brown. In contrast, females and juveniles are predominantly brown, with a paler blue patch around the eyes.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 5–6 in (12–15 cm) |
| Weight | 0.3–0.4 oz (8–11 g) |
| Lifespan | 5–10 years |
| Habitat | Grasslands, forests, and shrublands in Australia and New Guinea |
| Diet | Insects, spiders, and small seeds |
| Social Structure | Lives in cooperative breeding groups |
| Conservation | Least Concern |
Fun fact: The female typically initiates the song, and the male responds, which helps to strengthen the pairs bond.
33. Ferruginous Hawk
The Ferruginous Hawk (Buteo regalis) is a large bird of prey that belongs to the Buteo genus. Ferruginous Hawks are primarily found in open grasslands, shrub-steppe regions, and prairies of North America. The Ferruginous Hawk is one of the largest hawk species in North America. Its wingspan can measure up to 4.5 to 5.5 feet (1.4 to 1.7 meters), and its body length is about 20 to 26 inches (51 to 66 cm). The bird’s most distinctive feature is its feather coloration. Adults have a pale underside with white, reddish-brown, and rust-colored plumage on their backs, giving them a rusty or “ferruginous” appearance.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 20 to 26 inches (51 to 66 cm) |
| Weight | Males: 2 to 3 pounds (900 to 1,350 grams); Females: 3 to 4 pounds (1,350 to 1,800 grams) |
| Lifespan | 10 to 15 years |
| Habitat | Grasslands and sagebrush habitats in North America |
| Diet | Prairie dogs, ground squirrels, and jackrabbits. |
| Social Structure | Solitary birds |
| Conservation | Near Threatened |
34. Frigatebird
The Frigatebird (Man-of-War bird) is a seabird known for its striking appearance and remarkable flying abilities. There are five species of Frigatebirds, all belonging to the genus Fregata. They are found primarily in the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans. Frigatebirds have sharply pointed bills and long, deeply forked tails. Frigatebirds are among the largest of all seabirds. They can have wingspans that range from approximately 36 to 40 inches (90 to 102 cm). Despite their impressive wingspan, they are relatively light, weighing between 0.9 to 1.6 kilograms (2 to 3.5 pounds).

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 36 to 40 inches (90 to 102 cm) |
| Weight | 1.5 to 2.5 kg (3.3 to 5.5 pounds) |
| Lifespan | 30 to 40 years |
| Habitat | Tropical, islands, coastal cliffs, and open ocean waters |
| Diet | Fish, squid, and other marine creatures |
| Social Structure | Highly social, often living in large colonies during breeding season |
| Conservation | Near threatened |
Fun fact: Frigatebirds can soar for weeks without landing and even sleep while flying! From winged wonders, we dive into aquatic realms. Fish beginning with ‘F’ reveal the richness of underwater biodiversity, with species adapted to thrive in rivers, seas, and oceans.
Fish that start with F
Fish such as the flounder and fangtooth exhibit unique adaptations for survival underwater. Their diversity reflects the vastness and complexity of aquatic life.
| Flounder | Flying Fish | Frogfish |
| Flathead Catfish | Fire Eel | Freshwater Sunfish |
| Freshwater Drum | Football Fish | Fangtooth |
| Frilled Shark | Freshwater Eel |
35. Flounder
Flounder is a type of flatfish that belongs to the family Pleuronectidae. Flounders inhabit various habitats, including sandy and muddy bottoms, rocky reefs, and seagrass meadows. Flounders have a distinct body shape that is highly adapted for life on the seafloor. Common flounders typically grow to about 12 to 24 inches (30 to 60 centimeters). One of their eyes migrates during development, so both eyes are located on one side of the head, typically the upper side, when resting on the seafloor. This adaptation allows flounders to lie flat and blend in with their surroundings.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 12 to 24 inches (30 to 60 centimeters) |
| Weight | 1 to 10 kg (2 to 22 lbs) |
| Lifespan | 10 to 20 years |
| Habitat | Shallow coastal waters, including estuaries, sandy or muddy sea floors |
| Diet | Small fish, crustaceans, and mollusks |
| Social Structure | Solitary creatures |
| Conservation | Not evaluated |
Fun fact: Flounders have the ability to change their skin color and texture to match their surroundings, allowing them to blend seamlessly into the seafloor.
36. Flying Fish
Flying fish are a unique group known for their remarkable ability to glide through the air. Flying fish are found in warm and tropical waters worldwide, particularly in the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans. They are primarily aquatic, inhabiting the open ocean rather than coastal areas. Flying fish have a streamlined and torpedo-shaped body well-suited for swimming in water and gliding through the air. They have long, slender pectoral fins acting as wings and a deeply forked tail that helps propulsion. On average, flying fish measure between 6 to 14 inches (15 to 35 cm) in length.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 6 to 14 inches (15 to 35 cm) in length |
| Weight | 0.2 to 1 pound (90 to 450 grams) |
| Lifespan | 3 to 5 years |
| Habitat | Warm, open waters near the surface, often in areas with plenty of plankton and small fish |
| Diet | Small fish, zooplankton, and various marine invertebrates |
| Social Structure | Swimming together in groups to avoid predators. |
| Conservation | Not evaluated |
Fun fact: Flying fish can glide above the water’s surface for distances of up to 1,300 feet (400 meters).
37. Frogfish
Frogfishes are marine fish known for their exceptional camouflage and unique appearance. Frogfishes are found in tropical and subtropical waters of the Atlantic and Indo-Pacific oceans. They belong to the family Antennariidae, part of the order Lophiiformes. Frogfishes have a distinct body shape resembling a flattened, roundish blob. On average, most species of frogfishes measure between 6 to 16 inches (15 to 40cm) in length. Their bodies are often covered in small, fleshy protuberances called dermal spinules, giving them a warty or lumpy appearance.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 6 to 16 inches (15 to 40cm) |
| Weight | 1–2 kg (2.2–4.4 pounds) |
| Lifespan | 5 to 10 years |
| Habitat | Coral reefs, seagrass beds, and muddy or sandy ocean floors |
| Diet | Leaves, stems, and roots of various plants |
| Social Structure | Solitary animals |
| Conservation | Not evaluated |
Fun fact: Frogfishes can change their skin color and texture to blend in with their surroundings, making them nearly invisible to predators.
38. Flathead Catfish
The flathead catfish (Pylodictis olivaris) is a large freshwater species native to North America. Flathead catfish are primarily found in freshwater systems such as rivers, lakes, reservoirs, and large streams. Flathead catfish are characterized by their distinctive flattened head and wide mouth, equipped with sharp, backward-facing teeth. They have a robust body shape and can grow to impressive sizes. Adults can reach 2 to 3 feet (0.6 to 0.9 meters) and weigh over 5 to over 100 pounds (2.3 to 45.4 kg).

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 2 to 3 feet (0.6 to 0.9 meters) |
| Weight | 5 to 100 pounds (2.3 to 45.4 kg) |
| Lifespan | Up to 20 years |
| Habitat | Large rivers, reservoirs, and other slow-moving, warm waters in North America. |
| Diet | Smaller catfish, sunfish, and other freshwater species. |
| Social Structure | Solitary by nature |
| Conservation | Least Concern |
Fun fact: In the wild, the flathead catfish can live for several decades, with some individuals reaching 20 to 30 years of age or even more.
39. Fire Eel
The Fire Eel (Mastacembelus erythrotaenia) is a visually striking freshwater fish native to Southeast Asia. Despite its name, the Fire Eel is not an eel but a type of fish known as a spiny eel. The Fire Eel has an elongated, snake-like body with smooth, scaleless skin. It is typically dark brown or black, with bright red or orange stripes running along its sides. The dorsal fin runs along its back, with a small, fleshy appendage at the tip of its snout. Fire Eels are known for their impressive size. They can grow around 20–40 in (50–100 cm) or more in length, making them one of the largest species in the Mastacembelidae family.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 20–40 in (50–100 cm), occasionally larger |
| Weight | Up to 3 lbs (1.4 kg) |
| Lifespan | 10–20 years in captivity |
| Habitat | Slow-moving rivers, streams, and swamps in Southeast Asia |
| Diet | Carnivorous; feeds on insects, worms, crustaceans, and small fish |
| Social Structure | Solitary |
| Conservation | Least Concern |
Fun fact: Fire Eels belong to the family Mastacembelidae, considered one of the oldest fish families dates back millions of years.
40. Freshwater Sunfish
Freshwater sunfish are a group of species belonging to the family Centrarchidae, native to North America. They are found in various freshwater habitats, including lakes, rivers, ponds, and reservoirs. Sunfish are typically small to medium-sized fish with colorful patterns. On average, they measure around 4–18 inches (10–46 cm) in length. They have laterally compressed bodies, which means they are flattened from side to side. Their dorsal fins often have sharp spines. Sunfish are known for their vibrant colors, including shades of green, blue, yellow, orange, and red.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 4–18 inches (10–46 cm) |
| Weight | 0.2–4.5 lbs (90 grams–2 kg) |
| Lifespan | 5–12 years, varying by species |
| Habitat | Lakes, ponds, rivers, and streams with vegetation, primarily in North America |
| Diet | Omnivorous, consuming insects, crustaceans, small fish, and plant matter |
| Social Structure | Typically solitary or small groups |
| Conservation | Least Concern |
Fun fact: During the breeding season, male sunfish may engage in elaborate courtship displays to attract females, including visual cues, territorial behavior, and even vocalizations.
41. Freshwater Drum
The Freshwater Drum (Aplodinotus grunniens or sheepshead, grunt, or silver perch) is a fish species native to freshwater bodies across North America. It belongs to the family Sciaenidae. The Freshwater Drum has an elongated, cylindrical body with a slightly arched back. It typically has a silvery-gray coloration with a slightly brassy sheen. The scales are relatively large and rough to the touch. One distinctive feature is its large mouth with strong teeth. They can grow quite large, with adults commonly reaching lengths of 10–20 inches (25–50 cm) and weights of 5 to 15 pounds (2.3 to 6.8 kilograms).

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 10–20 inches (25–50 cm) |
| Weight | 5 to 15 pounds (2.3 to 6.8 kilograms) |
| Lifespan | 13–20 years |
| Habitat | Freshwater rivers, lakes, and reservoirs, primarily in North America |
| Diet | Grain-based products, such as flour, cereal, rice, pasta, and bread. |
| Social Structure | Highly social insects |
| Conservation | Least Concern |
Fun fact: The Freshwater Drum is known for the grunting or drumming sounds it can produce, created by the contraction of its swim bladder muscles.
42. Football Fish
The Football Fish (Himantolophus spp.) is a deep-sea anglerfish that belongs to the family Himantolophidae. They are found in the world’s oceans, typically at depths ranging from 8–24 in (20–60 cm). These fish are known for their unique appearance and specialized method of hunting. Football Fish have a distinctive appearance characterized by a large, football-shaped head, enormous mouth, and sharp, fang-like teeth. They possess a bioluminescent lure, called an esca, at the end of a stalk on their forehead. This lure emits light to attract prey in the darkness of the deep sea.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 8–24 in (20–60 cm) |
| Weight | 2–15 lbs (1–7 kg) |
| Lifespan | Estimated 5–10 years |
| Habitat | Deep-sea waters at depths of 650–3,300 ft (200–1,000 m) in oceans worldwide |
| Diet | Carnivorous; feeds on fish |
| Social Structure | Solitary; males attach to females as parasites during reproduction |
| Conservation | Least Concern |
Fun fact: The size difference between males and females Football Fish is one of the most extreme cases of sexual dimorphism in the animal kingdom.
43. Fangtooth
The Fangtooth (Anoplogaster cornuta) is a deep-sea fish that belongs to the family Anoplogastridae. Fangtooths are found in deep-sea environments worldwide, particularly in the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans. They are typically found at depths ranging from 6–7 inches (15–18 cm), inhabiting the abyssal plains and slopes. The Fangtooth has a distinct and intimidating appearance. It has an elongated body with a large head and a mouth full of long, sharp teeth. Its teeth are the most significantly proportional to the body size of any fish species in the ocean, giving it its name. The body is typically dark brown or black, which helps it blend into the dimly lit depths where it resides.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 6–7 inches (15–18 cm) |
| Weight | Up to 6 oz (170 grams) |
| Lifespan | Up to 10 years |
| Habitat | Deep ocean waters, typically between 200–2,000 meters |
| Diet | Carnivorous, feeding on fish and squid |
| Social Structure | Solitary |
| Conservation | Least Concern |
Fun fact: Their large eyes are susceptible to faint light, enabling it to detect the bioluminescent glow of potential prey and navigate.
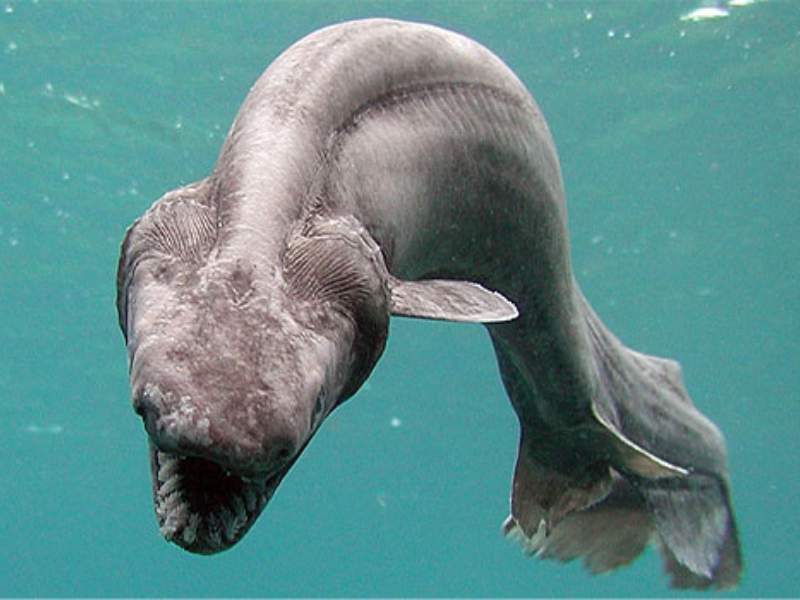
44. Frilled Shark
The Frilled Shark (Chlamydoselachus anguineus) is a rarely-seen and enigmatic species of shark that inhabits the deep-sea environments of the world’s oceans. They are found in various habitats, including woodlands, grasslands, and scrublands. The Frilled Shark are typically found in the depths of the world’s oceans, ranging from 6–7 ft (1.8–2.1 m) below the surface. On average, they measure around 4.9 to 6.6 feet (1.5 to 2 meters) in length. The frilled shark has a broad, flattened head with a wide mouth. Its jaws contain numerous rows of sharp, needle-like teeth.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 6–7 ft (1.8–2.1 m) |
| Weight | 110–220 lbs (50–100 kg) |
| Lifespan | Estimated 25 years |
| Habitat | Deep ocean waters, typically at depths of 500–4,000 ft (150–1,200 m), worldwide |
| Diet | Carnivorous; feeds on fish, squid, and other deep-sea creatures |
| Social Structure | Solitary |
| Conservation | Near Threatened |
Fun fact: They called a “living fossil” and is believed to have retained many features from ancestors who lived millions of years ago.
45. Freshwater Eel
Freshwater eels are a group of elongated, snake-like fish in Anguilliformes. Freshwater eels are found in various rivers, lakes, and estuaries worldwide. There are many species of freshwater eels, but some of the most well-known include the European eel (Anguilla anguilla), American eel (Anguilla rostrata), and Japanese eel (Anguilla japonica). These eels can reach lengths of up to 2–5 ft (60–150 cm) or more. Freshwater eels have elongated, snake-like bodies with smooth, slimy skin. They are typically brown or greenish, and their undersides are often lighter. They have small pectoral fins and lack pelvic fins.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 2–5 ft (60–150 cm), depending on species |
| Weight | 2–20 lbs (0.9–9 kg) |
| Lifespan | 15–50 years, varies by species |
| Habitat | Rivers, lakes, and estuaries; migrates to the ocean to spawn |
| Diet | Carnivorous; feeds on fish, crustaceans, and invertebrates |
| Social Structure | Solitary |
| Conservation | Critically Endangered |
Fun fact: Some species of freshwater eels are known for their impressive lifespans, up to 80 years in the wild. Transitioning from the depths of the ocean, we step onto the moist, murky habitats of amphibians. insect starting with ‘F’ reveal life at the water-land boundary.
Insects that start with F
Insects such as fireflies and fleas showcase diverse behaviors and ecological importance. Their roles are pivotal in processes like pollination and nutrient cycling.
| Flea | Fruit Fly | Flour Beetle |
| Flea Beetle | Fly | Figeater Beetle |
| Fritillary Butterfly | Florida Woods Cockroach | Furrow Bee |
| Field Cuckoo Bumblebee |
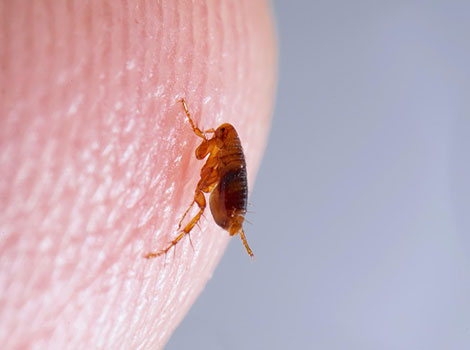
46. Flea
Fleas are small, only 1.5 to 3.3 mm in length, wingless insects that belong to the order Siphonaptera. Fleas are distributed worldwide and can be found on every continent except Antarctica. Adult fleas are typically tiny, ranging from 1 to 4 millimeters in length. They have flattened bodies, which enable them to move quickly through the fur or feathers of their hosts. Fleas have powerful hind legs adapted for jumping, allowing them to leap impressive distances relative to their size. Fleas are ectoparasites, meaning they live on the outside of their hosts. They are blood-feeding parasites and require a blood meal to survive and reproduce.
| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 1.5 to 3.3 mm |
| Weight | Generally measuring in micrograms |
| Lifespan | 2–3 months |
| Habitat | Animal fur, bedding, or nesting areas. They prefer warm and humid climates |
| Diet | Hematophagous; adult fleas feed exclusively on the blood of mammals or birds |
| Social Structure | Solitary parasites |
| Conservation | Not evaluated |
Fun fact: Fleas can launch into the air with incredible speed, reaching up to 8 inches (20 centimeters) per second.
47. Fruit Fly
The fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) is a tiny insect belonging to the family Drosophilidae. Fruit flies are attracted to and feed on ripe or decaying fruits, vegetables, and other organic matter. They are usually found in kitchens, grocery stores, fruit markets, and anywhere food is present. They are especially attracted to sweet, fermenting substances and can be a nuisance in homes and commercial settings. Fruit flies are typically small, measuring about 2-4 mm in length in length. They have a tan or yellowish-brown body, red eyes, and translucent wings with dark veins.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 2–4 mm in length |
| Weight | 1–2 milligrams |
| Lifespan | 30–50 days |
| Habitat | Orchards, kitchens, garbage bins, and compost piles |
| Diet | Fruits, vegetables, and other decaying organic materials |
| Social Structure | Solitary for the most part but form aggregations around food sources |
| Conservation | Not evaluated |
Fun fact: In the early 20th century, scientists such as Thomas Hunt Morgan conducted groundbreaking experiments on fruit flies, leading to the discovery of the principles of inheritance.
48. Flour Beetle
Flour beetles are a small, common household pest belonging to the Tenebrionidae family. There are several species of flour beetles, but two of the most notable ones are the confused flour beetle (Tribolium confusum) and the red flour beetle (Tribolium castaneum). Flour beetles are commonly found in stored food products such as flour, rice, cereals, grains, and other dried goods. Flour beetles are small, reddish-brown to black insects with elongated, flattened bodies. They are about 0.1-0.25 inches (3-6 mm) long, making them relatively small and often hard to spot.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 0.1–0.25 inches (3–6 mm) |
| Weight | 2–5 milligrams |
| Lifespan | 1–3 years |
| Habitat | Warm, humid environments; common in warehouses, kitchens, and food storage areas |
| Diet | Grain-based products such as flour, cereal, rice, pasta, and bread. |
| Social Structure | Highly social insects |
| Conservation | Not evaluated |
Fun fact: Flour beetles have developed resistance to some typical insecticide, which makes them a challenging pest to control in specific environments.
49. Flea Beetle
The flea beetle is a tiny insect from the Chrysomelidae family, part of the order Coleoptera. These beetles are widely distributed and known for their ability to jump like fleas when disturbed, giving them their common name. Flea beetles are found worldwide, with a diverse range of habitats. They are particularly abundant in agricultural fields, gardens, and natural areas with dense vegetation. Flea beetles are typically small, measuring around 0.08 to 0.2 inches (2 to 5 millimeters) in length. They have a compact and oval-shaped body with a hard exoskeleton.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 0.08–0.2 inches (2–5 mm) |
| Weight | Negligible; extremely lightweight |
| Lifespan | Few weeks to several months |
| Habitat | Grasslands, forests, agricultural fields, and gardens worldwide |
| Diet | Herbivorous; primarily feeds on leaves and roots of plants |
| Social Structure | Solitary but may aggregate on host plants |
| Conservation | Not evaluated |
Fun fact: In colder regions, flea beetles emerge in spring when temperatures rise and feeding and reproductive activities resume.
50. Fly
Flies are a diverse group of insects in the order Diptera, which means “two wings.” They are found in almost every corner of the world and are known for their ability to fly. Flies are an incredibly diverse group, with over 150,000 known species. Flies are characterized by compact bodies, large compound eyes, and two wings. Common house flies (Musca domestica), for instance, are medium-sized flies that typically measure around 1/8 inch to 1 inch (3–25 mm) in length. Unlike many other insects, flies have only one pair of functional wings, while the second pair is reduced to small, knob-like structures called halteres.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 1/8 inch to 1 inch (3–25 mm) |
| Weight | Around 12 milligrams |
| Lifespan | 15–30 days |
| Habitat | Worldwide, except in extreme climates like Antarctica |
| Diet | Liquids or decaying organic matter |
| Social Structure | Generally solitary but may gather in large groups when food is abundant |
| Conservation | Not evaluated |
Fun fact: Flies walk on their food to sample it, using specialized taste receptors to determine its suitability.
51. Figeater Beetle
The Figeater Beetle (Cotinis mutabilis or the Green June Beetle) is a large and colorful scarab beetle native to the western United States. They are commonly found in various habitats, including gardens, orchards, fields, and wooded areas, particularly in the southwestern United States and parts of Mexico. Figeater Beetles are strikingly colorful insects. They have a metallic green exoskeleton that shimmers in the sunlight. They are oval-shaped and measure about 1–1.5 in (2.5–4 cm) in length.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 1–1.5 in (2.5–4 cm) |
| Weight | Approximately 0.1–0.2 oz (3–6 g) |
| Lifespan | 1–2 years (mostly as larvae) |
| Habitat | Gardens, orchards, and urban areas in the southwestern United States and Mexico |
| Diet | Adults feed on ripe fruits and nectar; larvae feed on decaying organic matter |
| Social Structure | Solitary |
| Conservation | Least Concern |
Fun fact: When threatened or handled, Figeater Beetles can produce a distinctive hissing sound by expelling air through openings in their abdomen to startle or deter predators.
52. Fritillary Butterfly
Fritillary butterflies are a diverse group of butterflies belonging to the family Nymphalidae. They are known for their striking, colorful wing patterns in various regions worldwide, including North and South America, Europe, and Asia. Fritillary butterflies come in multiple sizes and colors but typically have distinctive, intricate wing patterns. The wingspan of fritillary butterflies typically ranges between 2–4 in (5–10 cm). Many species have orange or brown wings with intricate black markings, while others may have metallic hues or more subdued colors.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | Wingspan 2–4 in (5–10 cm) |
| Weight | Less than 0.01 oz (under 0.3 g) |
| Lifespan | 2–4 weeks as adults |
| Habitat | Meadows, forests, and grasslands in North America, Europe, and Asia |
| Diet | Adults feed on nectar; larvae feed on violets and other host plants |
| Social Structure | Solitary |
| Conservation | Least Concern |
Fun fact: Fritillary butterflies have specialized scent patches on their wings that release pheromones to attract potential mates.
53. Florida Woods Cockroach
The Florida Woods Cockroach (Eurycotis floridana) is a large species of cockroach native to the southeastern United States, particularly in Florida. It is also commonly referred to as the Palmetto Bug. Despite its name, the Florida Woods Cockroach is not limited to wooded areas and can be found in various habitats, including urban and suburban environments. The Florida Woods Cockroach is relatively large, with adults measuring about 1.5–2 in (4–5 cm) in length. They have a flattened, oval-shaped body and are typically dark brown to black in color.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 1.5–2 in (4–5 cm) |
| Weight | Approximately 0.1 oz (2–3 g) |
| Lifespan | 1–2 years |
| Habitat | Humid, wooded areas and decaying plant matter in the southeastern United States |
| Diet | Decaying organic material, such as wood and leaves |
| Social Structure | Solitary |
| Conservation | Least Concern |
Fun fact: Florida Woods Cockroaches play a vital role in their ecosystem by feeding on decaying plant material, fungi, and other organic matter.
54. Furrow Bee
Furrow Bees, belonging to the genus Halictus, are a diverse group of solitary bees found in various parts of the world, particularly in North America, Europe, and Asia. Furrow Bees can be found in multiple habitats, including grasslands, meadows, gardens, woodlands, and urban areas. Furrow Bees are generally small to medium-sized bees with various colors, including metallic green, brown, or black. The body length of adult furrow bees typically ranges from about 0.3–0.5 in (8–13 mm). They are often mistaken for wasps due to their slender bodies, but their branched body hairs can distinguish them.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 0.3–0.5 in (8–13 mm) |
| Weight | Less than 0.01 oz (under 0.3 g) |
| Lifespan | Several weeks (adults) |
| Habitat | Meadows, gardens, and open woodlands in temperate regions worldwide |
| Diet | Adults feed on nectar; larvae feed on pollen provisions |
| Social Structure | Solitary or semi-social, depending on species |
| Conservation | Least Concern |
Fun fact: Furrow Bees have branched hairs on their bodies, which help them effectively collect and distribute pollen.
55. Field Cuckoo Bumblebee
The Field Cuckoo Bumblebee (Bombus campestris) is a cuckoo bumblebee species belonging to the genus Bombus. The Field Cuckoo Bumblebee is primarily found in parts of Europe, including the United Kingdom, France, Germany, and Scandinavia. It prefers open habitats such as grasslands, meadows, and heathlands. The worker bumblebees of Field Cuckoo Bumblebee typically have a body length ranging from about 0.6–0.8 inches (15–20 mm). The queens and workers have black bodies with yellow collars and a few yellow bands on the abdomen. The males, on the other hand, have a more yellowish appearance with some black markings.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 0.6–0.8 inches (15–20 mm) |
| Weight | Approximately 0.03–0.07 oz (1–2 grams) |
| Lifespan | Several weeks to a few months |
| Habitat | Meadows, grasslands, and woodland edges across Europe and parts of Asia |
| Diet | Nectar and pollen |
| Social Structure | Parasitic species that infiltrates and relies on the colonies of other bumblebees |
| Conservation | Least Concern |
Fun fact: The queen produces pheromones that mimic those of the host queen, fooling the host workers into accepting her as their queen. Finally, beyond mammals, reptiles, and insects, we encounter other unique animals. These species starting with ‘F’ defy categorization but remain integral to biodiversity.
Other animals that start with F
Other animals like the fiddler crab and fanworm display unique characteristics. These creatures enrich our understanding of the lesser-known yet essential parts of nature.
56. Funnel-web Spider
Funnel-web spiders are a group of venomous spiders known for their distinctive burrow-shaped webs, which they use for hunting. They belong to the family Hexathelidae and are found in various parts of the world, including Australia, Asia, and Africa. One of the most notorious species in this family is the Sydney Funnel-web Spider (Atrax robustus), known for its potent venom. Funnel-web spiders vary in size but are generally robust and compact with shiny, dark-colored bodies. Their leg span can range from 0.4–2 in (1–5 cm) depending on the species. Males are often smaller than females.

| Attributes | Quick facts |
|---|---|
| Size | 0.4–2 in (1–5 cm), depending on species |
| Weight | 0.02–0.4 oz (1–10 g) |
| Lifespan | 5–20 years |
| Habitat | Forests, gardens, and burrows in Australia and other regions, depending on species |
| Diet | Carnivorous; preys on insects, small reptiles, and amphibians |
| Social Structure | Solitary |
| Conservation | Least Concern |
Fun fact: To protect themselves from flooding during heavy rain, some Funnel-web spiders use their silk to line the walls of their caves as a waterproof barrier. Having explored the diverse range of animals starting with ‘F,’ let’s address some frequently asked questions. These will provide deeper insights and clarify common curiosities about these fascinating creatures.
FAQs
What are Big Animals that Start With F?
Here are 5 big animals that start with the letter “F”:
- Falcon: While not a large bird in size, falcons are known for their impressive speed and agility. They are renowned for their ability to dive at high speeds to capture their prey.
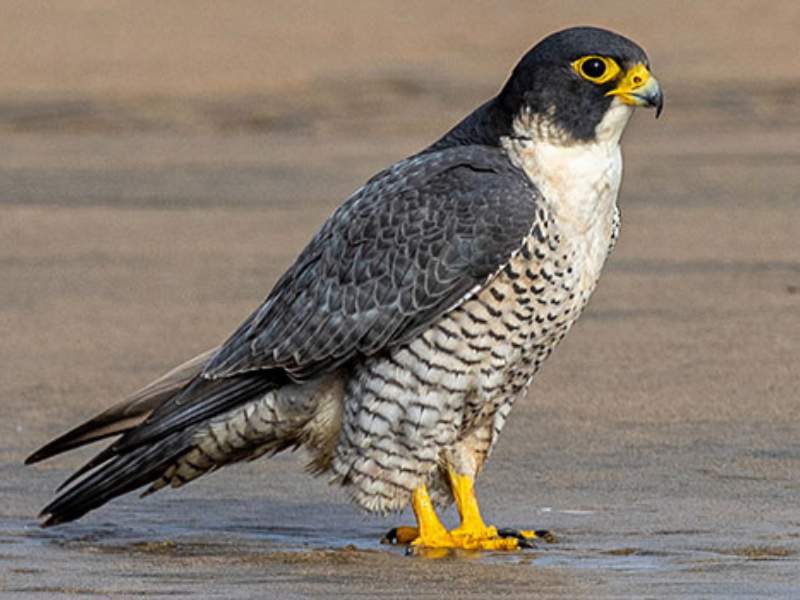

- Flamingo: Flamingos are large wading birds known for their vibrant pink plumage and long, slender legs. They can reach heights of up to 5 feet (1.5 meters) and have a wingspan of around 5 to 6 feet (1.5 to 1.8 meters).

- Frigatebird: Frigatebirds are large seabirds known for their impressive wingspan. They can have wingspans of up to 7.5 feet (2.3 meters), making them some of the most giant flying birds in the world.
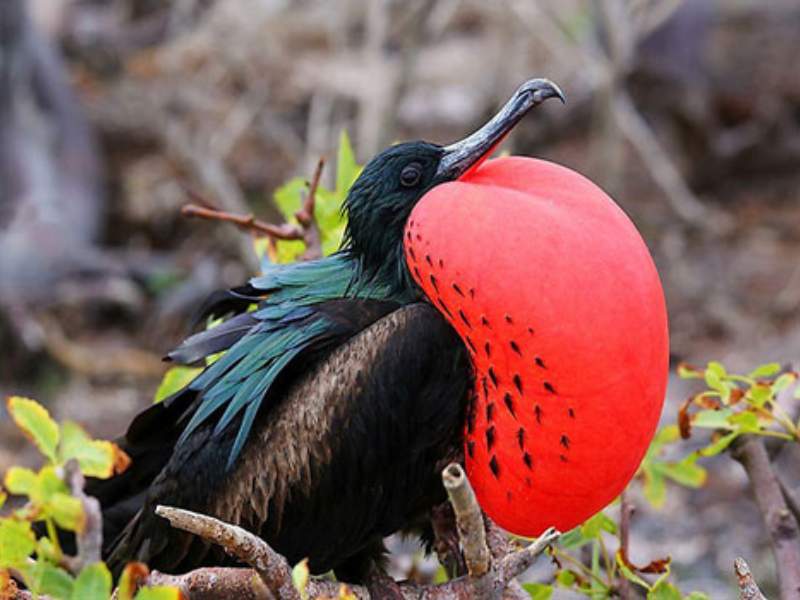

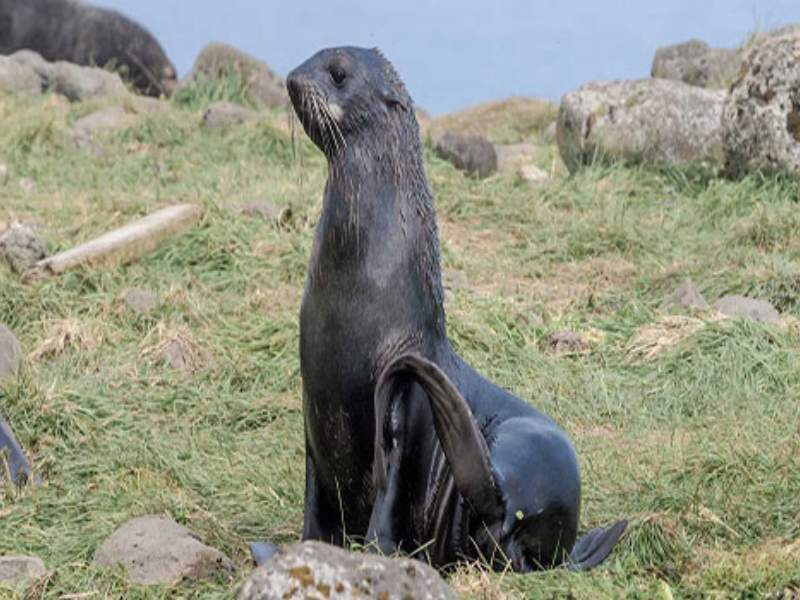
- Fur Seal: Fur seals are marine mammals that belong to the same family as sea lions. While not as large as some seal species, they can still reach lengths of up to 6.5 feet (2 meters) and weigh several hundred pounds.

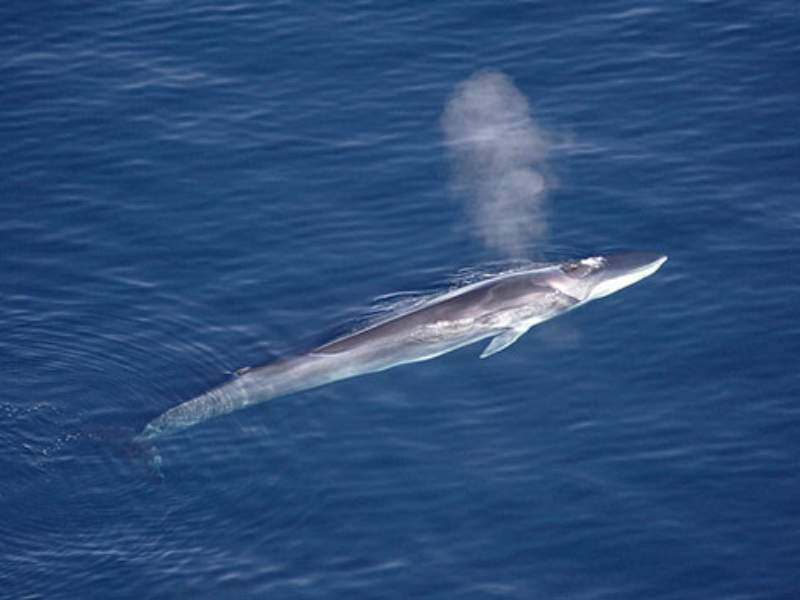
- Fin Whale: The fin whale is the second-largest animal after the blue whale. They can reach lengths of up to 79 feet (24 meters) and weigh up to 70 tons (64 metric tonnes). They are known for their streamlined bodies and distinctive dorsal fins.

What are Small Animals that Start With F?
Here are 6 small animals that start with the letter “F”:
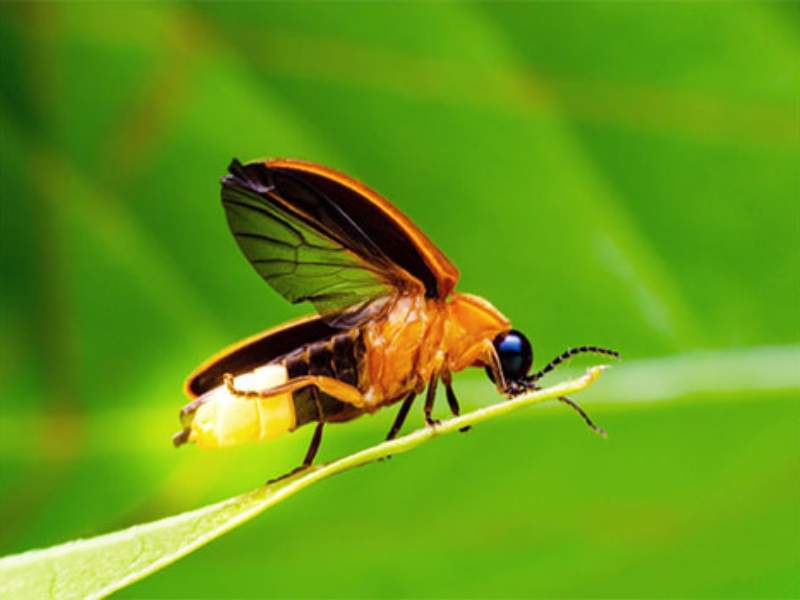
- Firefly: Fireflies, known as lightning bugs, are small beetles known for their bioluminescent ability. They emit light through their abdomen, creating a beautiful display, especially during warm summer evenings.

- Ferret: Ferrets are small domesticated carnivores belonging to the Mustelidae family. They have long, slender bodies and short legs and are known for their playful and curious nature.
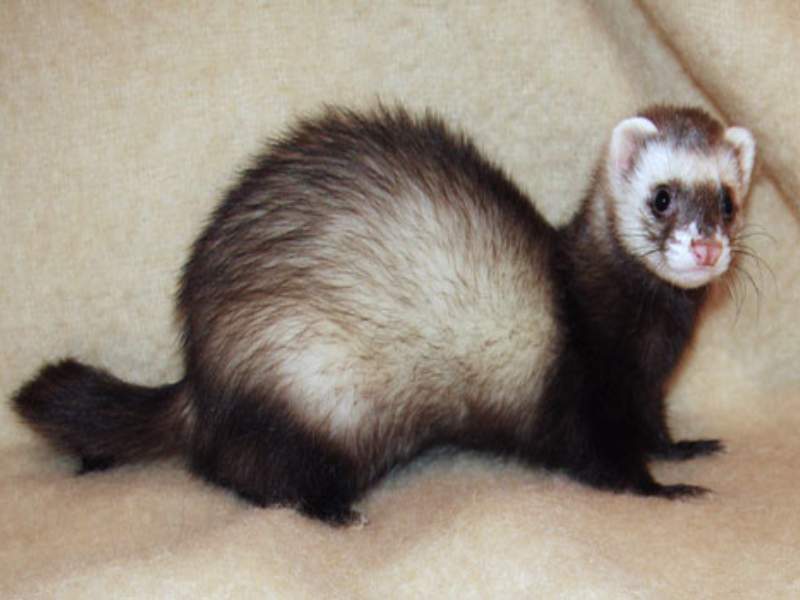

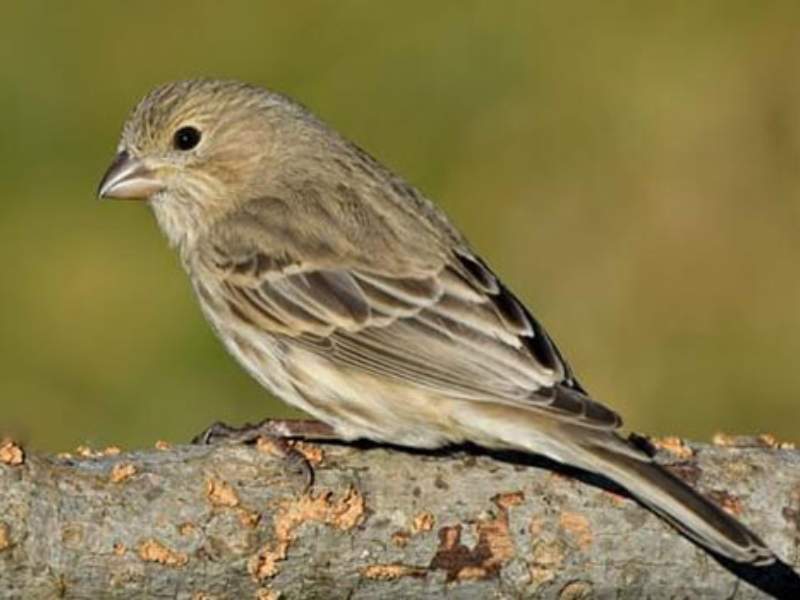
- Finch: Finches are small passerine birds known for their melodic songs and colorful plumage. They come in various species and can be found in different habitats worldwide.

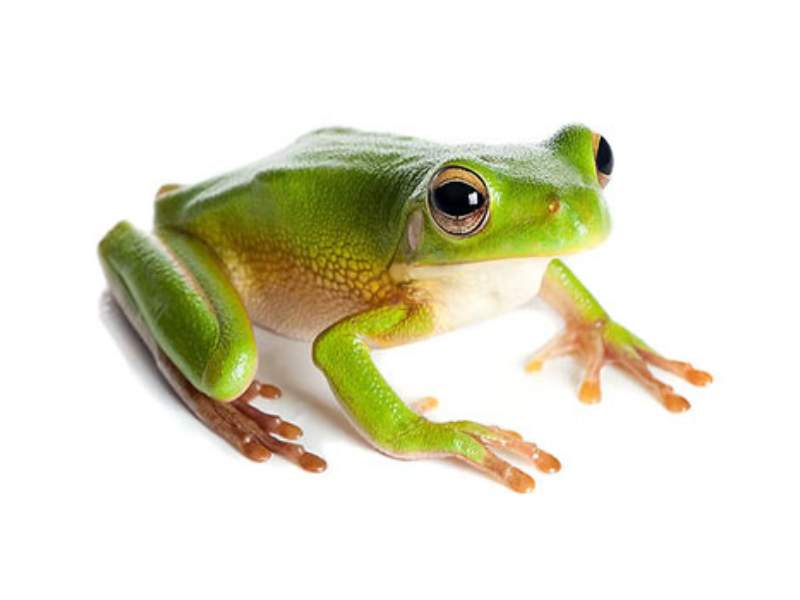
- Frog: Frogs are amphibians known for their unique life cycle that involves metamorphosis from tadpoles to adults. They come in various sizes, with some species being negligible, such as the tiny rainforest frogs.

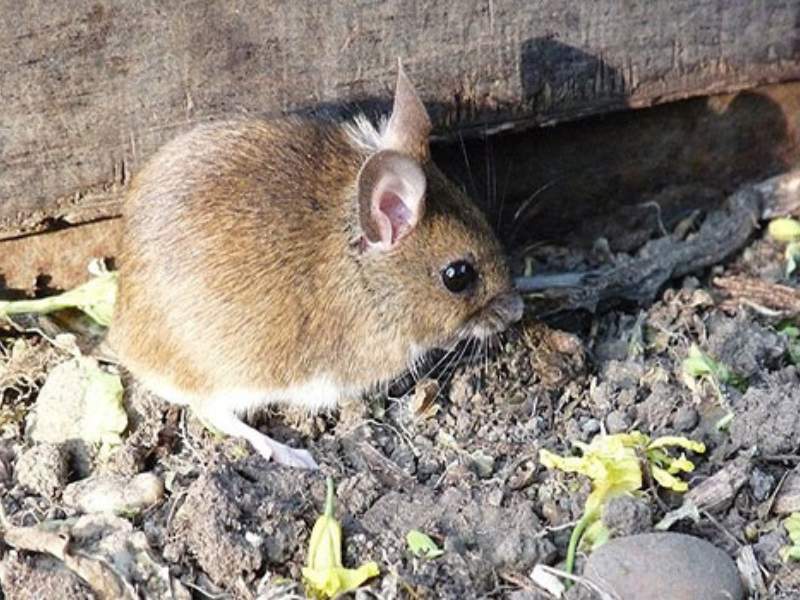
- Field Mouse: Field mice, or meadow mice, are small rodents that inhabit fields, meadows, and grassy areas. They are known for their agility and ability to burrow.

- Fiddler Crab: Fiddler crabs are small crustaceans that reside in coastal areas. They are named for the males’ disproportionately large claw, which they use for communication and courtship displays.
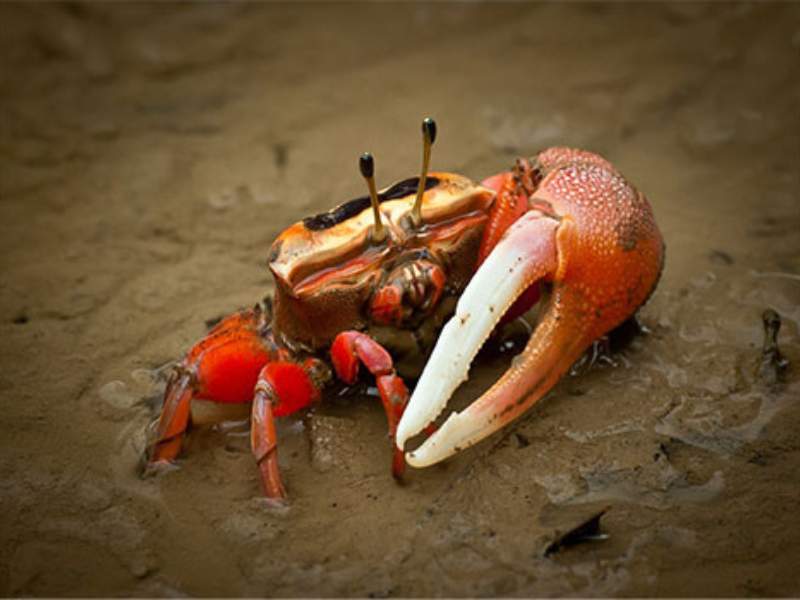

What are Dangerous Animals that Start With F?
Here are 5 dangerous animals that start with the letter “F”:
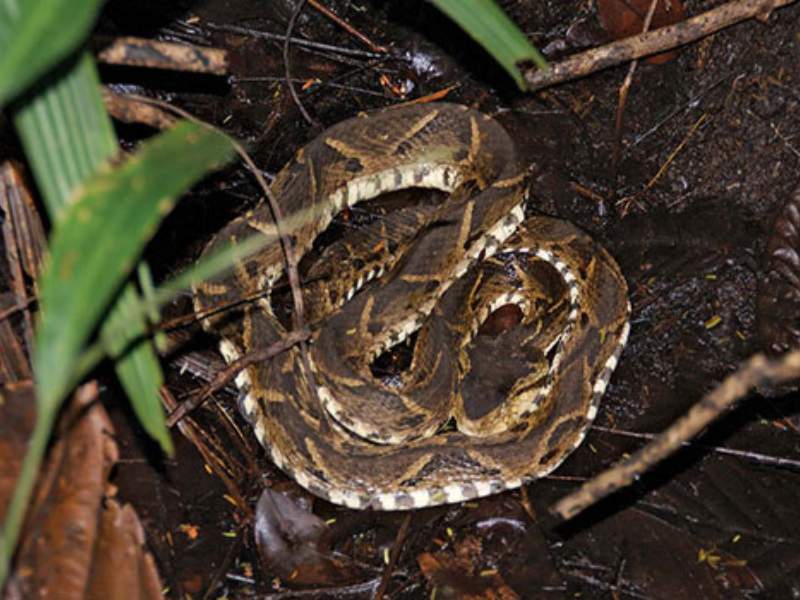
- Fer-de-Lance Snake: The Fer-de-Lance is a highly venomous snake in Central and South America. It is known for its aggressive behavior and potent venom, which can cause severe tissue damage and even death if untreated.

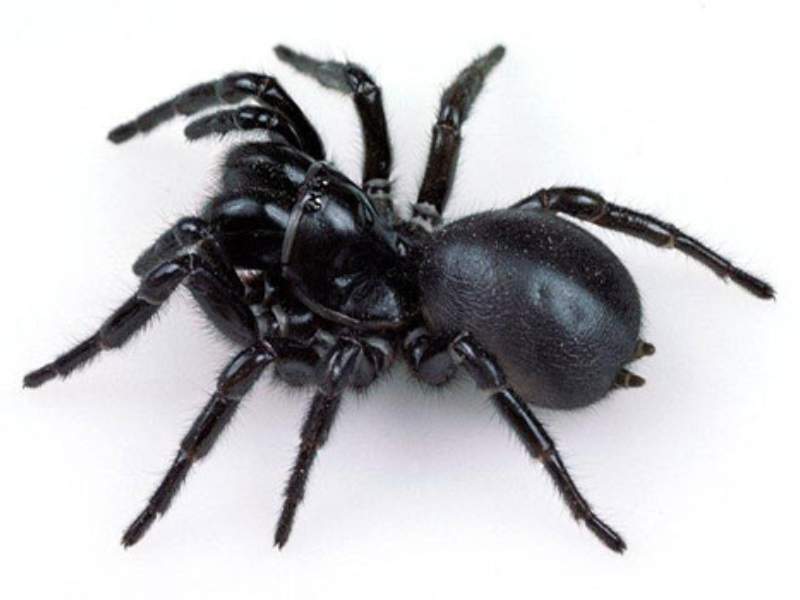
- Funnel-web Spider: Funnel-web spiders are a group of highly venomous spiders found in Australia. The Sydney funnel-web spider, in particular, is considered one of the deadliest spiders in the world, with a venom that can be potentially lethal to humans.

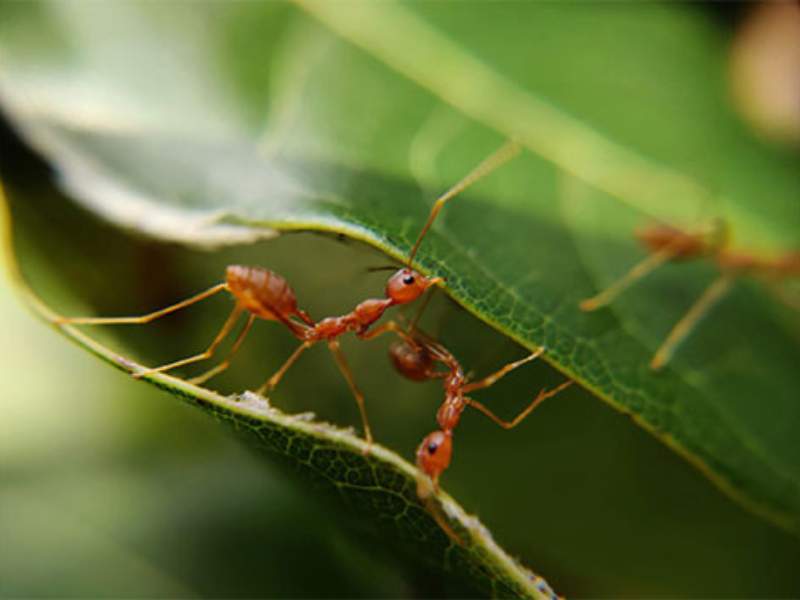
- Fire Ant: Fire ants are tiny but highly aggressive ants known for their painful stings. They are native to South America but have spread to other parts of the world. When disturbed, they can swarm and deliver multiple painful stings, which can cause allergic reactions in some individuals.

- Frilled Shark: The frilled shark is a deep-sea shark with a unique appearance and a reputation as a living fossil. While it is not known to be a direct threat to humans, it has sharp teeth and can be dangerous if mishandled.

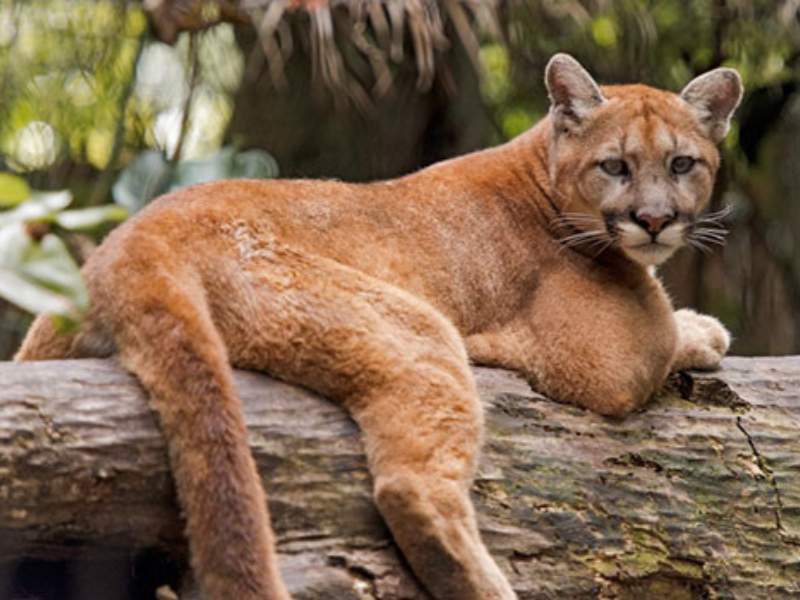
- Florida Panther: The Florida panther is a subspecies of the cougar (mountain lion) found in southern Florida, United States. While they generally avoid human interaction, any large predatory cat can be dangerous if cornered or threatened.

What are Fast Animals that Start With F?
Here are 3 fast animals that start with F:
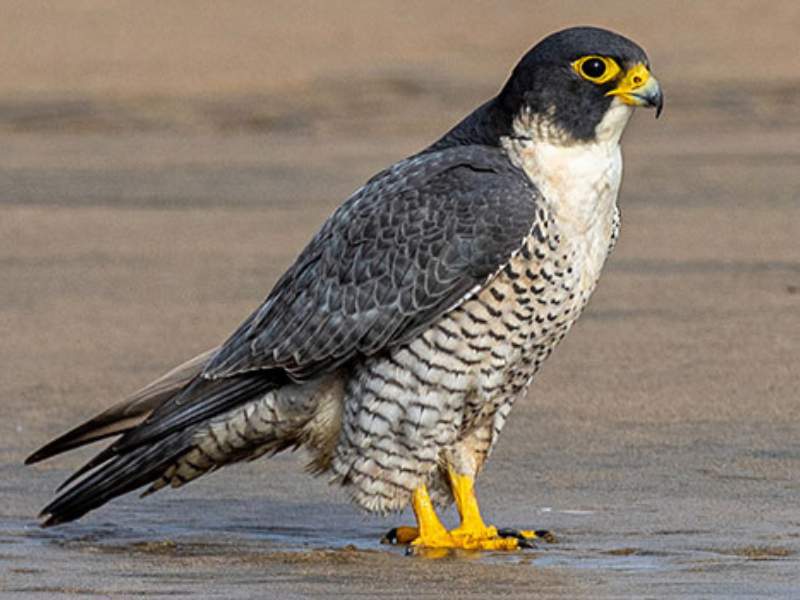
- Falcon: Falcons are known for their incredible speed and agility in flight. They are among the fastest birds in the world, with some species reaching speeds of over 240 miles per hour (386 kilometers per hour) during high-speed dives called stoops.

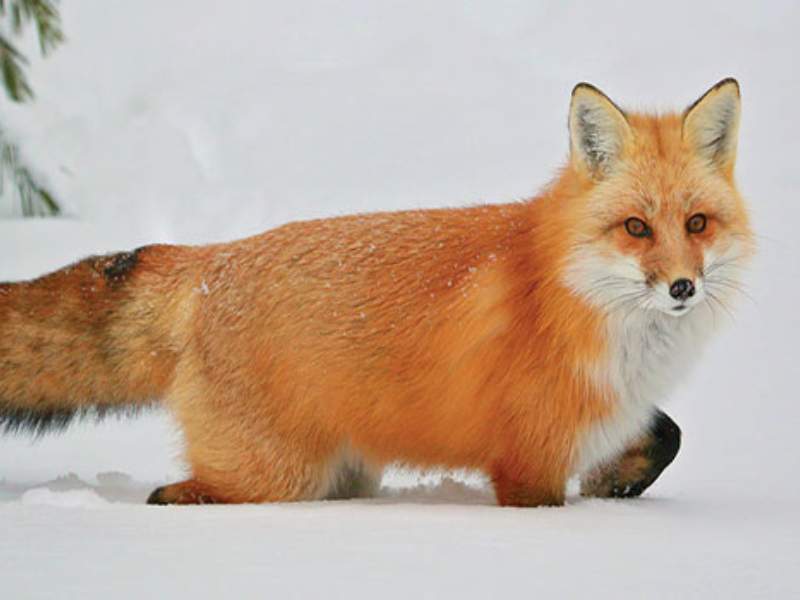
- Fox: Foxes are known for their agility and swiftness on land. They can reach up to 30 miles per hour (48 kilometers per hour) while sprinting, making them fast runners.

- Flying Fish: Flying fish are unique creatures that can glide above the water’s surface. They can achieve impressive speeds of up to 37 miles per hour (60 kilometers per hour) while flying, using their wing-like pectoral fins to stay in the air.
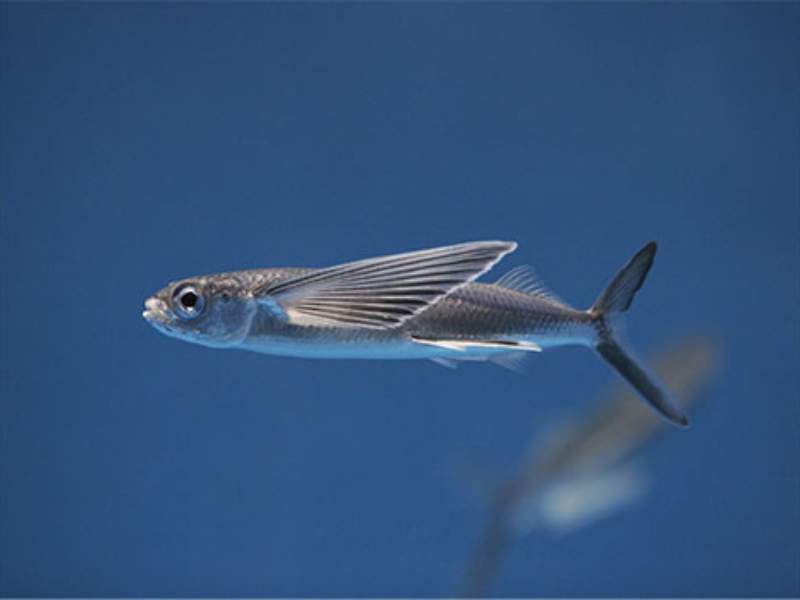

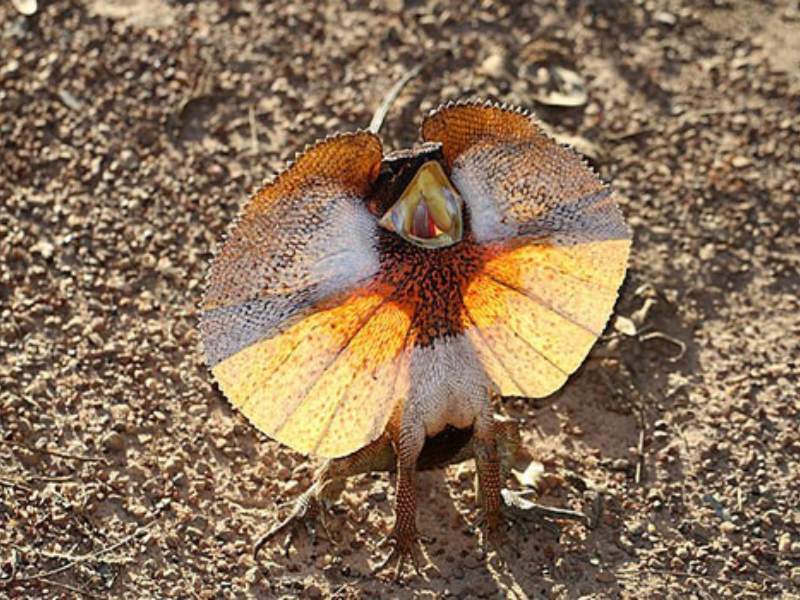
What are Ugly Animals that Start With F?
Here are 3 animals commonly perceived as less conventionally attractive starting with F:
- Frilled Lizard: The frilled lizard is a reptile found in Australia and New Guinea. While its behavior of extending a large frill around its neck is fascinating, some people might find its appearance unusual or less aesthetically pleasing.

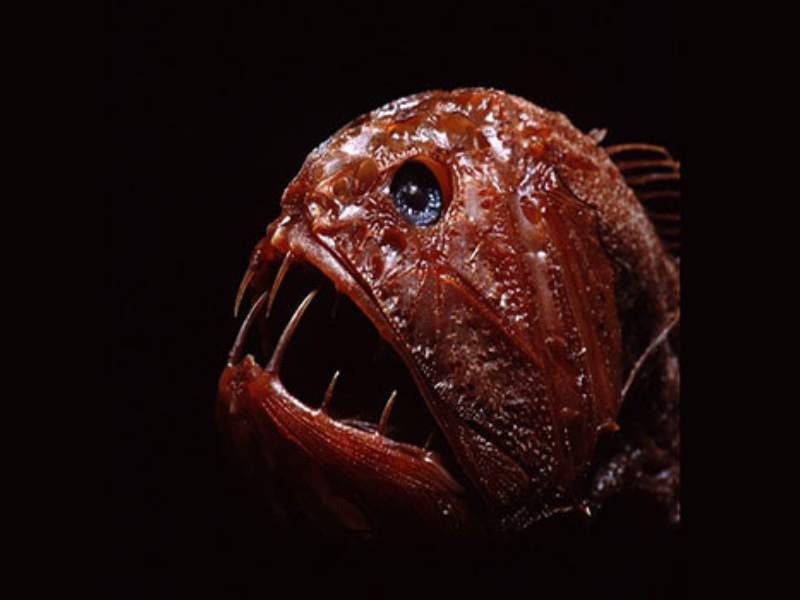
- Fangtooth Fish: The fangtooth fish, also known as the ogrefish, is a deep-sea fish with a peculiar appearance. It has an elongated body, a large mouth, and sharp, fang-like teeth that can appear intimidating or unattractive to some.

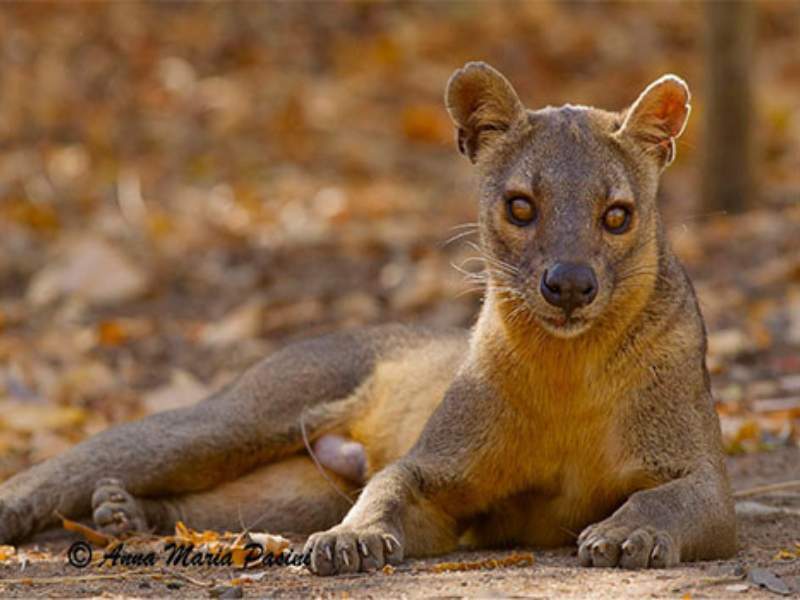
- Fossa: The fossa is a carnivorous mammal native to Madagascar. It has an elongated body, short legs, and a pointed snout. Some individuals might perceive its appearance as less visually appealing.

What are Cute Animals that Start With F?
Here are 5 adorable animals that start with F:
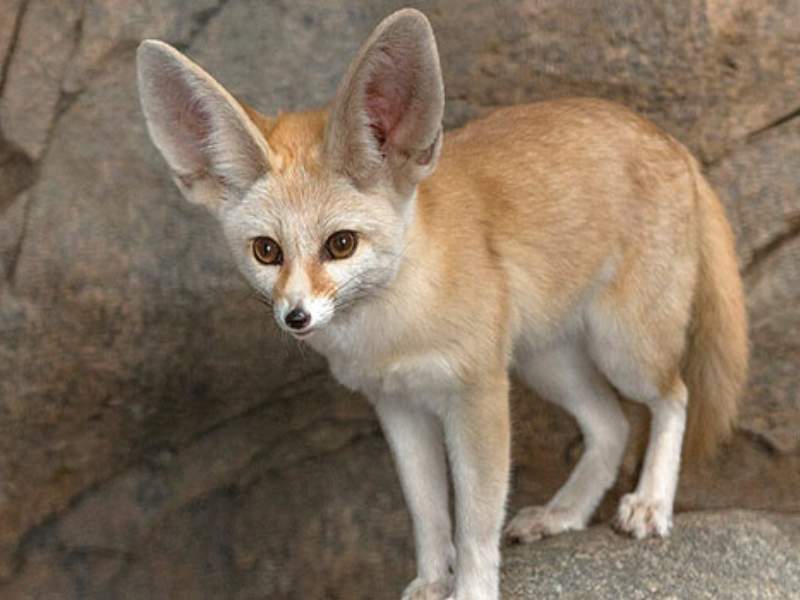
- Fennec Fox: The fennec fox is a small species native to the Sahara Desert. It is known for its large ears, which make it look incredibly charming and endearing. With its fluffy coat and expressive eyes, the fennec fox is often considered one of the cutest animals.

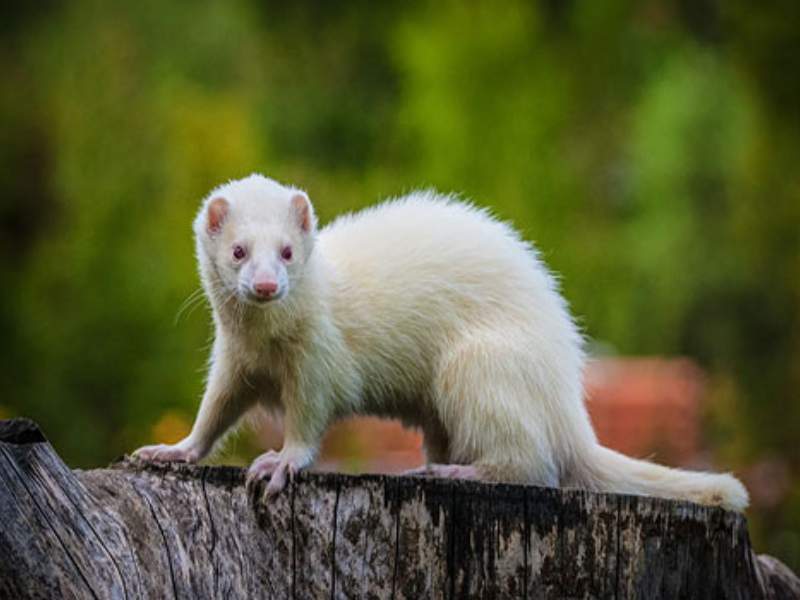
- Ferret: Ferrets are small domesticated carnivores well-known for their playful and mischievous nature. With their long bodies, short legs, and curious personalities, they are often adored as cute and entertaining pets.

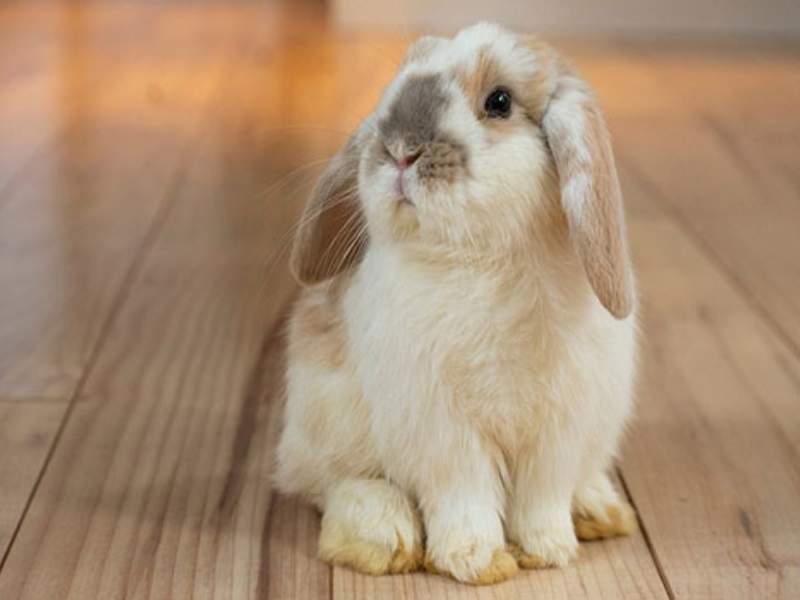
- Fluffy Bunny: Bunnies, or rabbits, are known for their soft fur, twitchy noses, and adorable floppy ears. They come in various breeds and sizes, but they all have a certain charm that makes them attractive and popular pets.

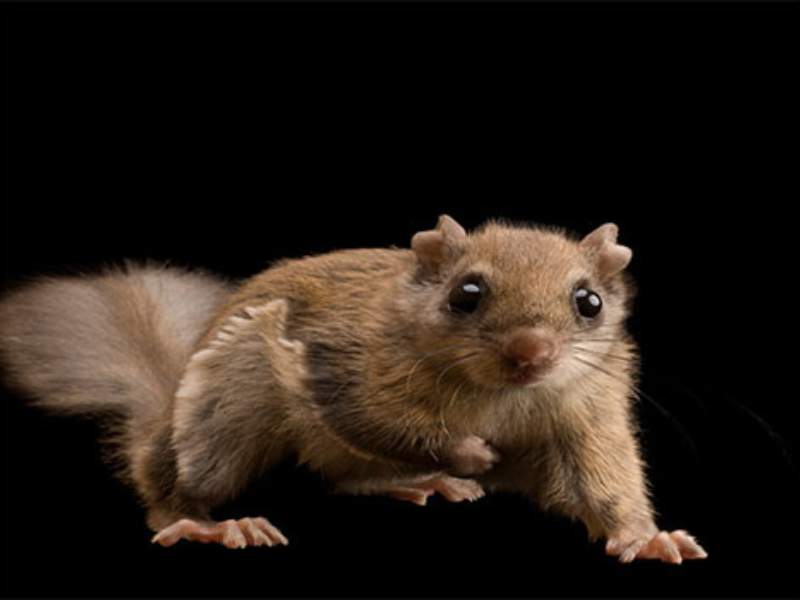
- Flying Squirrel: Flying squirrels are small rodents with a unique adaptation of gliding through the air using a patagium, a membrane between their limbs. Their big, round eyes, soft fur, and the ability to glide from tree to tree make them undeniably cute.

- Fawn: A fawn is a baby deer, typically known for its innocence and delicate features. With their large, gentle eyes and spotted fur, fawns are often considered incredibly cute and endearing.

What are Sea Animals that Start With F?
Here are 5 sea animals that start with F:
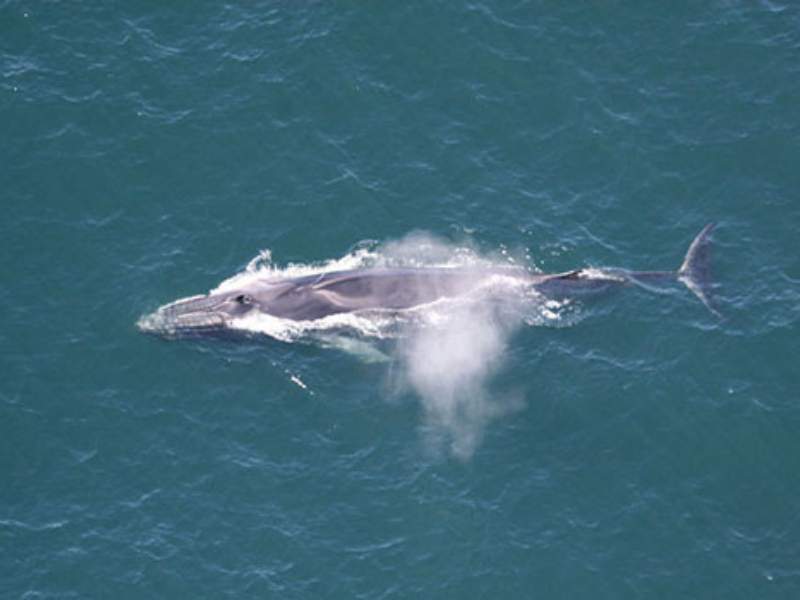
- Fin Whale: The fin whale is a giant baleen whale in oceans worldwide. It is the second-largest animal on Earth after the blue whale. Fin whales are known for their streamlined bodies and tall, curved dorsal fins.

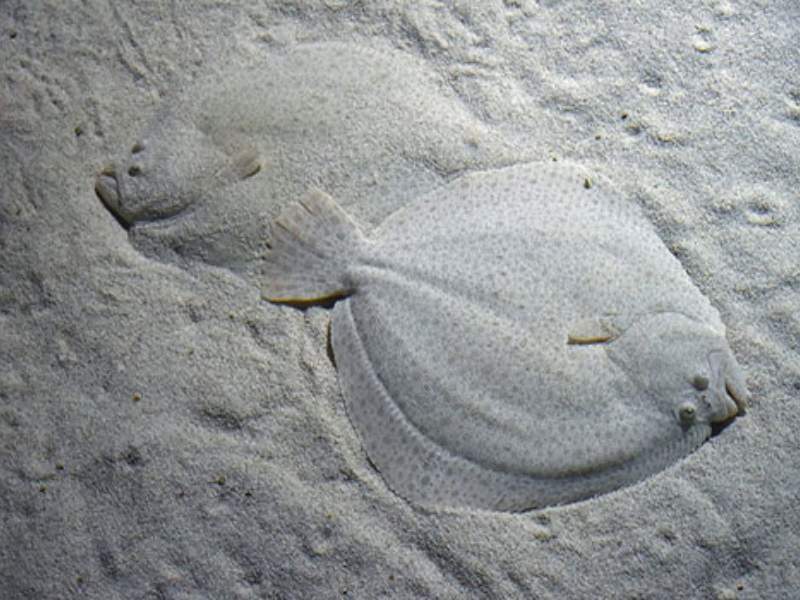
- Flatfish: Flatfish are a group of fish with flattened bodies and both eyes on one side of their head. Examples include flounders, halibuts, and sole. They are bottom-dwelling fish found in coastal areas.

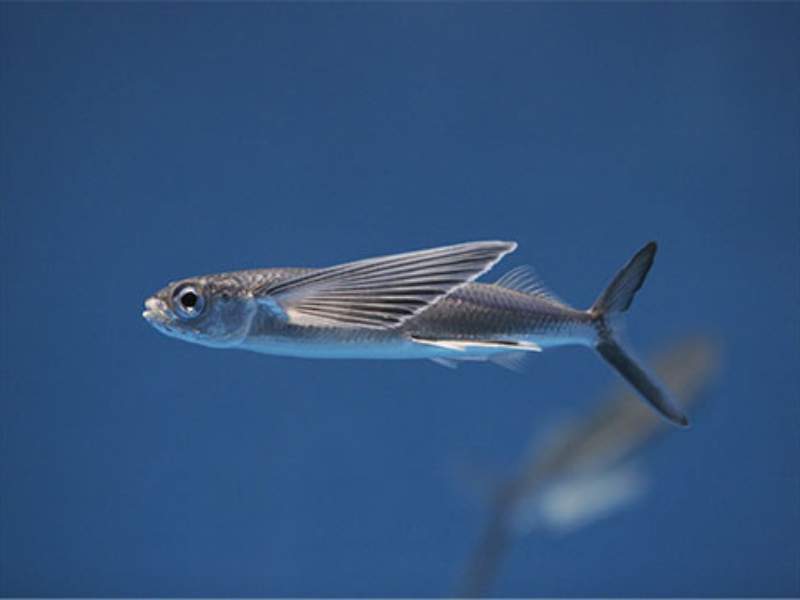
- Flying Fish: Flying fish are a group of fish known for their ability to glide above the water’s surface. They have enlarged pectoral fins that allow them to “fly” for short distances to escape predators or travel between areas.

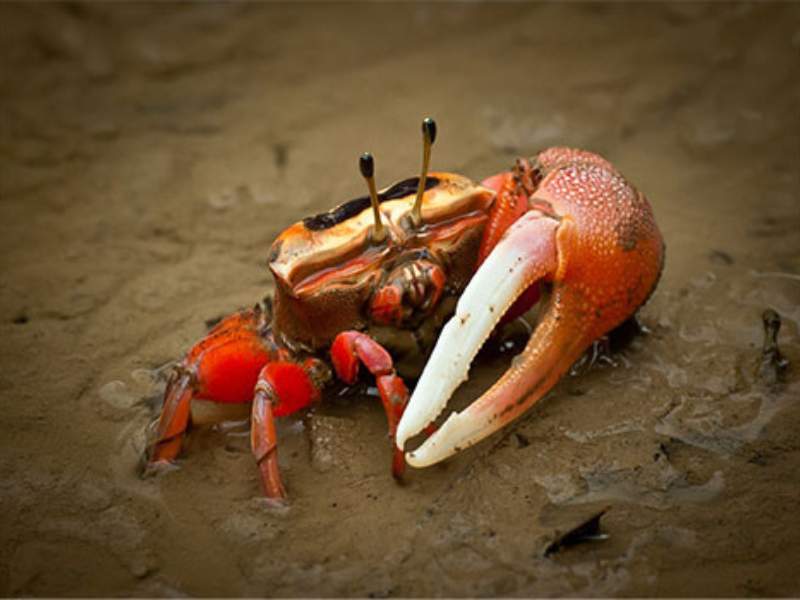
- Fiddler Crab: Fiddler crabs are tiny crustaceans in coastal areas, including intertidal zones and mangroves. They have distinctive oversized claws, with males having one significantly more giant claw for communication and courtship displays.

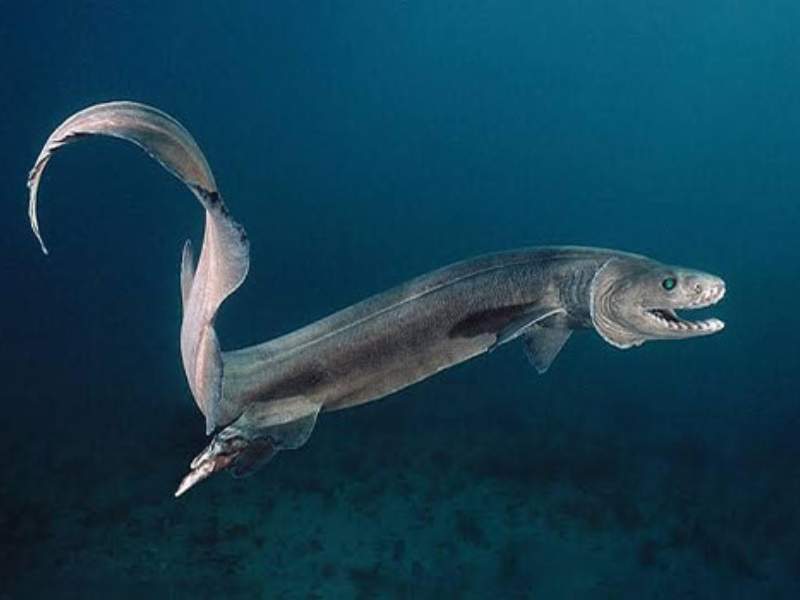
- Frilled Shark: The frilled shark is a deep-sea shark with a unique appearance. It has a long, eel-like body, a prominent mouth, and numerous sharp teeth. Frilled sharks are found in deep waters worldwide.

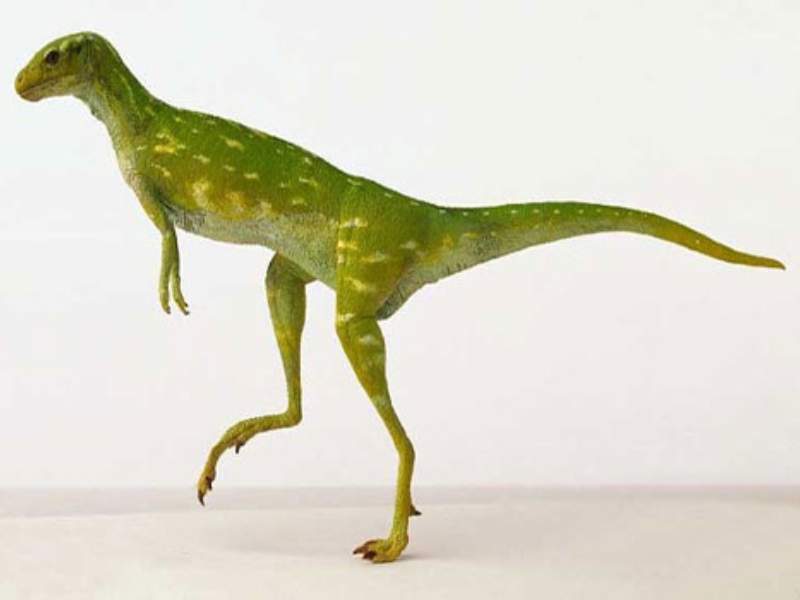
What are Dinosaurs Animals that Start With F?
Here are 4 dinosaurs that start with F:
- Fabrosaurus: Fabrosaurus was a small herbivorous dinosaur that lived during the Late Triassic period. It was a primitive dinosaur with a slender body and is believed to have been a fast runner.

- Falcarius: Falcarius was a therizinosaurid dinosaur that lived during the Early Cretaceous period. It had long arms with sharp claws and is thought to have been an herbivore or an omnivore.
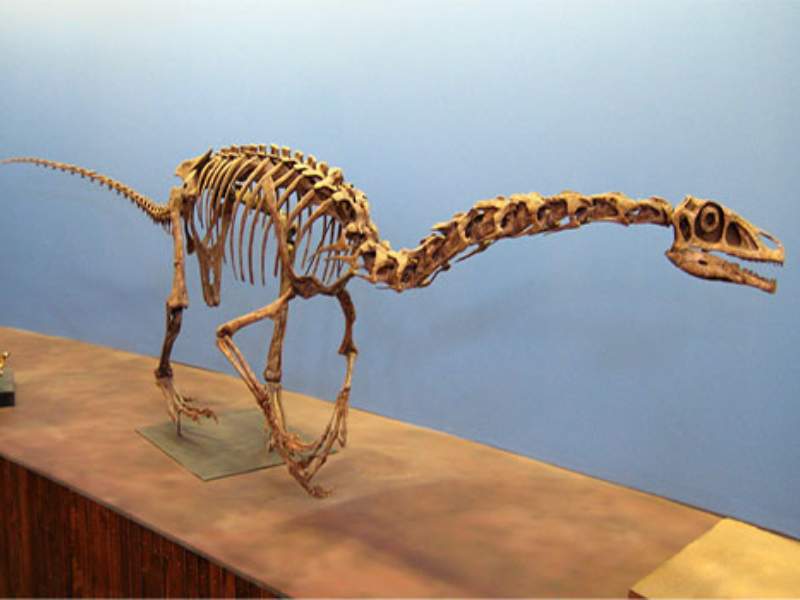

- Fukuiraptor: Fukuiraptor was a theropod dinosaur that lived during the Early Cretaceous period. It was a carnivorous dinosaur with sharp teeth and claws. Fukuiraptor is known from fossil remains found in Japan.
- Futalognkosaurus: Futalognkosaurus was a giant sauropod dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous period. It was one of the most enormous dinosaurs, reaching around 85 feet (26 meters). Its name means “giant chief lizard” in the Mapuche language.
What are some fun facts about Foxes?
Here are some fun facts about foxes:
- Foxes are known for their intelligence. Their problem-solving skills and adaptability contribute to their success in various habitats.
- Foxes produce various vocalizations, including barks, screams, howls, and a distinctive high-pitched call called “vixen’s scream.” These vocalizations serve multiple purposes: communication, territory marking, and mating.
- Foxes are highly adaptable creatures and thrive in diverse environments, including forests, deserts, mountains, and urban areas.
- Foxes are skilled hunters and have a diverse diet. They are opportunistic feeders and can eat small mammals, birds, reptiles, insects, fruits, and berries. They are known to cache surplus food for later consumption.
- Foxes are swift runners and can reach up to 30 miles per hour (48 kilometers per hour) while sprinting. Their speed helps them in hunting and evading predators.

From the ferret to the flamingo, animals starting with ‘F’ highlight the incredible diversity of life on Earth. Each species, whether mammal, reptile, or insect, contributes uniquely to our ecosystems. Exploring these creatures deepens our appreciation for the natural world and its intricate beauty.
If you’re searching for animal names starting with a different letter, explore our other comprehensive articles dedicated to animal names.




